-
 LeBron back in training, edges closer to Lakers return
LeBron back in training, edges closer to Lakers return
-
Climate talks run into night as COP30 hosts seek breakthrough

-
 Germany and Netherlands lock up World Cup spots in style
Germany and Netherlands lock up World Cup spots in style
-
Germany's Woltemade hopes for 2026 World Cup spot after scoring again

-
 Germany 'send message' with Slovakia rout to reach 2026 World Cup
Germany 'send message' with Slovakia rout to reach 2026 World Cup
-
Trump unveils fast-track visas for World Cup ticket holders

-
 Netherlands qualify for World Cup, Poland in play-offs
Netherlands qualify for World Cup, Poland in play-offs
-
Germany crush Slovakia to qualify for 2026 World Cup

-
 Stocks gloomy on earnings and tech jitters, US rate worries
Stocks gloomy on earnings and tech jitters, US rate worries
-
'In it to win it': Australia doubles down on climate hosting bid

-
 Former NFL star Brown could face 30 yrs jail for shooting case: prosecutor
Former NFL star Brown could face 30 yrs jail for shooting case: prosecutor
-
Fate of Canada government hinges on tight budget vote

-
 New research measures how much plastic is lethal for marine life
New research measures how much plastic is lethal for marine life
-
Mbappe, PSG face off in multi-million lawsuit

-
 EU defends carbon tax as ministers take over COP30 negotiations
EU defends carbon tax as ministers take over COP30 negotiations
-
McCartney to release silent AI protest song

-
 Stocks tepid on uncertainty over earnings, tech rally, US rates
Stocks tepid on uncertainty over earnings, tech rally, US rates
-
Louvre shuts gallery over ceiling safety fears

-
 'Stranded, stressed' giraffes in Kenya relocated as habitats encroached
'Stranded, stressed' giraffes in Kenya relocated as habitats encroached
-
US Supreme Court to hear migrant asylum claim case

-
 Western aid cuts could cause 22.6 million deaths, researchers say
Western aid cuts could cause 22.6 million deaths, researchers say
-
Clarke hails Scotland 'legends' ahead of crunch World Cup qualifier

-
 S.Africa says 'suspicious' flights from Israel show 'agenda to cleanse Palestinians'
S.Africa says 'suspicious' flights from Israel show 'agenda to cleanse Palestinians'
-
South Korea pledges to phase out coal plants at COP30

-
 Ex-PSG footballer Hamraoui claims 3.5m euros damages against club
Ex-PSG footballer Hamraoui claims 3.5m euros damages against club
-
Mbappe, PSG in counterclaims worth hundreds of millions

-
 Two newly discovered Bach organ works unveiled in Germany
Two newly discovered Bach organ works unveiled in Germany
-
Stocks lower on uncertainty over earnings, tech rally, US rates

-
 Barca to make long-awaited Camp Nou return on November 22
Barca to make long-awaited Camp Nou return on November 22
-
COP30 talks enter homestretch with UN warning against 'stonewalling'

-
 France makes 'historic' accord to sell Ukraine 100 warplanes
France makes 'historic' accord to sell Ukraine 100 warplanes
-
Delhi car bombing accused appears in Indian court, another suspect held

-
 Emirates orders 65 more Boeing 777X planes despite delays
Emirates orders 65 more Boeing 777X planes despite delays
-
Ex-champion Joshua to fight YouTube star Jake Paul

-
 Bangladesh court sentences ex-PM to be hanged for crimes against humanity
Bangladesh court sentences ex-PM to be hanged for crimes against humanity
-
Trade tensions force EU to cut 2026 eurozone growth forecast

-
 'Killed without knowing why': Sudanese exiles relive Darfur's past
'Killed without knowing why': Sudanese exiles relive Darfur's past
-
Stocks lower on uncertainty over tech rally, US rates

-
 Death toll from Indonesia landslides rises to 18
Death toll from Indonesia landslides rises to 18
-
Macron, Zelensky sign accord for Ukraine to buy French fighter jets

-
 India Delhi car bomb accused appears in court
India Delhi car bomb accused appears in court
-
Bangladesh ex-PM sentenced to be hanged for crimes against humanity

-
 Leftist, far-right candidates advance to Chilean presidential run-off
Leftist, far-right candidates advance to Chilean presidential run-off
-
Bangladesh's Hasina: from PM to crimes against humanity convict

-
 Rugby chiefs unveil 'watershed' Nations Championship
Rugby chiefs unveil 'watershed' Nations Championship
-
EU predicts less eurozone 2026 growth due to trade tensions

-
 Swiss growth suffered from US tariffs in Q3: data
Swiss growth suffered from US tariffs in Q3: data
-
Bangladesh ex-PM sentenced to death for crimes against humanity

-
 Singapore jails 'attention seeking' Australian over Ariana Grande incident
Singapore jails 'attention seeking' Australian over Ariana Grande incident
-
Tom Cruise receives honorary Oscar for illustrious career


