-
 Countries using internet blackouts to boost censorship: Proton
Countries using internet blackouts to boost censorship: Proton
-
Top US news anchor pleads with kidnappers for mom's life

-
 Thailand's pilot PM on course to keep top job
Thailand's pilot PM on course to keep top job
-
The coming end of ISS, symbol of an era of global cooperation

-
 New crew set to launch for ISS after medical evacuation
New crew set to launch for ISS after medical evacuation
-
Family affair: Thailand waning dynasty still election kingmaker

-
 Japan's first woman PM tipped for thumping election win
Japan's first woman PM tipped for thumping election win
-
Stocks in retreat as traders reconsider tech investment

-
 LA officials call for Olympic chief to resign over Epstein file emails
LA officials call for Olympic chief to resign over Epstein file emails
-
Ukraine, Russia, US to start second day of war talks

-
 Fiji football legend returns home to captain first pro club
Fiji football legend returns home to captain first pro club
-
Trump attacks US electoral system with call to 'nationalize' voting

-
 Barry Manilow cancels Las Vegas shows but 'doing great' post-surgery
Barry Manilow cancels Las Vegas shows but 'doing great' post-surgery
-
US households become increasingly strained in diverging economy

-
 Four dead men: the cold case that engulfed a Colombian cycling star
Four dead men: the cold case that engulfed a Colombian cycling star
-
Super Bowl stars stake claims for Olympic flag football

-
 On a roll, Brazilian cinema seizes its moment
On a roll, Brazilian cinema seizes its moment
-
Rising euro, falling inflation in focus at ECB meeting

-
 AI to track icebergs adrift at sea in boon for science
AI to track icebergs adrift at sea in boon for science
-
Indigenous Brazilians protest Amazon river dredging for grain exports

-
 Google's annual revenue tops $400 bn for first time, AI investments rise
Google's annual revenue tops $400 bn for first time, AI investments rise
-
Last US-Russia nuclear treaty ends in 'grave moment' for world

-
 Man City brush aside Newcastle to reach League Cup final
Man City brush aside Newcastle to reach League Cup final
-
Guardiola wants permission for Guehi to play in League Cup final

-
 Boxer Khelif reveals 'hormone treatments' before Paris Olympics
Boxer Khelif reveals 'hormone treatments' before Paris Olympics
-
'Bad Boy,' 'Little Pablo' and Mordisco: the men on a US-Colombia hitlist

-
 BHP damages trial over Brazil mine disaster to open in 2027
BHP damages trial over Brazil mine disaster to open in 2027
-
Dallas deals Davis to Wizards in blockbuster NBA trade: report

-
 Iran-US talks back on, as Trump warns supreme leader
Iran-US talks back on, as Trump warns supreme leader
-
Lens cruise into French Cup quarters, Endrick sends Lyon through

-
 No.1 Scheffler excited for Koepka return from LIV Golf
No.1 Scheffler excited for Koepka return from LIV Golf
-
Curling quietly kicks off sports programme at 2026 Winter Olympics

-
 Undav pokes Stuttgart past Kiel into German Cup semis
Undav pokes Stuttgart past Kiel into German Cup semis
-
Germany goalkeeper Ter Stegen to undergo surgery

-
 Bezos-led Washington Post announces 'painful' job cuts
Bezos-led Washington Post announces 'painful' job cuts
-
Iran says US talks are on, as Trump warns supreme leader

-
 Gaza health officials say strikes kill 24 after Israel says officer wounded
Gaza health officials say strikes kill 24 after Israel says officer wounded
-
Empress's crown dropped in Louvre heist to be fully restored: museum

-
 UK PM says Mandelson 'lied' about Epstein relations
UK PM says Mandelson 'lied' about Epstein relations
-
Shai to miss NBA All-Star Game with abdominal strain

-
 Trump suggests 'softer touch' needed on immigration
Trump suggests 'softer touch' needed on immigration
-
From 'flop' to Super Bowl favorite: Sam Darnold's second act

-
 Man sentenced to life in prison for plotting to kill Trump in 2024
Man sentenced to life in prison for plotting to kill Trump in 2024
-
Native Americans on high alert over Minneapolis crackdown

-
 Dallas deals Davis to Wizards in blockbuster NBA deal: report
Dallas deals Davis to Wizards in blockbuster NBA deal: report
-
Russia 'no longer bound' by nuclear arms limits as treaty with US ends

-
 Panama hits back after China warns of 'heavy price' in ports row
Panama hits back after China warns of 'heavy price' in ports row
-
Strike kills guerrillas as US, Colombia agree to target narco bosses
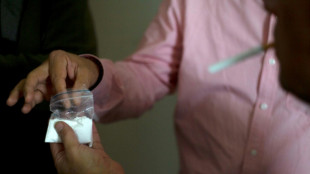
-
 Wildfire smoke kills more than 24,000 Americans a year: study
Wildfire smoke kills more than 24,000 Americans a year: study
-
Telegram founder slams Spain PM over under-16s social media ban

