-
 Loaf behind bars: Aussie inmate says Vegemite a human right
Loaf behind bars: Aussie inmate says Vegemite a human right
-
In film's second act, 'Wicked' goes beyond Broadway musical

-
 Asian markets track Wall St down with Nvidia, US jobs in view
Asian markets track Wall St down with Nvidia, US jobs in view
-
Scott Boland: the best 'spare' fast bowler around

-
 Fire and Ashes: England bank on fast bowling barrage in Australia
Fire and Ashes: England bank on fast bowling barrage in Australia
-
North Korea says Seoul-US sub deal will trigger 'nuclear domino' effect

-
 Education for girls hit hard by India's drying wells
Education for girls hit hard by India's drying wells
-
Haitian gangs getting rich off murky market for baby eels

-
 Trump says will talk to Venezuela's Maduro, 'OK' with US strikes on Mexico
Trump says will talk to Venezuela's Maduro, 'OK' with US strikes on Mexico
-
Oscar Piastri wins Australia's top sports honour

-
 'Severely restricted': Russia's Saint Petersburg faces cultural crackdown
'Severely restricted': Russia's Saint Petersburg faces cultural crackdown
-
Polish PM denounces 'sabotage' of railway supply line to Ukraine

-
 UK toughens asylum system with radical overhaul
UK toughens asylum system with radical overhaul
-
Carney's Liberals pass budget, avoiding snap Canada election

-
 LeBron back in training, edges closer to Lakers return
LeBron back in training, edges closer to Lakers return
-
Climate talks run into night as COP30 hosts seek breakthrough

-
 Germany and Netherlands lock up World Cup spots in style
Germany and Netherlands lock up World Cup spots in style
-
Germany's Woltemade hopes for 2026 World Cup spot after scoring again

-
 Germany 'send message' with Slovakia rout to reach 2026 World Cup
Germany 'send message' with Slovakia rout to reach 2026 World Cup
-
Trump unveils fast-track visas for World Cup ticket holders

-
 Netherlands qualify for World Cup, Poland in play-offs
Netherlands qualify for World Cup, Poland in play-offs
-
Germany crush Slovakia to qualify for 2026 World Cup

-
 Stocks gloomy on earnings and tech jitters, US rate worries
Stocks gloomy on earnings and tech jitters, US rate worries
-
'In it to win it': Australia doubles down on climate hosting bid

-
 Former NFL star Brown could face 30 yrs jail for shooting case: prosecutor
Former NFL star Brown could face 30 yrs jail for shooting case: prosecutor
-
Fate of Canada government hinges on tight budget vote

-
 New research measures how much plastic is lethal for marine life
New research measures how much plastic is lethal for marine life
-
Mbappe, PSG face off in multi-million lawsuit

-
 EU defends carbon tax as ministers take over COP30 negotiations
EU defends carbon tax as ministers take over COP30 negotiations
-
McCartney to release silent AI protest song

-
 Stocks tepid on uncertainty over earnings, tech rally, US rates
Stocks tepid on uncertainty over earnings, tech rally, US rates
-
Louvre shuts gallery over ceiling safety fears

-
 'Stranded, stressed' giraffes in Kenya relocated as habitats encroached
'Stranded, stressed' giraffes in Kenya relocated as habitats encroached
-
US Supreme Court to hear migrant asylum claim case

-
 Western aid cuts could cause 22.6 million deaths, researchers say
Western aid cuts could cause 22.6 million deaths, researchers say
-
Clarke hails Scotland 'legends' ahead of crunch World Cup qualifier

-
 S.Africa says 'suspicious' flights from Israel show 'agenda to cleanse Palestinians'
S.Africa says 'suspicious' flights from Israel show 'agenda to cleanse Palestinians'
-
South Korea pledges to phase out coal plants at COP30

-
 Ex-PSG footballer Hamraoui claims 3.5m euros damages against club
Ex-PSG footballer Hamraoui claims 3.5m euros damages against club
-
Mbappe, PSG in counterclaims worth hundreds of millions

-
 Two newly discovered Bach organ works unveiled in Germany
Two newly discovered Bach organ works unveiled in Germany
-
Stocks lower on uncertainty over earnings, tech rally, US rates

-
 Barca to make long-awaited Camp Nou return on November 22
Barca to make long-awaited Camp Nou return on November 22
-
COP30 talks enter homestretch with UN warning against 'stonewalling'

-
 France makes 'historic' accord to sell Ukraine 100 warplanes
France makes 'historic' accord to sell Ukraine 100 warplanes
-
Delhi car bombing accused appears in Indian court, another suspect held

-
 Emirates orders 65 more Boeing 777X planes despite delays
Emirates orders 65 more Boeing 777X planes despite delays
-
Ex-champion Joshua to fight YouTube star Jake Paul

-
 Bangladesh court sentences ex-PM to be hanged for crimes against humanity
Bangladesh court sentences ex-PM to be hanged for crimes against humanity
-
Trade tensions force EU to cut 2026 eurozone growth forecast


