
-
 Curling quietly kicks off sports programme at 2026 Winter Olympics
Curling quietly kicks off sports programme at 2026 Winter Olympics
-
Undav pokes Stuttgart past Kiel into German Cup semis

-
 Germany goalkeeper Ter Stegen to undergo surgery
Germany goalkeeper Ter Stegen to undergo surgery
-
Bezos-led Washington Post announces 'painful' job cuts

-
 Iran says US talks are on, as Trump warns supreme leader
Iran says US talks are on, as Trump warns supreme leader
-
Gaza health officials say strikes kill 24 after Israel says officer wounded

-
 Empress's crown dropped in Louvre heist to be fully restored: museum
Empress's crown dropped in Louvre heist to be fully restored: museum
-
UK PM says Mandelson 'lied' about Epstein relations

-
 Shai to miss NBA All-Star Game with abdominal strain
Shai to miss NBA All-Star Game with abdominal strain
-
Trump suggests 'softer touch' needed on immigration

-
 From 'flop' to Super Bowl favorite: Sam Darnold's second act
From 'flop' to Super Bowl favorite: Sam Darnold's second act
-
Man sentenced to life in prison for plotting to kill Trump in 2024

-
 Native Americans on high alert over Minneapolis crackdown
Native Americans on high alert over Minneapolis crackdown
-
Dallas deals Davis to Wizards in blockbuster NBA deal: report

-
 Russia 'no longer bound' by nuclear arms limits as treaty with US ends
Russia 'no longer bound' by nuclear arms limits as treaty with US ends
-
Panama hits back after China warns of 'heavy price' in ports row

-
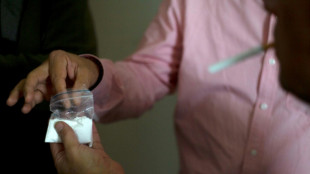 Strike kills guerrillas as US, Colombia agree to target narco bosses
Strike kills guerrillas as US, Colombia agree to target narco bosses
-
Wildfire smoke kills more than 24,000 Americans a year: study

-
 Telegram founder slams Spain PM over under-16s social media ban
Telegram founder slams Spain PM over under-16s social media ban
-
Curling kicks off sports programme at 2026 Winter Olympics

-
 Preventative cholera vaccination resumes as global supply swells: WHO
Preventative cholera vaccination resumes as global supply swells: WHO
-
Wales' Macleod ready for 'physical battle' against England in Six Nations

-
 Xi calls for 'mutual respect' with Trump, hails ties with Putin
Xi calls for 'mutual respect' with Trump, hails ties with Putin
-
'All-time great': Maye's ambitions go beyond record Super Bowl bid

-
 Shadow over Vonn as Shiffrin, Odermatt headline Olympic skiing
Shadow over Vonn as Shiffrin, Odermatt headline Olympic skiing
-
US seeks minerals trade zone in rare Trump move with allies

-
 Ukraine says Abu Dhabi talks with Russia 'substantive and productive'
Ukraine says Abu Dhabi talks with Russia 'substantive and productive'
-
Brazil mine disaster victims in London to 'demand what is owed'

-
 AI-fuelled tech stock selloff rolls on
AI-fuelled tech stock selloff rolls on
-
Russia vows to act 'responsibly' as nuclear pact ends with US

-
 White says time at Toulon has made him a better Scotland player
White says time at Toulon has made him a better Scotland player
-
Washington Post announces 'painful' job cuts

-
 All lights are go for Jalibert, says France's Dupont
All lights are go for Jalibert, says France's Dupont
-
Artist rubs out Meloni church fresco after controversy

-
 Palestinians in Egypt torn on return to a Gaza with 'no future'
Palestinians in Egypt torn on return to a Gaza with 'no future'
-
US removing 700 immigration officers from Minnesota

-
 Who is behind the killing of late ruler Gaddafi's son, and why now?
Who is behind the killing of late ruler Gaddafi's son, and why now?
-
Coach Thioune tasked with saving battling Bremen

-
 Russia vows to act 'responsibly' once nuclear pact with US ends
Russia vows to act 'responsibly' once nuclear pact with US ends
-
Son of Norway's crown princess admits excesses but denies rape

-
 US calls for minerals trade zone in rare move with allies
US calls for minerals trade zone in rare move with allies
-
Vowles dismisses Williams 2026 title hopes as 'not realistic'

-
 'Dinosaur' Glenn chasing skating gold in first Olympics
'Dinosaur' Glenn chasing skating gold in first Olympics
-
Gaza health officials say strikes kill 23 after Israel says shots wounded officer