Venezuela’s economic roadmap
Following the dramatic removal of Nicolás Maduro from power in early January 2026, U.S. President Donald Trump set out a bold vision for Venezuela’s economic transformation. At a press conference after the operation that brought Maduro to U.S. custody, the White House announced that Washington would oversee Venezuela’s recovery, manage its oil sector and steer it toward democracy. The administration’s three‑phase strategy – stabilisation, recovery and transition – is described as an “economic revolution” that will lift the country out of a humanitarian and financial abyss. Critics, however, warn that the plan effectively turns the South American nation into a protectorate and underestimates the scale of the challenge.
Phase 1 – Stabilisation and control
The first phase began immediately after Venezuelan forces loyal to Maduro were neutralised and U.S. special forces escorted the former president to a waiting aircraft. Stabilising the country and preventing chaos has been the stated priority. To achieve this, the United States has assumed temporary control of Venezuela’s oil exports, pledging that revenue from sales will be channelled into essential services rather than siphoned off by corrupt networks. A significant naval and air presence remains near Venezuela’s coast to deter smuggling and protect critical infrastructure.
U.S. officials argue that proceeds from oil sales will fund the ongoing presence in Venezuela, meaning the operation will not “cost” the United States. Energy analysts caution that this is unrealistic. Production collapsed from about 3.2 million barrels per day in 2000 to roughly one million barrels per day by 2024, and the national oil company PDVSA lacks investment and expertise. Venezuela’s reserves consist mainly of heavy, sour crude, which is expensive to extract and sells at a discount. Restoring output to previous levels will require billions of dollars and years of work, and refineries already operating at high capacity would struggle to process the crude. Without major reforms and greater political stability, oil revenues alone cannot finance the stabilisation effort.
Phase 2 – Economic recovery and reconciliation
Once order is secured, the administration plans to revive Venezuela’s shattered economy. U.S. Treasury officials have begun easing some sanctions to allow limited oil sales and encourage foreign investment. At a televised meeting in Washington on 9 January 2026, Trump sat down with chief executives from Chevron, Exxon Mobil, ConocoPhillips and European oil majors. He urged them to commit at least $100 billion to modernise Venezuela’s oil infrastructure and pledged to open new fields.
Industry leaders responded cautiously. Exxon Mobil’s chief executive warned that the country was “un‑investible” under current legal and commercial conditions. Others pointed out that security, property rights and repayment of old debts must be guaranteed before they could justify multibillion‑dollar investments. Analysts noted that lifting sanctions, reforming the tax and royalty structure and breaking PDVSA’s monopoly will be essential to attract capital. Without these changes, even optimistic scenarios suggest production could rise by only a few hundred thousand barrels per day.
Phase 2 also includes a national reconciliation programme. Secretary of State Marco Rubio outlined plans to release political prisoners, grant amnesty to opponents, invite exiled leaders to return and rebuild civil society. He said U.S. oversight of oil revenues would ensure that funds benefit Venezuelan citizens rather than entrenched elites. The success of this phase depends on whether interim authorities—currently headed by Delcy Rodríguez, a Maduro loyalist—can deliver services and curb corruption while working under Washington’s guidance.
Phase 3 – Political transition
The final stage envisions a transition to a new political order. Rubio has described this phase as the moment when Venezuelans will choose their own future, suggesting elections and constitutional reforms. Yet the timeline and mechanisms remain vague. Critics inside and outside Congress note that the plan risks entrenching U.S. influence and undermining sovereignty. Some lawmakers said they left classified briefings with more questions than answers, including concerns about the role of opposition leader María Corina Machado and the interim government’s legitimacy.
Challenges and prospects
Experts warn that the three‑phase strategy overlooks the scale of Venezuela’s institutional decay. Rebuilding the oil sector will require not only capital but also profound legal reform and technological upgrades. Foreign companies burned by past nationalisations remain wary of returning. Moreover, the plan’s heavy reliance on oil risks repeating the very dependency that fuelled past crises. Political stability is far from guaranteed; factions within the ruling party and opposition are vying for power, and U.S. control may trigger nationalist backlash.
Nevertheless, many Venezuelans welcome Maduro’s removal and hope that renewed international engagement can halt the humanitarian collapse. The three phases offer a roadmap for recovery if accompanied by transparent governance, institutional reform and broad participation from Venezuelan society. Whether Trump’s economic revolution succeeds will depend not on rhetoric but on delivering tangible improvements—from reliable electricity and healthcare to restored oil output and fair elections.

Border violence: What is going on in Bulgaria?

Sánchez's aim to reinstate leftist coalition set to fail!

Russland als Terror-Staat / Russia as a terror state!

Ukraine in the fight against the russian terror State

The Russian terrorist state will never own Ukraine!

ATTENTION, ATENCIÓN, УВАГА, ВНИМАНИЕ, 注意事项, DİKKAT, 주의, ATENÇÃO

BRAVO: This is how the Russian scum in Ukraine ends!

Video, ビデオ, 视频, Відео, 비디오, Wideo, 動画, Βίντεο, Видео!!

UKRAINA, Україна, Украина, Ucraina, ウクライナ, Ουκρανία, 우크라이나, Ucrânia, 乌克兰, Ukrayna

Poland erects wall along Belarusian border to stop migration

Ukraine: War terror of the russian army!




