-
 North Korea says Seoul-US sub deal will trigger 'nuclear domino' effect
North Korea says Seoul-US sub deal will trigger 'nuclear domino' effect
-
Education for girls hit hard by India's drying wells

-
 Haitian gangs getting rich off murky market for baby eels
Haitian gangs getting rich off murky market for baby eels
-
Trump says will talk to Venezuela's Maduro, 'OK' with US strikes on Mexico

-
 Oscar Piastri wins Australia's top sports honour
Oscar Piastri wins Australia's top sports honour
-
'Severely restricted': Russia's Saint Petersburg faces cultural crackdown
-
 Polish PM denounces 'sabotage' of railway supply line to Ukraine
Polish PM denounces 'sabotage' of railway supply line to Ukraine
-
UK toughens asylum system with radical overhaul

-
 Carney's Liberals pass budget, avoiding snap Canada election
Carney's Liberals pass budget, avoiding snap Canada election
-
LeBron back in training, edges closer to Lakers return

-
 Climate talks run into night as COP30 hosts seek breakthrough
Climate talks run into night as COP30 hosts seek breakthrough
-
Germany and Netherlands lock up World Cup spots in style

-
 Germany's Woltemade hopes for 2026 World Cup spot after scoring again
Germany's Woltemade hopes for 2026 World Cup spot after scoring again
-
Germany 'send message' with Slovakia rout to reach 2026 World Cup

-
 Trump unveils fast-track visas for World Cup ticket holders
Trump unveils fast-track visas for World Cup ticket holders
-
Netherlands qualify for World Cup, Poland in play-offs

-
 Germany crush Slovakia to qualify for 2026 World Cup
Germany crush Slovakia to qualify for 2026 World Cup
-
Stocks gloomy on earnings and tech jitters, US rate worries

-
 'In it to win it': Australia doubles down on climate hosting bid
'In it to win it': Australia doubles down on climate hosting bid
-
Former NFL star Brown could face 30 yrs jail for shooting case: prosecutor

-
 Fate of Canada government hinges on tight budget vote
Fate of Canada government hinges on tight budget vote
-
New research measures how much plastic is lethal for marine life

-
 Mbappe, PSG face off in multi-million lawsuit
Mbappe, PSG face off in multi-million lawsuit
-
EU defends carbon tax as ministers take over COP30 negotiations

-
 McCartney to release silent AI protest song
McCartney to release silent AI protest song
-
Stocks tepid on uncertainty over earnings, tech rally, US rates

-
 Louvre shuts gallery over ceiling safety fears
Louvre shuts gallery over ceiling safety fears
-
'Stranded, stressed' giraffes in Kenya relocated as habitats encroached

-
 US Supreme Court to hear migrant asylum claim case
US Supreme Court to hear migrant asylum claim case
-
Western aid cuts could cause 22.6 million deaths, researchers say

-
 Clarke hails Scotland 'legends' ahead of crunch World Cup qualifier
Clarke hails Scotland 'legends' ahead of crunch World Cup qualifier
-
S.Africa says 'suspicious' flights from Israel show 'agenda to cleanse Palestinians'

-
 South Korea pledges to phase out coal plants at COP30
South Korea pledges to phase out coal plants at COP30
-
Ex-PSG footballer Hamraoui claims 3.5m euros damages against club

-
 Mbappe, PSG in counterclaims worth hundreds of millions
Mbappe, PSG in counterclaims worth hundreds of millions
-
Two newly discovered Bach organ works unveiled in Germany

-
 Stocks lower on uncertainty over earnings, tech rally, US rates
Stocks lower on uncertainty over earnings, tech rally, US rates
-
Barca to make long-awaited Camp Nou return on November 22

-
 COP30 talks enter homestretch with UN warning against 'stonewalling'
COP30 talks enter homestretch with UN warning against 'stonewalling'
-
France makes 'historic' accord to sell Ukraine 100 warplanes

-
 Delhi car bombing accused appears in Indian court, another suspect held
Delhi car bombing accused appears in Indian court, another suspect held
-
Emirates orders 65 more Boeing 777X planes despite delays

-
 Ex-champion Joshua to fight YouTube star Jake Paul
Ex-champion Joshua to fight YouTube star Jake Paul
-
Bangladesh court sentences ex-PM to be hanged for crimes against humanity

-
 Trade tensions force EU to cut 2026 eurozone growth forecast
Trade tensions force EU to cut 2026 eurozone growth forecast
-
'Killed without knowing why': Sudanese exiles relive Darfur's past

-
 Stocks lower on uncertainty over tech rally, US rates
Stocks lower on uncertainty over tech rally, US rates
-
Death toll from Indonesia landslides rises to 18

