
-
 Lens cruise into French Cup quarters, Endrick sends Lyon through
Lens cruise into French Cup quarters, Endrick sends Lyon through
-
No.1 Scheffler excited for Koepka return from LIV Golf

-
 Curling quietly kicks off sports programme at 2026 Winter Olympics
Curling quietly kicks off sports programme at 2026 Winter Olympics
-
Undav pokes Stuttgart past Kiel into German Cup semis

-
 Germany goalkeeper Ter Stegen to undergo surgery
Germany goalkeeper Ter Stegen to undergo surgery
-
Bezos-led Washington Post announces 'painful' job cuts

-
 Iran says US talks are on, as Trump warns supreme leader
Iran says US talks are on, as Trump warns supreme leader
-
Gaza health officials say strikes kill 24 after Israel says officer wounded

-
 Empress's crown dropped in Louvre heist to be fully restored: museum
Empress's crown dropped in Louvre heist to be fully restored: museum
-
UK PM says Mandelson 'lied' about Epstein relations

-
 Shai to miss NBA All-Star Game with abdominal strain
Shai to miss NBA All-Star Game with abdominal strain
-
Trump suggests 'softer touch' needed on immigration

-
 From 'flop' to Super Bowl favorite: Sam Darnold's second act
From 'flop' to Super Bowl favorite: Sam Darnold's second act
-
Man sentenced to life in prison for plotting to kill Trump in 2024

-
 Native Americans on high alert over Minneapolis crackdown
Native Americans on high alert over Minneapolis crackdown
-
Dallas deals Davis to Wizards in blockbuster NBA deal: report

-
 Russia 'no longer bound' by nuclear arms limits as treaty with US ends
Russia 'no longer bound' by nuclear arms limits as treaty with US ends
-
Panama hits back after China warns of 'heavy price' in ports row

-
 Strike kills guerrillas as US, Colombia agree to target narco bosses
Strike kills guerrillas as US, Colombia agree to target narco bosses
-
Wildfire smoke kills more than 24,000 Americans a year: study

-
 Telegram founder slams Spain PM over under-16s social media ban
Telegram founder slams Spain PM over under-16s social media ban
-
Curling kicks off sports programme at 2026 Winter Olympics

-
 Preventative cholera vaccination resumes as global supply swells: WHO
Preventative cholera vaccination resumes as global supply swells: WHO
-
Wales' Macleod ready for 'physical battle' against England in Six Nations

-
 Xi calls for 'mutual respect' with Trump, hails ties with Putin
Xi calls for 'mutual respect' with Trump, hails ties with Putin
-
'All-time great': Maye's ambitions go beyond record Super Bowl bid

-
 Shadow over Vonn as Shiffrin, Odermatt headline Olympic skiing
Shadow over Vonn as Shiffrin, Odermatt headline Olympic skiing
-
US seeks minerals trade zone in rare Trump move with allies

-
 Ukraine says Abu Dhabi talks with Russia 'substantive and productive'
Ukraine says Abu Dhabi talks with Russia 'substantive and productive'
-
Brazil mine disaster victims in London to 'demand what is owed'

-
 AI-fuelled tech stock selloff rolls on
AI-fuelled tech stock selloff rolls on
-
Russia vows to act 'responsibly' as nuclear pact ends with US

-
 White says time at Toulon has made him a better Scotland player
White says time at Toulon has made him a better Scotland player
-
Washington Post announces 'painful' job cuts

-
 All lights are go for Jalibert, says France's Dupont
All lights are go for Jalibert, says France's Dupont
-
Artist rubs out Meloni church fresco after controversy

-
 Palestinians in Egypt torn on return to a Gaza with 'no future'
Palestinians in Egypt torn on return to a Gaza with 'no future'
-
US removing 700 immigration officers from Minnesota

-
 Who is behind the killing of late ruler Gaddafi's son, and why now?
Who is behind the killing of late ruler Gaddafi's son, and why now?
-
Coach Thioune tasked with saving battling Bremen

-
 Russia vows to act 'responsibly' once nuclear pact with US ends
Russia vows to act 'responsibly' once nuclear pact with US ends
-
Son of Norway's crown princess admits excesses but denies rape

-
 US calls for minerals trade zone in rare move with allies
US calls for minerals trade zone in rare move with allies
-
Vowles dismisses Williams 2026 title hopes as 'not realistic'

-
 'Dinosaur' Glenn chasing skating gold in first Olympics
'Dinosaur' Glenn chasing skating gold in first Olympics
-
Gaza health officials say strikes kill 23 after Israel says shots wounded officer

-
 Italy foils Russian cyberattacks targeting Olympics
Italy foils Russian cyberattacks targeting Olympics
-
Stocks stabilise after Wall St AI-fuelled sell-off

-
 Figure skating favourite Malinin feeling 'the pressure' in Milan
Figure skating favourite Malinin feeling 'the pressure' in Milan
-
Netflix film probes conviction of UK baby killer nurse


