
-
 Sudan 'lost all sources of revenue' in the war: finance minister to AFP
Sudan 'lost all sources of revenue' in the war: finance minister to AFP
-
Freezing rain hampers transport in Central Europe

-
 Nuuk, Copenhagen cautiously mull Greenland independence
Nuuk, Copenhagen cautiously mull Greenland independence
-
'Proving the boys wrong': Teenage racers picked for elite driver programme

-
 Mbappe absent from training as Arbeloa takes charge at Real Madrid
Mbappe absent from training as Arbeloa takes charge at Real Madrid
-
Iran worries push up oil price as world stocks diverge
-
 Volvo Cars pauses battery factory after fruitless partner search
Volvo Cars pauses battery factory after fruitless partner search
-
Social media harms teens, watchdog warns, as France weighs ban

-
 Central bank chiefs voice 'full solidarity' with US Fed, Powell
Central bank chiefs voice 'full solidarity' with US Fed, Powell
-
Greece airspace shutdown exposes badly outdated systems

-
 France climate goals off track as emissions cuts slow again
France climate goals off track as emissions cuts slow again
-
Boeing sells 50 737 MAX jets to leasing group ACG

-
 Freezing rain paralyses transport in Central Europe
Freezing rain paralyses transport in Central Europe
-
Man Utd reach deal to appoint Carrick as interim boss: reports

-
 Trump hits Iran trade partners with tariffs as protest toll soars
Trump hits Iran trade partners with tariffs as protest toll soars
-
Is China a threat to Greenland as Trump argues?

-
 Takaichi says urged S. Korea's Lee to help 'ensure regional stability'
Takaichi says urged S. Korea's Lee to help 'ensure regional stability'
-
South Korean prosecutors set to demand heavy sentence for Yoon

-
 Honduras electoral authorities reject vote recount
Honduras electoral authorities reject vote recount
-
Tractors in Paris to protest EU's trade deal with S. America

-
 Asian markets rise, Iran worries push up oil
Asian markets rise, Iran worries push up oil
-
Williams loses golden oldie clash in final Australian Open warm-up

-
 Kyrgios stands by decision to skip Australian Open singles
Kyrgios stands by decision to skip Australian Open singles
-
Disaster losses drop in 2025, picture still 'alarming': Munich Re

-
 Williams, 45, loses in first round of final Australian Open warm-up
Williams, 45, loses in first round of final Australian Open warm-up
-
Doncic scores 42 points but Lakers humbled by Kings

-
 'Serious threat': Indonesia legal reform sparks rights challenges
'Serious threat': Indonesia legal reform sparks rights challenges
-
Rodgers misery as Texans rout Steelers to advance in NFL playoffs

-
 Morocco's Bono 'one of best goalkeepers in the world'
Morocco's Bono 'one of best goalkeepers in the world'
-
Salah and Mane meet again with AFCON final place on the line

-
 French museum fare hikes for non-European tourists spark outcry
French museum fare hikes for non-European tourists spark outcry
-
In 'big trouble'? The factors determining Iran's future

-
 Osimhen finds AFCON scoring touch to give Nigeria cutting edge
Osimhen finds AFCON scoring touch to give Nigeria cutting edge
-
Trump announces tariffs on Iran trade partners as protest toll rises

-
 Sabalenka favourite at Australian Open but faces Swiatek, US threats
Sabalenka favourite at Australian Open but faces Swiatek, US threats
-
Gay Australian footballer Cavallo alleges former club was homophobic

-
 Global Sports Brand U.S. Polo Assn. Announced as Official Jersey and Apparel Sponsor for the Legendary Snow Polo World Cup St. Moritz
Global Sports Brand U.S. Polo Assn. Announced as Official Jersey and Apparel Sponsor for the Legendary Snow Polo World Cup St. Moritz
-
Trump has options on Iran, but first must define goal

-
 Paris FC's Ikone stuns PSG to knock out former club from French Cup
Paris FC's Ikone stuns PSG to knock out former club from French Cup
-
Australia's ambassador to US leaving post, marked by Trump rift

-
 Slot angered by 'weird' Szoboszlai error in Liverpool FA Cup win
Slot angered by 'weird' Szoboszlai error in Liverpool FA Cup win
-
Szoboszlai plays hero and villain in Liverpool's FA Cup win

-
 Hawaii's Kilauea volcano puts on spectacular lava display
Hawaii's Kilauea volcano puts on spectacular lava display
-
US stocks at records despite early losses on Fed independence angst

-
 Koepka rejoins PGA Tour under new rules for LIV players
Koepka rejoins PGA Tour under new rules for LIV players
-
Ex-France, Liverpool defender Sakho announces retirement

