-
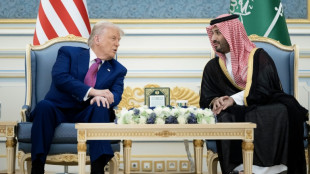 Trump hosts Saudi prince for first time since Khashoggi killing
Trump hosts Saudi prince for first time since Khashoggi killing
-
Tonga's Katoa out of NRL season after brain surgery

-
 Japan warns citizens in China over safety amid Taiwan row
Japan warns citizens in China over safety amid Taiwan row
-
In Somalia, a shaky front line barely holds back the 'dogs of war'

-
 Shares in 'Baby Shark' studio jump on market debut
Shares in 'Baby Shark' studio jump on market debut
-
Thunder breeze past Pelicans, Pistons overpower Pacers

-
 Grieving Cowboys remember Kneeland, defeat Raiders
Grieving Cowboys remember Kneeland, defeat Raiders
-
Loaf behind bars: Aussie inmate says Vegemite a human right

-
 In film's second act, 'Wicked' goes beyond Broadway musical
In film's second act, 'Wicked' goes beyond Broadway musical
-
Asian markets track Wall St down with Nvidia, US jobs in view

-
 Scott Boland: the best 'spare' fast bowler around
Scott Boland: the best 'spare' fast bowler around
-
Fire and Ashes: England bank on fast bowling barrage in Australia

-
 North Korea says Seoul-US sub deal will trigger 'nuclear domino' effect
North Korea says Seoul-US sub deal will trigger 'nuclear domino' effect
-
Education for girls hit hard by India's drying wells

-
 Haitian gangs getting rich off murky market for baby eels
Haitian gangs getting rich off murky market for baby eels
-
Trump says will talk to Venezuela's Maduro, 'OK' with US strikes on Mexico

-
 Oscar Piastri wins Australia's top sports honour
Oscar Piastri wins Australia's top sports honour
-
'Severely restricted': Russia's Saint Petersburg faces cultural crackdown
-
 Polish PM denounces 'sabotage' of railway supply line to Ukraine
Polish PM denounces 'sabotage' of railway supply line to Ukraine
-
UK toughens asylum system with radical overhaul

-
 Carney's Liberals pass budget, avoiding snap Canada election
Carney's Liberals pass budget, avoiding snap Canada election
-
LeBron back in training, edges closer to Lakers return

-
 Climate talks run into night as COP30 hosts seek breakthrough
Climate talks run into night as COP30 hosts seek breakthrough
-
Germany and Netherlands lock up World Cup spots in style

-
 Germany's Woltemade hopes for 2026 World Cup spot after scoring again
Germany's Woltemade hopes for 2026 World Cup spot after scoring again
-
Germany 'send message' with Slovakia rout to reach 2026 World Cup

-
 Trump unveils fast-track visas for World Cup ticket holders
Trump unveils fast-track visas for World Cup ticket holders
-
Netherlands qualify for World Cup, Poland in play-offs

-
 Germany crush Slovakia to qualify for 2026 World Cup
Germany crush Slovakia to qualify for 2026 World Cup
-
Stocks gloomy on earnings and tech jitters, US rate worries

-
 'In it to win it': Australia doubles down on climate hosting bid
'In it to win it': Australia doubles down on climate hosting bid
-
Former NFL star Brown could face 30 yrs jail for shooting case: prosecutor

-
 Fate of Canada government hinges on tight budget vote
Fate of Canada government hinges on tight budget vote
-
New research measures how much plastic is lethal for marine life

-
 Mbappe, PSG face off in multi-million lawsuit
Mbappe, PSG face off in multi-million lawsuit
-
EU defends carbon tax as ministers take over COP30 negotiations

-
 McCartney to release silent AI protest song
McCartney to release silent AI protest song
-
Stocks tepid on uncertainty over earnings, tech rally, US rates

-
 Louvre shuts gallery over ceiling safety fears
Louvre shuts gallery over ceiling safety fears
-
'Stranded, stressed' giraffes in Kenya relocated as habitats encroached

-
 US Supreme Court to hear migrant asylum claim case
US Supreme Court to hear migrant asylum claim case
-
Western aid cuts could cause 22.6 million deaths, researchers say

