-
 EU defends carbon tax as ministers take over COP30 negotiations
EU defends carbon tax as ministers take over COP30 negotiations
-
McCartney to release silent AI protest song

-
 Stocks tepid on uncertainty over earnings, tech rally, US rates
Stocks tepid on uncertainty over earnings, tech rally, US rates
-
Louvre shuts gallery over ceiling safety fears

-
 'Stranded, stressed' giraffes in Kenya relocated as habitats encroached
'Stranded, stressed' giraffes in Kenya relocated as habitats encroached
-
US Supreme Court to hear migrant asylum claim case

-
 Western aid cuts could cause 22.6 million deaths, researchers say
Western aid cuts could cause 22.6 million deaths, researchers say
-
Clarke hails Scotland 'legends' ahead of crunch World Cup qualifier

-
 S.Africa says 'suspicious' flights from Israel show 'agenda to cleanse Palestinians'
S.Africa says 'suspicious' flights from Israel show 'agenda to cleanse Palestinians'
-
South Korea pledges to phase out coal plants at COP30

-
 Ex-PSG footballer Hamraoui claims 3.5m euros damages against club
Ex-PSG footballer Hamraoui claims 3.5m euros damages against club
-
Mbappe, PSG in counterclaims worth hundreds of millions

-
 Two newly discovered Bach organ works unveiled in Germany
Two newly discovered Bach organ works unveiled in Germany
-
Stocks lower on uncertainty over earnings, tech rally, US rates

-
 Barca to make long-awaited Camp Nou return on November 22
Barca to make long-awaited Camp Nou return on November 22
-
COP30 talks enter homestretch with UN warning against 'stonewalling'

-
 France makes 'historic' accord to sell Ukraine 100 warplanes
France makes 'historic' accord to sell Ukraine 100 warplanes
-
Delhi car bombing accused appears in Indian court, another suspect held

-
 Emirates orders 65 more Boeing 777X planes despite delays
Emirates orders 65 more Boeing 777X planes despite delays
-
Ex-champion Joshua to fight YouTube star Jake Paul

-
 Bangladesh court sentences ex-PM to be hanged for crimes against humanity
Bangladesh court sentences ex-PM to be hanged for crimes against humanity
-
Trade tensions force EU to cut 2026 eurozone growth forecast

-
 'Killed without knowing why': Sudanese exiles relive Darfur's past
'Killed without knowing why': Sudanese exiles relive Darfur's past
-
Stocks lower on uncertainty over tech rally, US rates

-
 Death toll from Indonesia landslides rises to 18
Death toll from Indonesia landslides rises to 18
-
Macron, Zelensky sign accord for Ukraine to buy French fighter jets

-
 India Delhi car bomb accused appears in court
India Delhi car bomb accused appears in court
-
Bangladesh ex-PM sentenced to be hanged for crimes against humanity

-
 Leftist, far-right candidates advance to Chilean presidential run-off
Leftist, far-right candidates advance to Chilean presidential run-off
-
Bangladesh's Hasina: from PM to crimes against humanity convict

-
 Rugby chiefs unveil 'watershed' Nations Championship
Rugby chiefs unveil 'watershed' Nations Championship
-
EU predicts less eurozone 2026 growth due to trade tensions

-
 Swiss growth suffered from US tariffs in Q3: data
Swiss growth suffered from US tariffs in Q3: data
-
Bangladesh ex-PM sentenced to death for crimes against humanity

-
 Singapore jails 'attention seeking' Australian over Ariana Grande incident
Singapore jails 'attention seeking' Australian over Ariana Grande incident
-
Tom Cruise receives honorary Oscar for illustrious career

-
 Fury in China over Japan PM's Taiwan comments
Fury in China over Japan PM's Taiwan comments
-
Carbon capture promoters turn up in numbers at COP30: NGO

-
 Japan-China spat over Taiwan comments sinks tourism stocks
Japan-China spat over Taiwan comments sinks tourism stocks
-
No Wemby, no Castle, no problem as NBA Spurs rip Kings

-
 In reversal, Trump supports House vote to release Epstein files
In reversal, Trump supports House vote to release Epstein files
-
Gauff-led holders USA to face Spain, Argentina at United Cup

-
 Ecuador voters reject return of US military bases
Ecuador voters reject return of US military bases
-
Bodyline and Bradman to Botham and Stokes: five great Ashes series

-
 Iran girls kick down social barriers with karate
Iran girls kick down social barriers with karate
-
Asian markets struggle as fears build over tech rally, US rates

-
 Australia's 'Dad's Army' ready to show experience counts in Ashes
Australia's 'Dad's Army' ready to show experience counts in Ashes
-
UN Security Council set to vote on international force for Gaza

