-
 LeBron back in training, edges closer to Lakers return
LeBron back in training, edges closer to Lakers return
-
Climate talks run into night as COP30 hosts seek breakthrough

-
 Germany and Netherlands lock up World Cup spots in style
Germany and Netherlands lock up World Cup spots in style
-
Germany's Woltemade hopes for 2026 World Cup spot after scoring again

-
 Germany 'send message' with Slovakia rout to reach 2026 World Cup
Germany 'send message' with Slovakia rout to reach 2026 World Cup
-
Trump unveils fast-track visas for World Cup ticket holders

-
 Netherlands qualify for World Cup, Poland in play-offs
Netherlands qualify for World Cup, Poland in play-offs
-
Germany crush Slovakia to qualify for 2026 World Cup

-
 Stocks gloomy on earnings and tech jitters, US rate worries
Stocks gloomy on earnings and tech jitters, US rate worries
-
'In it to win it': Australia doubles down on climate hosting bid

-
 Former NFL star Brown could face 30 yrs jail for shooting case: prosecutor
Former NFL star Brown could face 30 yrs jail for shooting case: prosecutor
-
Fate of Canada government hinges on tight budget vote

-
 New research measures how much plastic is lethal for marine life
New research measures how much plastic is lethal for marine life
-
Mbappe, PSG face off in multi-million lawsuit

-
 EU defends carbon tax as ministers take over COP30 negotiations
EU defends carbon tax as ministers take over COP30 negotiations
-
McCartney to release silent AI protest song

-
 Stocks tepid on uncertainty over earnings, tech rally, US rates
Stocks tepid on uncertainty over earnings, tech rally, US rates
-
Louvre shuts gallery over ceiling safety fears

-
 'Stranded, stressed' giraffes in Kenya relocated as habitats encroached
'Stranded, stressed' giraffes in Kenya relocated as habitats encroached
-
US Supreme Court to hear migrant asylum claim case

-
 Western aid cuts could cause 22.6 million deaths, researchers say
Western aid cuts could cause 22.6 million deaths, researchers say
-
Clarke hails Scotland 'legends' ahead of crunch World Cup qualifier

-
 S.Africa says 'suspicious' flights from Israel show 'agenda to cleanse Palestinians'
S.Africa says 'suspicious' flights from Israel show 'agenda to cleanse Palestinians'
-
South Korea pledges to phase out coal plants at COP30

-
 Ex-PSG footballer Hamraoui claims 3.5m euros damages against club
Ex-PSG footballer Hamraoui claims 3.5m euros damages against club
-
Mbappe, PSG in counterclaims worth hundreds of millions

-
 Two newly discovered Bach organ works unveiled in Germany
Two newly discovered Bach organ works unveiled in Germany
-
Stocks lower on uncertainty over earnings, tech rally, US rates

-
 Barca to make long-awaited Camp Nou return on November 22
Barca to make long-awaited Camp Nou return on November 22
-
COP30 talks enter homestretch with UN warning against 'stonewalling'

-
 France makes 'historic' accord to sell Ukraine 100 warplanes
France makes 'historic' accord to sell Ukraine 100 warplanes
-
Delhi car bombing accused appears in Indian court, another suspect held

-
 Emirates orders 65 more Boeing 777X planes despite delays
Emirates orders 65 more Boeing 777X planes despite delays
-
Ex-champion Joshua to fight YouTube star Jake Paul

-
 Bangladesh court sentences ex-PM to be hanged for crimes against humanity
Bangladesh court sentences ex-PM to be hanged for crimes against humanity
-
Trade tensions force EU to cut 2026 eurozone growth forecast

-
 'Killed without knowing why': Sudanese exiles relive Darfur's past
'Killed without knowing why': Sudanese exiles relive Darfur's past
-
Stocks lower on uncertainty over tech rally, US rates

-
 Death toll from Indonesia landslides rises to 18
Death toll from Indonesia landslides rises to 18
-
Macron, Zelensky sign accord for Ukraine to buy French fighter jets

-
 India Delhi car bomb accused appears in court
India Delhi car bomb accused appears in court
-
Bangladesh ex-PM sentenced to be hanged for crimes against humanity

-
 Leftist, far-right candidates advance to Chilean presidential run-off
Leftist, far-right candidates advance to Chilean presidential run-off
-
Bangladesh's Hasina: from PM to crimes against humanity convict

-
 Rugby chiefs unveil 'watershed' Nations Championship
Rugby chiefs unveil 'watershed' Nations Championship
-
EU predicts less eurozone 2026 growth due to trade tensions

-
 Swiss growth suffered from US tariffs in Q3: data
Swiss growth suffered from US tariffs in Q3: data
-
Bangladesh ex-PM sentenced to death for crimes against humanity

-
 Singapore jails 'attention seeking' Australian over Ariana Grande incident
Singapore jails 'attention seeking' Australian over Ariana Grande incident
-
Tom Cruise receives honorary Oscar for illustrious career


