
-
 Sudan 'lost all sources of revenue' in the war: finance minister to AFP
Sudan 'lost all sources of revenue' in the war: finance minister to AFP
-
Freezing rain hampers transport in Central Europe

-
 Nuuk, Copenhagen cautiously mull Greenland independence
Nuuk, Copenhagen cautiously mull Greenland independence
-
'Proving the boys wrong': Teenage racers picked for elite driver programme

-
 Mbappe absent from training as Arbeloa takes charge at Real Madrid
Mbappe absent from training as Arbeloa takes charge at Real Madrid
-
Iran worries push up oil price as world stocks diverge
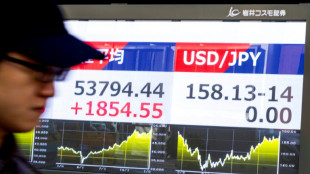
-
 Volvo Cars pauses battery factory after fruitless partner search
Volvo Cars pauses battery factory after fruitless partner search
-
Social media harms teens, watchdog warns, as France weighs ban

-
 Central bank chiefs voice 'full solidarity' with US Fed, Powell
Central bank chiefs voice 'full solidarity' with US Fed, Powell
-
Greece airspace shutdown exposes badly outdated systems

-
 France climate goals off track as emissions cuts slow again
France climate goals off track as emissions cuts slow again
-
Boeing sells 50 737 MAX jets to leasing group ACG

-
 Freezing rain paralyses transport in Central Europe
Freezing rain paralyses transport in Central Europe
-
Man Utd reach deal to appoint Carrick as interim boss: reports

-
 Trump hits Iran trade partners with tariffs as protest toll soars
Trump hits Iran trade partners with tariffs as protest toll soars
-
Is China a threat to Greenland as Trump argues?

-
 Takaichi says urged S. Korea's Lee to help 'ensure regional stability'
Takaichi says urged S. Korea's Lee to help 'ensure regional stability'
-
South Korean prosecutors set to demand heavy sentence for Yoon

-
 Honduras electoral authorities reject vote recount
Honduras electoral authorities reject vote recount
-
Tractors in Paris to protest EU's trade deal with S. America

-
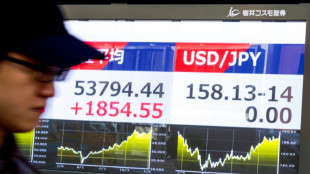 Asian markets rise, Iran worries push up oil
Asian markets rise, Iran worries push up oil
-
Williams loses golden oldie clash in final Australian Open warm-up

-
 Kyrgios stands by decision to skip Australian Open singles
Kyrgios stands by decision to skip Australian Open singles
-
Disaster losses drop in 2025, picture still 'alarming': Munich Re

-
 Williams, 45, loses in first round of final Australian Open warm-up
Williams, 45, loses in first round of final Australian Open warm-up
-
Doncic scores 42 points but Lakers humbled by Kings

-
 'Serious threat': Indonesia legal reform sparks rights challenges
'Serious threat': Indonesia legal reform sparks rights challenges
-
Rodgers misery as Texans rout Steelers to advance in NFL playoffs

-
 Morocco's Bono 'one of best goalkeepers in the world'
Morocco's Bono 'one of best goalkeepers in the world'
-
Salah and Mane meet again with AFCON final place on the line

-
 French museum fare hikes for non-European tourists spark outcry
French museum fare hikes for non-European tourists spark outcry
-
In 'big trouble'? The factors determining Iran's future

-
 Osimhen finds AFCON scoring touch to give Nigeria cutting edge
Osimhen finds AFCON scoring touch to give Nigeria cutting edge
-
Trump announces tariffs on Iran trade partners as protest toll rises

-
 Sabalenka favourite at Australian Open but faces Swiatek, US threats
Sabalenka favourite at Australian Open but faces Swiatek, US threats
-
Gay Australian footballer Cavallo alleges former club was homophobic

-
 Global Sports Brand U.S. Polo Assn. Announced as Official Jersey and Apparel Sponsor for the Legendary Snow Polo World Cup St. Moritz
Global Sports Brand U.S. Polo Assn. Announced as Official Jersey and Apparel Sponsor for the Legendary Snow Polo World Cup St. Moritz
-
Trump has options on Iran, but first must define goal

-
 Paris FC's Ikone stuns PSG to knock out former club from French Cup
Paris FC's Ikone stuns PSG to knock out former club from French Cup
-
Australia's ambassador to US leaving post, marked by Trump rift