-
 Clarke hails Scotland 'legends' ahead of crunch World Cup qualifier
Clarke hails Scotland 'legends' ahead of crunch World Cup qualifier
-
S.Africa says 'suspicious' flights from Israel show 'agenda to cleanse Palestinians'

-
 South Korea pledges to phase out coal plants at COP30
South Korea pledges to phase out coal plants at COP30
-
Ex-PSG footballer Hamraoui claims 3.5m euros damages against club

-
 Mbappe, PSG in counterclaims worth hundreds of millions
Mbappe, PSG in counterclaims worth hundreds of millions
-
Two newly discovered Bach organ works unveiled in Germany

-
 Stocks lower on uncertainty over earnings, tech rally, US rates
Stocks lower on uncertainty over earnings, tech rally, US rates
-
Barca to make long-awaited Camp Nou return on November 22


Glimpses of the 'galactic zoo': The five new Euclid images
The first images from Europe's Euclid space telescope released Tuesday range from a well-known nebula to never-before-seen galaxies 10 billion light years away, illustrating its wide-lens view of the universe.
Here are the five images -- described by Euclid scientist Jean-Charles Cuillandre as "a range of objects from the galactic zoo in terms of diversity, colours and shapes" -- starting with the closest to Earth and moving out into the cosmos.
- Horsehead Nebula -
A giant red horse seems to rear its head against a background of swirling stars, some still being formed in a stellar nursery.
The Horsehead Nebula -- also known as Barnard 33 -- is 1,375 light years away.
The horse's head is in fact dark clouds in front of ultraviolet radiation coming from Sigma Orionis, which is the eastern star on the belt of the Orion constellation.
The Horsehead Nebula has been observed before, but the European Space Agency's Euclid telescope is the first to deliver such a complete view in just an hour, thanks to its wide lens.
Scientists hope that by scouring through Euclid's observations of the nebula, they will find previously unseen Jupiter-sized planets, as well as stars still in their infancy.
- Globular cluster NGC 6397 -
At 7,800 light years away -- but still in our Milky Way galaxy -- this cluster is a collection of hundreds of thousands of stars bound together by gravity.
"Currently no other telescope than Euclid can observe the entire globular cluster and at the same time distinguish its faint stellar members in the outer regions from other cosmic sources," Euclid Consortium scientist Davide Massari said in a statement.
Scientists hope to use Euclid's observations to spot stars trailing such globular clusters as they travel through our galaxy.
"The surprising thing is that we don't see these stars trailing," Euclid project scientist Rene Laureijs told AFP.
"One of the theories is that there might be dark matter around the globular cluster, which keeps all the stars together," he said.
The ESA hopes Euclid will shed more light on dark matter and dark energy, which are thought to make up 95 percent of the universe but remain shrouded in mystery.
- An irregular galaxy -
Not all galaxies are pretty spirals like our own. Images of the irregular dwarf galaxy NGC 6822, some 1.6 million light years from Earth, have been captured before, including by the James Webb Space Telescope.
However Euclid is the first to be able to capture the whole galaxy in barely an hour.
As is often the case in the early universe, this galaxy's stars are low on metal, and the scientists hope that analysing them will shed light on how galaxies evolve.
- The 'hidden galaxy' -
The spiral galaxy IC 342 earned the nickname the "hidden galaxy" because it can be difficult to spot behind the disc of our own Milky Way.
It is relatively nearby -- in galactic terms at least -- some 11 million light years from Earth.
However Euclid's infrared vision was able to peer through the dust to spot never-before-seen globular clusters, ESA said.
- Perseus Cluster -
ESA described this image as "a revolution for astronomy".
It depicts the Perseus Cluster, which contains a thousand galaxies some 240 million light years away.
But in the background there are more than 100,000 additional galaxies, some 10 billion light years away, ESA said. Many of those distant galaxies have never been spotted before.
Laureijs said it was "very exciting" when the team saw the image for the first time and found low-level light coming not from the cluster, but from stars left over from collisions between galaxies.
That these stars were not being pulled back into the galaxies could suggest the presence of dark matter, he said.
Laureijs emphasised that this remains "circumstantial evidence," and that future research could reveal more about dark matter's distribution throughout the universe.
E.Aziz--SF-PST