China's space programme: Five things to know
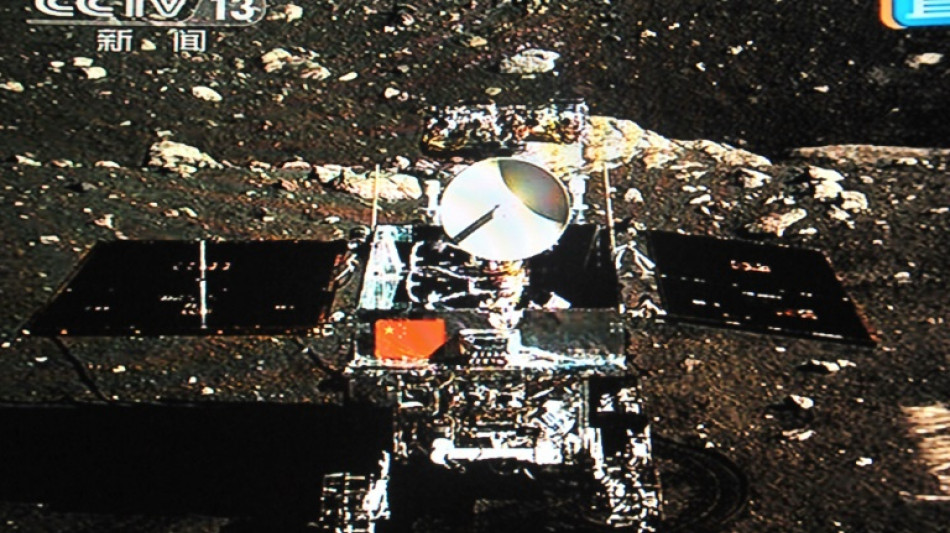
When Chang'e-3 became the first Chinese craft to land on the Moon 10 years ago, it kicked off nationwide celebrations -- and a decade of major successes for a rapidly accelerating space programme.
Since the December 14, 2013 landing, China has built a crewed space station, sent a robotic rover to Mars and become the first nation to make a controlled landing on the far side of the Moon.
Here are five things to know about China's space programme:
- A slow start -
Chinese leader Mao Zedong declared his nation's space ambitions soon after the Soviet Union launched the world's first satellite, Sputnik 1, in 1957.
It took 13 years for China to launch its first satellite Dong Fang Hong, or "The East is Red" -- named after the famous Communist revolutionary song it broadcast from orbit.
It was not until the late 1980s that the programme began to pick up pace, alongside China's ascent into the world's richest and most powerful nations.
Overseen by the military, its secretive space programme's goals became more ambitious. In 1992, it formally began a project to send humans into space.
- 'Taikonauts' -
More than three decades after its first satellite launch, on October 15, 2003, Yang Liwei became the first Chinese to travel into space, and an instant national hero.
With the success of his Shenzhou 5 mission, China became only the third nation after the United States and Russia to demonstrate the ability to launch humans into space.
In total, 20 Chinese astronauts have made the journey into space, including two women. State media have used the term "taikonaut" to describe China's spacefarers.
Many of them have journeyed to Tiangong, China's first long-term space station whose construction was completed last year.
Though much smaller than the International Space Station, it contains living quarters for a rotating crew, robotic arms and airlocks for conducting spacewalks.
- To the Moon -
China has also sent exploration missions to the Moon.
Named after the Moon goddess in Chinese folklore, Chang'e-3 touched down on the surface in 2013, making China only the third nation to successfully land there.
Two other milestones followed. In 2019, China became the first nation to make a controlled landing on the far side of the Moon with Chang'e-4.
A year later, Chang'e-5 brought the first lunar samples to Earth in more than 40 years.
Chinese space authorities have said they plan to land humans on the Moon by 2030, as well as build a lunar base.
- Mars and deep space -
One of the most spectacular successes of the Chinese space programme came in 2021 when its Tianwen-1 mission landed a rover named Zhurong on the surface of Mars.
China is only the second nation after the United States to put a robotic rover on the Red Planet.
Officials have said they aim to send a crewed mission there by 2033.
Aside from landers and orbiters, China is soon expected to launch a space telescope named Xuntian.
Orbiting close to the Tiangong space station, with which it can dock, Xuntian is expected to have a field of view far greater than NASA's Hubble telescope.
- Defence and prestige -
While China says it opposes the weaponisation of space, its policy makers have also identified space as critical to national defence and security.
Its military is a core player in the national space programme, and China is developing spy satellites, anti-satellite missiles and electronic warfare capabilities, according to the US military.
China "sees counterspace operations as a means to deter and counter a US intervention during a regional military conflict", the Pentagon said in a report to Congress this year.
And beyond the direct applications of these technologies, China considers success in space as a major driver of its image as a global power at home and abroad.
"National prestige is perhaps one of the most important, if not the most important, motives driving Chinese space ambitions," said Robert Hines, an assistant professor at the Georgia Institute of Technology in the United States.
"These symbols of increasing international status provide a powerful form of domestic propaganda."
A.AlHaj--SF-PST