-
 Japan-China spat sinks tourism stocks
Japan-China spat sinks tourism stocks
-
Ecuador voters set to reject return of US military bases


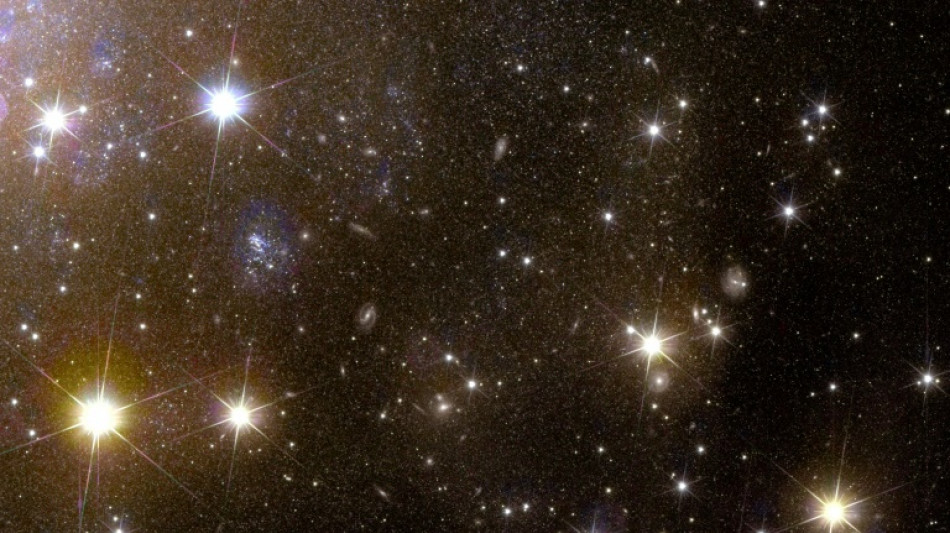
Creeping ice clouding vision of Europe space telescope Euclid
Scientists are trying to melt a thin layer of ice that is increasingly clouding the vision of the "dark universe detective" space telescope Euclid, the European Space Agency said on Tuesday.
It is the latest of several technical setbacks for the wide-eyed telescope, which blasted off into space in July on a mission to chart a third of the sky.
By doing so, the ESA hopes Euclid will reveal out more about the nature of dark matter and dark energy, which are thought to make up 95 percent of the universe but remain shrouded in mystery.
During checks in November, the team on the ground first noticed that they were losing a little light coming into the telescope's visible light imager, Euclid instrument operations scientist Ralf Kohley told AFP.
After digging into the data, they believe the problem is a layer of ice -- thought to be just the width of a strand of DNA -- that is building up on the telescope's optical surfaces.
"It's a big problem," Kohley acknowledged.
But researchers have been working on it, Kohley said, adding that he had no doubt Euclid would be able to finish its mission.
Keeping out water is a common problem for all spacecrafts.
Despite best efforts on the ground, a tiny amount of water absorbed during a spacecraft's assembly on Earth can smuggle its way to space.
Faced with the cold vastness of space, the water molecules freeze to the first surface they can -- in this case, some may have landed on the Euclid's mirrors.
- Thin ice -
Shortly after the telescope launched, scientists used its on-board heaters to heat up everything on the spacecraft, hoping to blast out any potential water.
This could be done again.
"But heating out everything is very disruptive for the mission," Kohley said.
Because heat expands most materials, warming up the whole spacecraft involves careful recalibration.
It would take at least a month to get the telescope back to its job surveying the sky, Kohley said.
So last week, the ESA started warming just two of the telescope's mirrors, turning the temperature up just enough to hopefully melt away the ice.
This "minimally invasive" partial warming will last until Thursday, Kohley said.
The scientists may not know if it works until mid-April.
Part of the problem is that the scientists do not know exactly where the ice is accumulating -- or how much there is.
And even if the scientists do manage to melt the ice, it could come back over time, Kohley warned.
If the partial warming plan fails, the ESA will have to heat up the whole spacecraft.
If the team have to do this every year during the telescope's planned-six year mission it could result in a six-month delay, Kohley said.
"But that's all speculation," he said.
"For the moment, we have to wait and see -- and hope we can rid of this problem in a more elegant fashion."
It is not the first problem for Euclid.
Cosmic rays previously confused the spacecraft's fine guidance sensor, which required a complicated software update.
Some unwanted sunlight also interfered with its observations, a problem solved by slightly rotating the telescope, Kohley said.
However nothing can be done about particularly strong solar flares occasionally projecting X-ray images on the visible imager.
Euclid, which the ESA calls its "dark universe detective," officially started its survey last month.
Its first images, released in November, revealed swirling galaxies bursting with colour in the distant cosmos.
J.AbuShaban--SF-PST