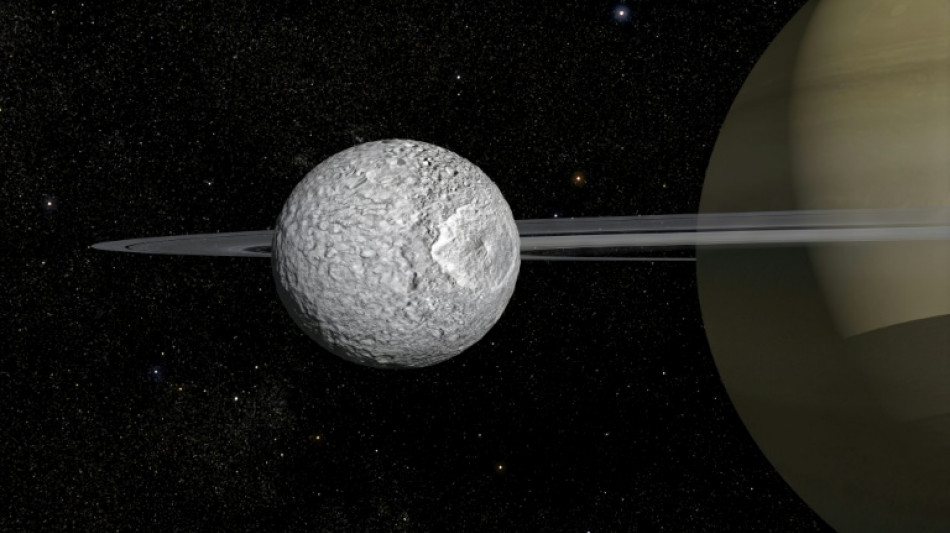
Life on 'Death Star'? Saturn moon Mimas has hidden ocean
Saturn's small moon Mimas seems an unlikely suspect in the hunt for life in Earth's backyard -- it is probably best known for looking like the "Death Star" in the Star Wars films.
But scientists said on Wednesday that underneath the unassuming moon's icy shell is a vast hidden ocean that has many of the ingredients necessary to host primitive alien life.
Mimas is the latest to join a growing family of icy moons thought to harbour inner oceans in our Solar System which also includes fellow Saturn satellites Enceladus and Titan as well as Jupiter's Europa and Ganymede.
But the inclusion of Mimas in this list has come as a surprise.
"If there is one place in the universe where we did not expect to find conditions favourable to life, it is Mimas," said Paris Observatory astronomer Valery Lainey, the lead author of a new study in the journal Nature.
Mimas, which is only 400 kilometres (250 miles) in diameter, was "not at all suitable for the job", Lainey told a press conference.
Discovered by English astronomer William Herschel in 1789, the moon has the nickname "Death Star" because one particularly huge crater makes it look eerily similar to the space station used by Darth Vader and the villainous Empire in Star Wars.
Its craggy, crater-riddled surface is inert, showing no sign of underlying geologic activity that would suggest a hidden ocean.
- 'Something happening inside' -
Other water worlds such as Mimas' big sibling Enceladus have smooth surfaces due to their rumbling internal oceans and many geysers.
These geysers, which shoot out material from the surface, also demonstrate that there is enough heat below to keep the water in a liquid state.
Despite its seemingly desolate exterior, Lainey said the researchers suspected that "something was happening inside" Mimas.
They studied how the moon's rotation is affected by its interior structure, first publishing research in 2014 which was not strong enough to prove the presence of a hidden ocean.
Most scientists remained convinced by the other main hypothesis: that Mimas has a solid core of rock.
"We could have left it there," Lainey said, adding that they were "frustrated".
For the new study, the team carefully analysed the moon's rotation and orbit in dozens of images taken by NASA's Cassini spacecraft, which orbited Saturn from 2004 to 2017.
They detected tiny oscillations -- rotations of just a few hundred metres -- which could not have occurred if the moon had a solid rock interior.
"The only viable conclusion is that Mimas has a subsurface ocean," said two US-based scientists not involved in the study.
"The finding calls for a fresh take on what constitutes an ocean moon," Matija Cuk of the Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence (SETI) and planetary scientist Alyssa Rose Rhoden wrote in a comment article in Nature.
- The right stuff for life -
Mimas' ice-covered shell is between 20 and 30 kilometres thick, similar to Enceladus, the study estimated.
The researchers believe the ocean formed relatively recently -- between five to 15 million years ago -- which could explain why signs of its existence have yet to rise and smooth the moon's surface.
The ocean likely exists due to the influence of Saturn's many other moons, whose tidal effects shook Mimas and created the necessary heat, they said.
Mimas "brings together all the conditions necessary for habitability: water maintained by a heat source that is in contact with rocks so that chemical exchanges develop," said study co-author Nicolas Rambaux, also of the Paris Observatory.
So could this nearby water world harbour primitive forms of life such as bacteria?
"That question will be addressed by future space missions over the coming decades," Lainey said.
"One thing is certain: if you are looking for the most recent conditions of habitability to have formed in the Solar System, Mimas is the place to look."
Y.Zaher--SF-PST