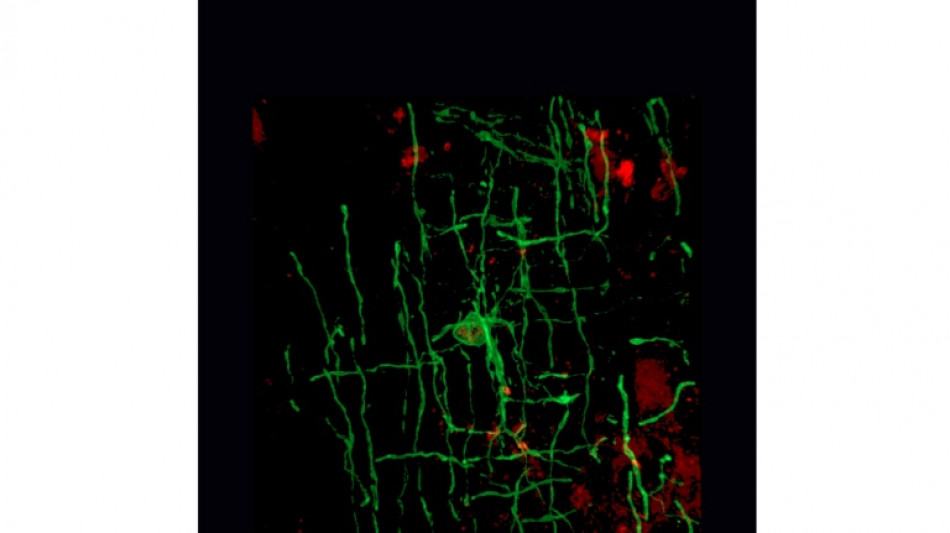
Ancient viruses responsible for our big brains and bodies: study
Ancient viruses that infected vertebrates hundreds of millions of years ago played a pivotal role in the evolution of our advanced brains and large bodies, a study said Thursday.
The research, published in the journal Cell, examined the origins of myelin, an insulating layer of fatty tissue that forms around nerves and allows electrical impulses to travel faster.
According to the authors, a gene sequence acquired from retroviruses -- viruses that invade their host's DNA -- is crucial for myelin production, and that code is now found in modern mammals, amphibians and fish.
"The thing I find the most remarkable is that all of the diversity of modern vertebrates that we know of, and the size they've achieved: elephants, giraffes, anacondas, bullfrogs, condors wouldn't have happened," senior author and neuroscientist Robin Franklin of Altos Labs-Cambridge Institute of Science told AFP.
In new research led by Tanay Ghosh, a computational biologist and geneticist in Franklin's lab, analysts trawled through genome databases to try to discover the genetics that were likely associated with the cells that produce myelin.
Specifically, he was interested in exploring mysterious "noncoding regions" of the genome that have no obvious function and were once dismissed as junk, but are now recognized as having evolutionary importance.
Ghosh's search landed upon a particular sequence derived from an endogenous retrovirus, long lurking in our genes, which the team dubbed "RetroMyelin."
To test their finding, researchers carried out experiments in which they knocked down the RetroMyelin sequence in rat cells, and found they no longer produced a basic protein required for myelin formation.
- Faster reactions, bigger bodies -
Next, they searched for RetroMyelin-like sequences in the genomes of other species, finding similar code in jawed vertebrates -- fellow mammals, birds, fish, reptiles and amphibians -- but not in jawless vertebrates or invertebrates.
This led them to believe the sequence appeared in the tree of life around the same time as jaws, which first evolved around 360 million years ago in the Devonian period, called the Age of Fishes.
"There's always been an evolutionary pressure to make nerve fibers conduct electrical impulses quicker," said Franklin. "If they do that quicker, then you can act quicker," he added, which is useful for both predators trying to catch things, and prey trying to flee.
Myelin enables rapid impulse conduction without widening the diameter of nerve cells, allowing them to be packed closer together.
It also provides structural support, meaning nerves can grow longer, allowing for longer limbs.
In myelin's absence, invertebrates have found other ways to transmit signals faster -- giant squids for example have evolved wider nerve cells.
Finally, the team wanted to learn whether the retroviral infection happened once, to a single ancestor species, or whether it happened more than once.
- More discoveries await? -
To answer this, they used computational methods to analyze the RetroMyelin sequences of 22 jawed vertebrate species, finding the sequences were more similar within than between species.
The finding suggested multiple waves of infection led to the diversity of vertebrate species we see today, the team said.
"One tends to think of viruses as pathogens, or disease causing agents," said Franklin.
But the reality is more complicated, he said: at various points in history retroviruses have entered the genome and integrated themselves into a species' reproductive cells, allowing them to be passed down to future generations.
One of the most well known examples is the placenta -- one of the defining characteristics of most mammals -- which we acquired from a pathogen embedded in our genome in the deep past.
Ghosh said the myelin finding could be just another step in an emerging field. "There are still a lot of things to understand still in terms of biology about how these sequences are driving different processes of evolution," he said.
H.Jarrar--SF-PST