
-
 South Korea pledges to phase out coal plants at COP30
South Korea pledges to phase out coal plants at COP30
-
Ex-PSG footballer Hamraoui claims 3.5m euros damages against club

-
 Mbappe, PSG in counterclaims worth hundreds of millions
Mbappe, PSG in counterclaims worth hundreds of millions
-
Two newly discovered Bach organ works unveiled in Germany

-
 Stocks lower on uncertainty over earnings, tech rally, US rates
Stocks lower on uncertainty over earnings, tech rally, US rates
-
Barca to make long-awaited Camp Nou return on November 22

-
 COP30 talks enter homestretch with UN warning against 'stonewalling'
COP30 talks enter homestretch with UN warning against 'stonewalling'
-
France makes 'historic' accord to sell Ukraine 100 warplanes

-
 Delhi car bombing accused appears in Indian court, another suspect held
Delhi car bombing accused appears in Indian court, another suspect held
-
Emirates orders 65 more Boeing 777X planes despite delays

-
 Ex-champion Joshua to fight YouTube star Jake Paul
Ex-champion Joshua to fight YouTube star Jake Paul
-
Bangladesh court sentences ex-PM to be hanged for crimes against humanity

-
 Trade tensions force EU to cut 2026 eurozone growth forecast
Trade tensions force EU to cut 2026 eurozone growth forecast
-
'Killed without knowing why': Sudanese exiles relive Darfur's past

-
 Stocks lower on uncertainty over tech rally, US rates
Stocks lower on uncertainty over tech rally, US rates
-
Death toll from Indonesia landslides rises to 18

-
 Macron, Zelensky sign accord for Ukraine to buy French fighter jets
Macron, Zelensky sign accord for Ukraine to buy French fighter jets
-
India Delhi car bomb accused appears in court

-
 Bangladesh ex-PM sentenced to be hanged for crimes against humanity
Bangladesh ex-PM sentenced to be hanged for crimes against humanity
-
Leftist, far-right candidates advance to Chilean presidential run-off

-
 Bangladesh's Hasina: from PM to crimes against humanity convict
Bangladesh's Hasina: from PM to crimes against humanity convict
-
Rugby chiefs unveil 'watershed' Nations Championship

-
 EU predicts less eurozone 2026 growth due to trade tensions
EU predicts less eurozone 2026 growth due to trade tensions
-
Swiss growth suffered from US tariffs in Q3: data

-
 Bangladesh ex-PM sentenced to death for crimes against humanity
Bangladesh ex-PM sentenced to death for crimes against humanity
-
Singapore jails 'attention seeking' Australian over Ariana Grande incident

-
 Tom Cruise receives honorary Oscar for illustrious career
Tom Cruise receives honorary Oscar for illustrious career
-
Fury in China over Japan PM's Taiwan comments

-
 Carbon capture promoters turn up in numbers at COP30: NGO
Carbon capture promoters turn up in numbers at COP30: NGO
-
Japan-China spat over Taiwan comments sinks tourism stocks

-
 No Wemby, no Castle, no problem as NBA Spurs rip Kings
No Wemby, no Castle, no problem as NBA Spurs rip Kings
-
In reversal, Trump supports House vote to release Epstein files

-
 Gauff-led holders USA to face Spain, Argentina at United Cup
Gauff-led holders USA to face Spain, Argentina at United Cup
-
Ecuador voters reject return of US military bases

-
 Bodyline and Bradman to Botham and Stokes: five great Ashes series
Bodyline and Bradman to Botham and Stokes: five great Ashes series
-
Iran girls kick down social barriers with karate

-
 Asian markets struggle as fears build over tech rally, US rates
Asian markets struggle as fears build over tech rally, US rates
-
Australia's 'Dad's Army' ready to show experience counts in Ashes

-
 UN Security Council set to vote on international force for Gaza
UN Security Council set to vote on international force for Gaza
-
Japan-China spat sinks tourism stocks

-
 Ecuador voters set to reject return of US military bases
Ecuador voters set to reject return of US military bases
-
Trump signals possible US talks with Venezuela's Maduro

-
 Australian Paralympics gold medallist Greco dies aged 28
Australian Paralympics gold medallist Greco dies aged 28
-
Leftist, far-right candidates go through to Chilean presidential run-off

-
 Zelensky in Paris to seek air defence help for Ukraine
Zelensky in Paris to seek air defence help for Ukraine
-
Bangladesh verdict due in ex-PM's crimes against humanity trial

-
 A pragmatic communist and a far-right leader: Chile's presidential finalists
A pragmatic communist and a far-right leader: Chile's presidential finalists
-
England ready for World Cup after perfect campaign