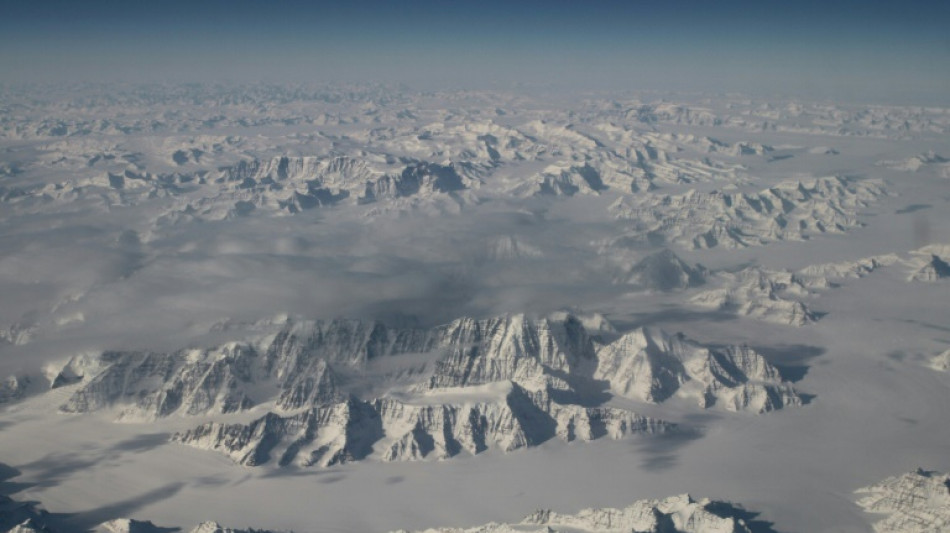
Dire sea level rise likely even in a 1.5C world: study
Rising seas will severely test humanity's resilience in the second half of the 21st century and beyond, even if nations defy the odds and cap global warming at the ambitious 1.5 degrees Celsius target, researchers said Tuesday.
The pace at which global oceans are rising has doubled in three decades, and on current trends will double again by 2100 to about one centimetre per year, they reported in a study.
"Limiting global warming to 1.5C would be a major achievement" and avoid many dire climate impacts, lead author Chris Stokes, a professor at Durham University in England, told AFP.
"But even if this target is met," he added, "sea level rise is likely to accelerate to rates that are very difficult to adapt to."
Absent protective measures such as sea walls, an additional 20 centimetres (7.8 inches) of sea level rise -- the width of a letter-size sheet of paper -- by 2050 would cause some $1 trillion in flood damage annually in the world's 136 largest coastal cities, earlier research has shown.
Some 230 million people live on land within one metre (3.2 feet) of sea level, and more than a billion reside within 10 metres.
Sea level rise is driven in roughly equal measure by the disintegration of ice sheets and mountain glaciers, as well as the expansion of warming oceans, which absorb more than 90 percent of the excess heat due to climate change.
Averaged across 20 years, Earth's surface temperature is currently 1.2C above pre-industrial levels, already enough to lift the ocean watermark by several metres over the coming centuries, Stokes and colleagues noted in the journal Communications Earth & Environment.
The world is on track to see temperatures rise 2.7C above that benchmark by the end of the century.
- Tipping points -
In a review of scientific literature since the last major climate assessment by the UN-mandated Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), Stokes and his team focused on the growing contribution of ice sheets to rising seas.
In 2021, the IPCC projected "likely" sea level rise of 40 to 80 centimetres by 2100, depending on how how quickly humanity draws down greenhouse gas emissions, but left ice sheets out of their calculations due to uncertainty.
The picture has become alarmingly more clear since then.
"We are probably heading for the higher numbers within that range, possibly higher," said Stokes.
The scientist and his team looked at three baskets of evidence, starting with what has been observed and measured to date.
Satellite data has revealed that ice sheets with enough frozen water to lift oceans some 65 metres are far more sensitive to climate change than previously suspected.
The amount of ice melting or breaking off into the ocean from Greenland and West Antarctica, now averaging about 400 billion tonnes a year, has quadrupled over the last three decades, eclipsing runoff from mountain glaciers.
Estimates of how much global warming it would take to push dwindling ice sheets past a point of no return, known as tipping points, have also shifted.
"We used to think that Greenland wouldn't do anything until the world warmed 3C," said Stokes. "Now the consensus for tipping points for Greenland and West Antarctica is about 1.5C."
The 2015 Paris climate treaty calls for capping global warming at "well below" 2C, and 1.5C if possible.
The scientists also looked at fresh evidence from the three most recent periods in Earth's history with comparable temperatures and atmospheric levels of CO2, the main driver of global warming.
About 125,000 years ago during the previous "interglacial" between ice ages, sea levels were two to nine metres higher than today despite a slightly lower average global temperature and significantly less CO2 in the air -- 287 parts per million, compared to 424 ppm today.
A slightly warmer period 400,000 ago with CO2 concentrations at about 286 ppm saw oceans 6-to-13 metres higher.
And if we go back to the last moment in Earth's history with CO2 levels like today, some three million years ago, sea levels were 10-to-20 metres higher.
Finally, scientists reviewed recent projections of how ice sheets will behave in the future.
"If you want to slow sea level rise from ice sheets, you clearly have to cool back from present-day temperatures," Stokes told AFP.
"To slow sea level rise from ice sheets to a manageable level requires a long-term temperature goal that is close to +1C, or possibly lower."
E.Aziz--SF-PST