-
 Macron, Zelensky sign accord for Ukraine to buy French fighter jets
Macron, Zelensky sign accord for Ukraine to buy French fighter jets
-
India Delhi car bomb accused appears in court


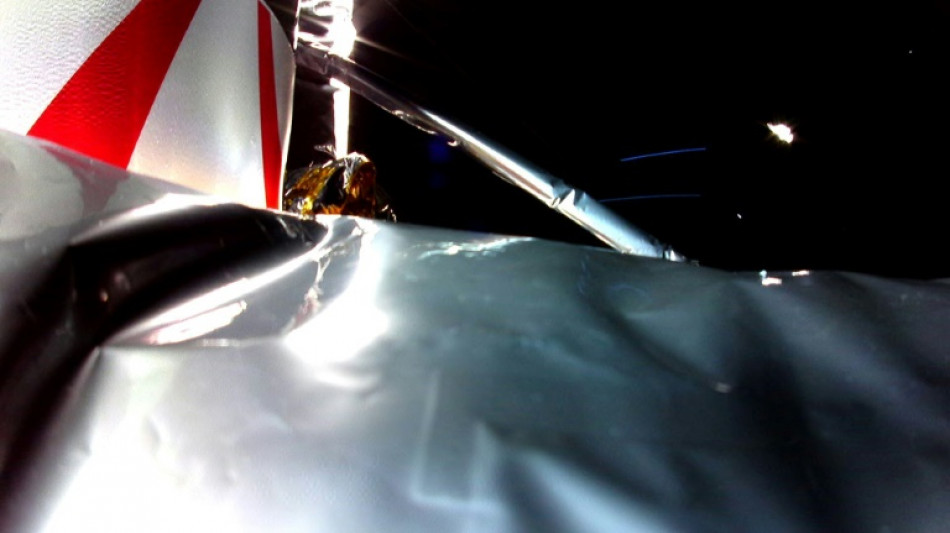
Doomed US lunar lander's space odyssey continues...for now
Is it the little spaceship that could?
A private US lunar lander that's been hemorrhaging fuel since an onboard explosion at the start of its journey is somehow still chugging along, snapping selfies and running science instruments as it continues its journey through space.
Though Astrobotic, the company that built the Peregrine robot, has said a controlled touchdown on the Moon is no longer possible, it hasn't ruled out a so-called "hard landing" or crash -- a prospect that has space watchers gripped.
"Peregrine has now been operating in space for more than 4 days," Astrobotic said in its latest update posted on X on Friday, adding it remained "stable and operational."
The rate of fuel loss has steadily diminished as the pressure inside its tank drops, meaning the company has been able to extend the spacecraft's life far longer than it initially thought possible.
Meanwhile, the US, German and Mexican space agencies have been able to power on the scientific instruments they wanted to run on the Moon.
"Measurements and operations of the NASA-provided science instruments on board will provide valuable experience, technical knowledge, and scientific data to future CLPS lunar deliveries," said Joel Kearns, deputy associate administrator for exploration for NASA.
Commercial Lunar Payload Services is the experimental NASA program under which the space agency paid Astrobotic more than $100 million to ship its hardware of Peregrine, as part of a strategy to seed a commercial lunar economy and reduce its own overheads.
Astrobotic is the third private entity to have failed in a soft landing, following an Israeli nonprofit and a Japanese company.
- 'Shots on goal' -
Though it hasn't worked out this time, NASA officials have made clear their strategy of "more shots on goal" means more chances to score, and the next attempt, by Houston-based Intuitive Machines, launches in February.
Astrobotic itself will get another chance in November with its Griffin lander transporting NASA's VIPER rover to the lunar south pole.
For now, the Pittsburgh-based company is staying tight-lipped on Peregrine's intended destination, leaving enthusiasts to make their own calculations.
Amateur astronomer Tony Dunn used publicly available data provided by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) to plot out the spaceship's current course, posting a graphic on social media platform X showing it would collide with the Moon on January 23.
But "it's really anybody's guess as to what is actually going to happen because of the leaking fuel," which could easily push it off course, he told AFP.
Or, Astrobotic could intentionally point Peregrine another way, such as flying by the Moon and shooting for interplanetary space.
While a hard lunar landing might satisfy some of Astrobotic's clients, such as those flying human ashes and DNA to the Moon, it could anger others like the Navajo Nation, which had called that cargo a "desecration" of the celestial body.
"I think it would be a shame if they completed their failed mission by littering the surface of the Moon with debris," Justin Walsh, a professor of art history, archaeology, and space studies at USC told AFP, adding that humanity had left some 180 tons of material on the surface since the first Soviet impactor crashed in 1959.
T.Samara--SF-PST