-
 Cervical cancer vaccine push has saved 1.4 million lives: Gavi
Cervical cancer vaccine push has saved 1.4 million lives: Gavi
-
Graid Technology Finalizes Intel VROC Licensing Agreement, Expanding Leadership in Enterprise Storage Solutions
| RBGPF | 0.46% | 76 | $ | |
| CMSC | -0.21% | 23.849 | $ | |
| BCC | -0.66% | 68.585 | $ | |
| JRI | -0.74% | 13.55 | $ | |
| SCS | -0.48% | 15.625 | $ | |
| NGG | 0.72% | 77.94 | $ | |
| GSK | 1.39% | 47.845 | $ | |
| RIO | 0.83% | 71.22 | $ | |
| BTI | 1.29% | 54.84 | $ | |
| AZN | 0.69% | 89.72 | $ | |
| RYCEF | -1.04% | 14.4 | $ | |
| RELX | -1.3% | 40.8 | $ | |
| BCE | -0.48% | 22.72 | $ | |
| CMSD | -0.42% | 23.89 | $ | |
| BP | 0.64% | 36.765 | $ | |
| VOD | -0.12% | 12.305 | $ |

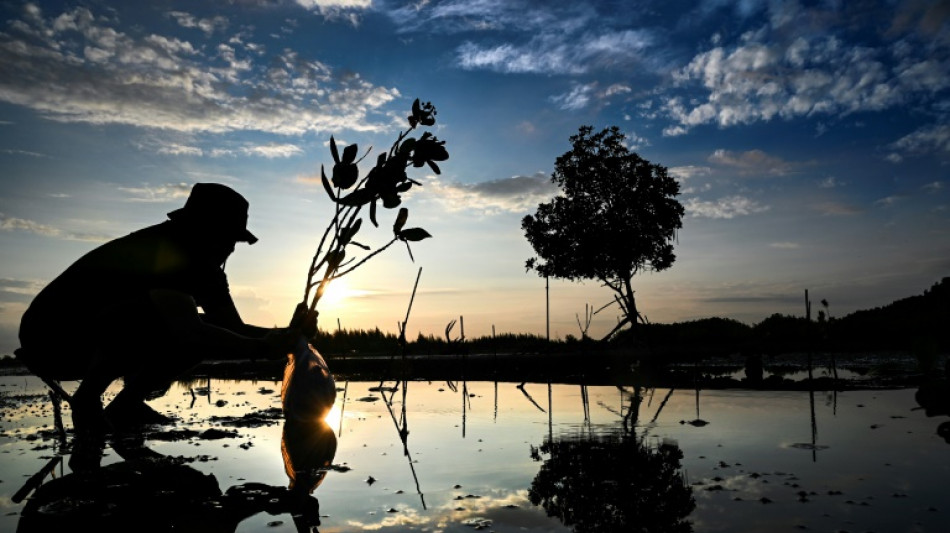
Half of mangrove ecosystems at risk: conservationists
Half of the world's mangrove ecosystems are at risk of collapse due to climate change, deforestation and pollution, according to a study published Wednesday.
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), known for its red list of threatened species, has for the first time taken stock of the world's mangroves, evaluating 36 different regions.
IUCN director general Grethel Aguilar said the assessment "highlights the urgent need for coordinated conservation of mangroves -- crucial habitats for millions in vulnerable communities worldwide".
Mangroves are trees or shrubs that grow mainly in seawater or brackish water along coastlines and tidal rivers, in equatorial climes.
Released on the International Day for Biodiversity, IUCN said its findings show that "50 percent of the mangrove ecosystems assessed are at risk of collapse" -- categorised as either vulnerable, endangered or critically endangered.
According to the assessment, 20 percent were at severe risk of collapse.
Mangroves are threatened by deforestation, development, pollution, and dam construction.
However, the risk is increasing due to sea-level rise and the greater frequency of severe storms associated with climate change.
Around 15 percent of the world's coasts are covered by mangroves, covering about 150,000 square kilometres.
- Disastrous disappearance -
Climate change threatens a third of mangrove ecosystems assessed, due to rising sea levels.
According to estimates, at the current rate, a quarter of the global area of mangroves is expected to be submerged in the next 50 years, IUCN said.
The northwest Atlantic Ocean, the northern Indian Ocean, the Red Sea, the South China Sea, and the Gulf of Aden coasts are expected to be particularly severely affected.
"Mangrove ecosystems are exceptional in their ability to provide essential services to people, including coastal disaster risk reduction, carbon storage and sequestration, and support for fisheries," said Angela Andrade, chair of the IUCN commission on ecosystem management.
"Their loss stands to be disastrous for nature and people across the globe."
The study said looking after mangroves was essential for mitigating the effects of climate change, with healthy ecosystems coping better with sea level rise and providing inland protection from the effects of severe storms.
Without significant improvement by 2050, climate change and rising sea levels will lead to the loss of 1.8 billion tonnes of carbon stored in mangroves.
Mangroves currently store nearly 11 billion tons of carbon -- almost three times the amount of carbon stored by tropical forests of the same size.
Maintaining good sediment circulation and allowing mangroves to expand inland will help them cope with sea level rise, IUCN said. It also called for the restoration of mangroves which have already disappeared.
"A very good study of mangrove change globally that was published in 2022 indicates about 5,000 square kilometres of mangrove were lost" between 1996 and 2020, IUCN's Marco Valderrabano told AFP.
B.AbuZeid--SF-PST



