-
 North Korea says Seoul-US sub deal will trigger 'nuclear domino' effect
North Korea says Seoul-US sub deal will trigger 'nuclear domino' effect
-
Education for girls hit hard by India's drying wells

-
 Haitian gangs getting rich off murky market for baby eels
Haitian gangs getting rich off murky market for baby eels
-
Trump says will talk to Venezuela's Maduro, 'OK' with US strikes on Mexico

-
 Oscar Piastri wins Australia's top sports honour
Oscar Piastri wins Australia's top sports honour
-
'Severely restricted': Russia's Saint Petersburg faces cultural crackdown
-
 Polish PM denounces 'sabotage' of railway supply line to Ukraine
Polish PM denounces 'sabotage' of railway supply line to Ukraine
-
UK toughens asylum system with radical overhaul

-
 Carney's Liberals pass budget, avoiding snap Canada election
Carney's Liberals pass budget, avoiding snap Canada election
-
LeBron back in training, edges closer to Lakers return

-
 Climate talks run into night as COP30 hosts seek breakthrough
Climate talks run into night as COP30 hosts seek breakthrough
-
Germany and Netherlands lock up World Cup spots in style

-
 Germany's Woltemade hopes for 2026 World Cup spot after scoring again
Germany's Woltemade hopes for 2026 World Cup spot after scoring again
-
Germany 'send message' with Slovakia rout to reach 2026 World Cup

-
 Trump unveils fast-track visas for World Cup ticket holders
Trump unveils fast-track visas for World Cup ticket holders
-
Netherlands qualify for World Cup, Poland in play-offs

-
 Germany crush Slovakia to qualify for 2026 World Cup
Germany crush Slovakia to qualify for 2026 World Cup
-
Stocks gloomy on earnings and tech jitters, US rate worries

-
 'In it to win it': Australia doubles down on climate hosting bid
'In it to win it': Australia doubles down on climate hosting bid
-
Former NFL star Brown could face 30 yrs jail for shooting case: prosecutor

-
 Fate of Canada government hinges on tight budget vote
Fate of Canada government hinges on tight budget vote
-
New research measures how much plastic is lethal for marine life

-
 Mbappe, PSG face off in multi-million lawsuit
Mbappe, PSG face off in multi-million lawsuit
-
EU defends carbon tax as ministers take over COP30 negotiations

-
 McCartney to release silent AI protest song
McCartney to release silent AI protest song
-
Stocks tepid on uncertainty over earnings, tech rally, US rates

-
 Louvre shuts gallery over ceiling safety fears
Louvre shuts gallery over ceiling safety fears
-
'Stranded, stressed' giraffes in Kenya relocated as habitats encroached

-
 US Supreme Court to hear migrant asylum claim case
US Supreme Court to hear migrant asylum claim case
-
Western aid cuts could cause 22.6 million deaths, researchers say

-
 Clarke hails Scotland 'legends' ahead of crunch World Cup qualifier
Clarke hails Scotland 'legends' ahead of crunch World Cup qualifier
-
S.Africa says 'suspicious' flights from Israel show 'agenda to cleanse Palestinians'

-
 South Korea pledges to phase out coal plants at COP30
South Korea pledges to phase out coal plants at COP30
-
Ex-PSG footballer Hamraoui claims 3.5m euros damages against club

-
 Mbappe, PSG in counterclaims worth hundreds of millions
Mbappe, PSG in counterclaims worth hundreds of millions
-
Two newly discovered Bach organ works unveiled in Germany

-
 Stocks lower on uncertainty over earnings, tech rally, US rates
Stocks lower on uncertainty over earnings, tech rally, US rates
-
Barca to make long-awaited Camp Nou return on November 22

-
 COP30 talks enter homestretch with UN warning against 'stonewalling'
COP30 talks enter homestretch with UN warning against 'stonewalling'
-
France makes 'historic' accord to sell Ukraine 100 warplanes

-
 Delhi car bombing accused appears in Indian court, another suspect held
Delhi car bombing accused appears in Indian court, another suspect held
-
Emirates orders 65 more Boeing 777X planes despite delays

-
 Ex-champion Joshua to fight YouTube star Jake Paul
Ex-champion Joshua to fight YouTube star Jake Paul
-
Bangladesh court sentences ex-PM to be hanged for crimes against humanity

-
 Trade tensions force EU to cut 2026 eurozone growth forecast
Trade tensions force EU to cut 2026 eurozone growth forecast
-
'Killed without knowing why': Sudanese exiles relive Darfur's past