-
 Slot angered by 'weird' Szoboszlai error in Liverpool FA Cup win
Slot angered by 'weird' Szoboszlai error in Liverpool FA Cup win
-
Szoboszlai plays hero and villain in Liverpool's FA Cup win

-
 Hawaii's Kilauea volcano puts on spectacular lava display
Hawaii's Kilauea volcano puts on spectacular lava display
-
US stocks at records despite early losses on Fed independence angst

-
 Koepka rejoins PGA Tour under new rules for LIV players
Koepka rejoins PGA Tour under new rules for LIV players
-
Ex-France, Liverpool defender Sakho announces retirement

-
 Jerome Powell: The careful Fed chair standing firm against Trump
Jerome Powell: The careful Fed chair standing firm against Trump
-
France scrum-half Le Garrec likely to miss start of Six Nations

-
 AI helps fuel new era of medical self-testing
AI helps fuel new era of medical self-testing
-
Leaders of Japan and South Korea meet as China flexes muscles


Ailing oceans in the spotlight at major UN meet
A long-delayed UN conference on how to restore the faltering health of global oceans kicks off in Lisbon Monday, with thousands of policymakers, experts and advocates on the case.
Humanity needs healthy oceans. They generate 50 percent of the oxygen we breathe and provide essential protein and nutrients to billions of people every day.
Covering more than two-thirds of Earth's surface, the seven seas have also softened the impact of climate change for life on land.
But at a terrible cost.
Absorbing around a quarter of CO2 pollution -- even as emissions increased by half over the last 60 years -- has turned sea water acidic, threatening aquatic food chains and the ocean's capacity to pull down carbon.
And soaking up more than 90 percent of the excess heat from global warming has spawned massive marine heatwaves that are killing off precious coral reefs and expanding dead zones bereft of oxygen.
"We have only begun to understand the extent to which climate change is going to wreak havoc on ocean health," said Charlotte de Fontaubert, the World Bank's global lead for the blue economy.
Making things worse is an unending torrent of pollution, including a garbage truck's worth of plastic every minute, according the UN Environment Programme (UNEP).
On current trends, yearly plastic waste will nearly triple to one billion tonnes by 2060, according to a recent OECD report.
- Wild fish stocks -
Microplastics -- found inside Arctic ice and fish in the ocean's deepest trenches -- are estimated to kill more than a million seabirds and over 100,000 marine mammals each year.
Solutions on the table range from recycling to global caps on plastic production.
Global fisheries will also be under the spotlight during the five-day UN Ocean Conference, originally slated for April 2020 and jointly hosted by Portugal and Kenya.
"At least one-third of wild fish stocks are overfished and less than 10 percent of the ocean is protected," Kathryn Matthews, chief scientist for US-based NGO Oceana, told AFP.
"Destructive and illegal fishing vessels operate with impunity in many coastal waters and on the high seas."
One culprit is nearly $35 billion in subsidies. Baby steps taken last week by the World Trade Organization (WTO) to reduce handouts to industry will hardly make a dent, experts said.
The conference will also see a push for a moratorium on deep-sea mining of rare metals needed for a boom electric vehicle battery construction.
Scientists say poorly understood seabed ecosystems are fragile and could take decades or longer to heal once disrupted.
Another major focus will be "blue food", the new watchword for ensuring that marine harvests from all sources are sustainable and socially responsible.
- Protected areas -
Rising aquaculture yields -- from salmon and tuna to shellfish and algae -- are on track to overtake wild marine harvests in decline since the 1990s, with each producing roughly 100 million tonnes per year.
If properly managed, "wild ocean fish can provide a climate-friendly, micro-nutrient protein source that can feed one billion people a healthy seafood meal every day -- forever," said Matthews.
The Lisbon meet will see ministers and even a few heads of state, including French President Emmanuel Macron, but is not a formal negotiating session.
But participants will push for a strong oceans agenda at two critical summits later this year: the COP27 UN climate talks in November, hosted by Egypt, followed by the long-delayed COP15 biodiversity negotiations, recently moved from China to Montreal.
Oceans are already at the heart of a draft biodiversity treaty tasked with halting what many scientists fear is the first "mass extinction" event in 65 million years.
Nearly 100 nations support a cornerstone provision that would designate 30 percent of the planet's land and ocean as protected areas.
For climate change, the focus will be on carbon sequestration: boosting the ocean's capacity to soak up CO2, whether by enhancing natural sinks such as mangroves or through geoengineering schemes.
At the same time, scientists warn, a drastic reduction of greenhouse gases is needed to restore ocean health.
K.AbuTaha--SF-PST