-
 Jerome Powell: The careful Fed chair standing firm against Trump
Jerome Powell: The careful Fed chair standing firm against Trump
-
France scrum-half Le Garrec likely to miss start of Six Nations

-
 AI helps fuel new era of medical self-testing
AI helps fuel new era of medical self-testing
-
Leaders of Japan and South Korea meet as China flexes muscles


France climate goals off track as emissions cuts slow again
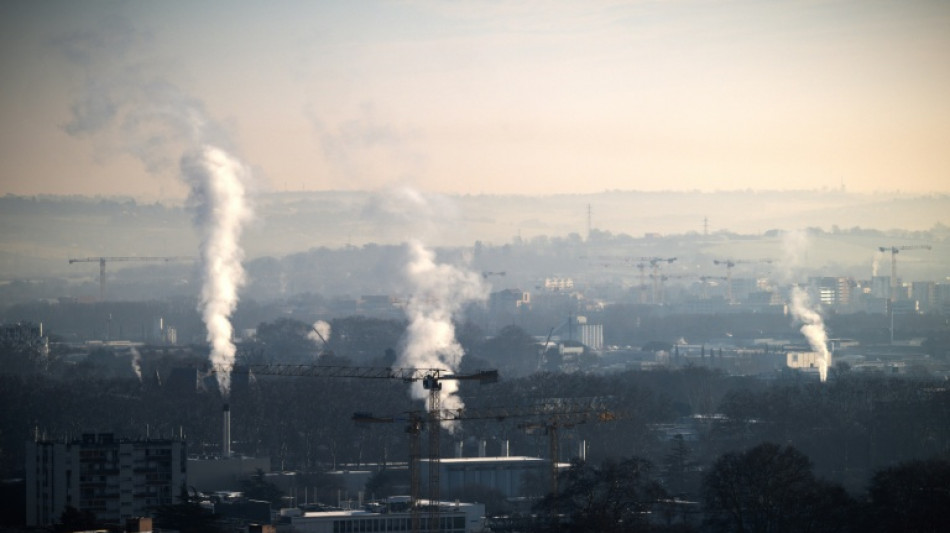
France's cuts to greenhouse gas emissions slowed for a second straight year in 2025 and remain well off track to meeting its climate goals, according to provisional government-commissioned estimates published Tuesday.
The slowdown comes as appetite for climate action flags and major economies in Europe and elsewhere struggle to make good on their pledges to reduce planet-warming pollution.
France's emissions were estimated to have declined 1.6 percent year-on-year, said Citepa, a non-profit organisation tasked by France's ecology ministry with tallying the country's greenhouse gas inventory.
The reduction of 5.8 million tonnes of CO2 equivalent was "far below the pace needed to reach 2030 targets" which would require cuts nearly three times larger, Citepa said.
"The decrease in emissions is confirmed for 2025. This is an encouraging sign, but it is not enough. We must collectively remobilise with all emitting sectors," Monique Barbut, France's Minister for Ecological Transition, said in a press release.
France, often seen as a leader in transitioning to a low-carbon future, unveiled in December its updated pathway for achieving carbon neutrality by 2050.
To stay on track, greenhouse gas emissions need to fall 4.6 percent on average every year until 2030.
After France slashed its output by 3.9 percent in 2022 and 6.8 percent in 2023, the rate slowed sharply to 1.8 percent in 2024.
Citepa had earlier predicted a decline of just 0.8 percent in 2025 but said fresh data and updated methods of calculation had allowed a "more accurate" estimate for the full year.
- Climate risk -
Big polluting nations most responsible for climate change are under pressure to make faster and deeper cuts to the emissions driving record-breaking global temperatures and more extreme weather events.
Scientists say the last three years have been the hottest globally on record.
The result in France echoes a slowdown in neighbouring Germany, where emissions fell just 1.5 percent in 2025, the Agora Energiewende expert group said in its annual report last week.
France encouraged energy conservation after Russia's invasion of Ukraine in 2022 but since then has faltered in decarbonising some of its most polluting industries.
While improvements were recorded in 2025 in heavy-emitting sectors such as industry, agriculture and transport, they remained virtually flat in energy and waste treatment, Citepa said.
The latest assessment highlighted the urgency for France to phase out its use of fossil fuels, said Anne Bringault, a director at Climate Action Network France.
"It is high time to take seriously the climate risk but also the geopolitical risk of making us suffer from our dependence on fossil fuels, which are overwhelmingly imported," she told AFP.
The European Union has pledged to cut its net greenhouse gas emissions by 90 percent by 2040 compared to 1990 levels. It had already achieved a 37 percent reduction by 2023.
C.AbuSway--SF-PST