-
 Stocks lower on uncertainty over tech rally, US rates
Stocks lower on uncertainty over tech rally, US rates
-
Death toll from Indonesia landslides rises to 18

-
 Macron, Zelensky sign accord for Ukraine to buy French fighter jets
Macron, Zelensky sign accord for Ukraine to buy French fighter jets
-
India Delhi car bomb accused appears in court


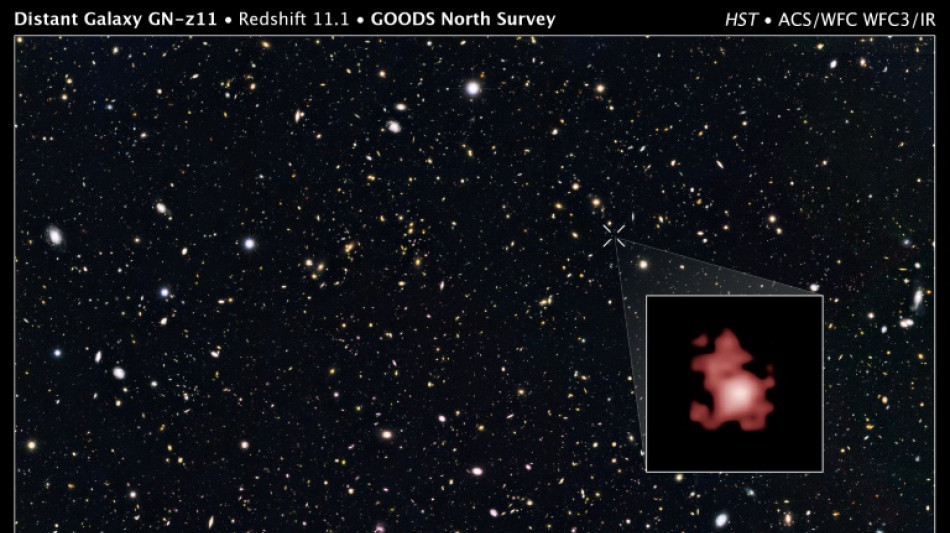
Webb telescope discovers oldest black hole yet
The James Webb space telescope has discovered the oldest black hole ever detected, which was thriving so soon after the Big Bang that it challenges our understanding of how these celestial behemoths form, astronomers said Wednesday.
The black hole was vigorously gobbling up its host galaxy just 430 million years after the birth of the universe during a period called the cosmic dawn, according to a study in the journal Nature.
That makes it 200 million years older than any other massive black hole ever observed, study co-author and Cambridge University astronomer Jan Scholtz told AFP.
Yet it has a mass 1.6 million times greater than our Sun.
Exactly how it had time to grow that big so quickly after the Big Bang 13.8 billion years ago will provide new information "for the next generation of theoretical models" aiming to explain what creates black holes, Scholtz said.
Like all black holes, it is invisible and can only be detected by the vast explosions of light created when it gobbles up whatever matter is unlucky enough to be nearby.
It was this light that allowed the Hubble space telescope in 2016 to spot its host galaxy GN-z11, which is in the direction of the Ursa Major constellation.
At the time GN-z11 was the oldest -- and therefore most distant -- galaxy ever observed. However Hubble did not spot the black hole lurking at its centre.
In 2022, Webb usurped Hubble as the most powerful space telescope, unleashing a torrent of discoveries that have scientists rushing to keep up.
Not only has it spotted the black hole at the heart of GN-z11, but it has also discovered galaxies even further back in time and space, which are also bigger than had been thought possible.
- Growing up fast -
The black hole was energetically eating up GN-z11 during the cosmic dawn, a period which came right after the universe's "dark ages," when stars and galaxies were first born.
It normally takes the supermassive black holes squatting at the centre of galaxies hundreds of millions -- if not billions -- of years to form.
So how could this one have grown so quickly?
Study co-author Stephane Charlot, an astrophysicist at France's Institut d'Astrophysique de Paris, suggested that black holes in the early universe could have been formed in a different way than those closer by.
One theory is that they were born huge due to the explosion of especially massive stars that only existed in the early universe, he told AFP.
Or they could have been created by the "direct collapse of a dense gas cloud, without going through the star formation phase," he added.
Once born, the black hole would have been able to gorge itself on the plentiful gas nearby, prompting an almighty growth spurt.
Scholtz emphasised that what has been discovered so far about the black hole of GN-z11 "doesn't rule out any of these scenarios".
And it could be just the beginning.
Scholtz hopes that Webb -- and other telescopes on the way, such as the European Space Agency's Euclid -- will discover more of these black holes in the earliest glimmers of the universe.
J.AbuHassan--SF-PST