-
 Italy foils Russian cyberattacks targeting Olympics
Italy foils Russian cyberattacks targeting Olympics
-
Stocks stabilise after Wall St AI-fuelled sell-off

-
 Figure skating favourite Malinin feeling 'the pressure' in Milan
Figure skating favourite Malinin feeling 'the pressure' in Milan
-
Netflix film probes conviction of UK baby killer nurse

-
 Timber hopes League Cup can be catalyst for Arsenal success
Timber hopes League Cup can be catalyst for Arsenal success
-
China calls EU 'discriminatory' over probe into energy giant Goldwind


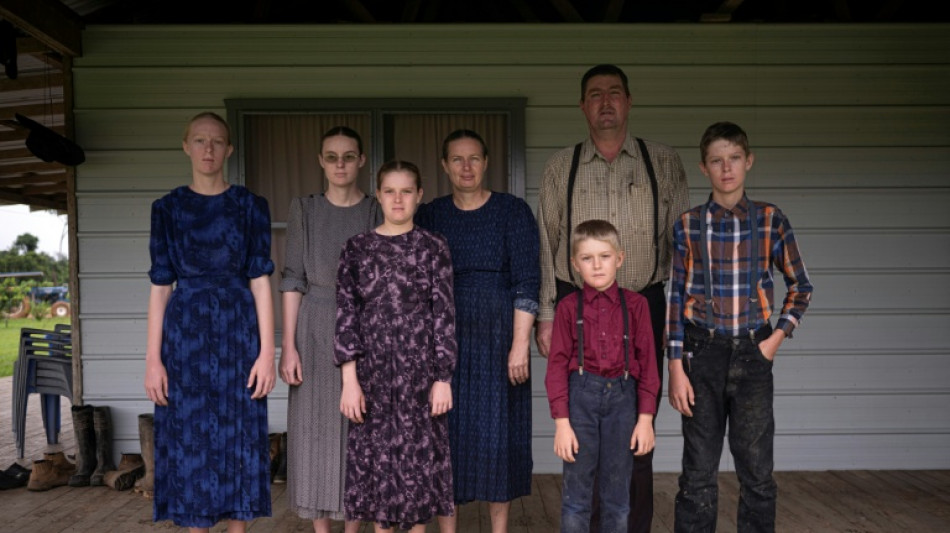
Mennonite communities raise hackles in Peruvian Amazon
When they saw men with arrows and machetes bearing down on them, Daniel Braun and other Mennonites living in the Peruvian Amazon fled across rice paddies, some of their barns ablaze behind them.
In Masisea, a remote settlement near Peru's border with Brazil accessible only by boat along a tributary of the Amazon or over dirt paths, members of the austere Protestant sect are under siege.
Here, as in several other South American countries, the reclusive Christians, who have roots in 16th-century Europe and who eschew modernity, are accused of destroying forests as they expand their agricultural imprint on the continent.
In 2024, Peruvian prosecutors charged 44 men from the Masisea Mennonite colony with destroying 894 hectares (2,209 acres) of virgin forest and requested that each be sentenced to between eight and 10 years in prison.
The trial would be the first of a Mennonite colony in Latin America for environmental crimes.
The men's lawyer, Carlos Sifuentes, argues that the land was "already cleared" when the community bought it.
- Rich versus poor -
A 2021 study carried out by researchers at Canada's McGill University counted 214 Mennonite colonies in Latin America occupying some 3.9 million hectares, an area bigger than the Netherlands.
In Peru, Mennonites have established five thriving colonies in the Amazon in the past decade.
Their presence is a thorn in the side of the 780-strong Shipibo-Konibo Indigenous community, which lives on the shores of Lake Imiria about 10 miles (16 kilometers) from Masisea.
The Shipibo-Konibo live in wooden huts of palm or zinc roofs with no electricity or running water, surviving off fishing and subsistence farming.
They accuse the wealthier Mennonites, whom they call "forest termites," of illegally occupying around 600 hectares of their 5,000-hectare territory.
"The Mennonites build ranches on communal land... They engage in deforestation. What they are doing is a crime against the environment," Indigenous leader Abner Ancon, 54, told AFP.
- Horse-drawn carriages -
The Mennonites arrived in Peru from neighboring Bolivia.
David Klassen, a 45-year-old father of five children ranging in age from seven to 20, said they were driven to emigrate because of a shortage of farmland and because of Bolivia's "radical left" policies.
Today, the self-sufficient enclave is comprised of some 63 families who raise cattle and pigs and grow rice and soybeans on 3,200 hectares while using diesel generators for power.
The men and boys wear checked shirts, suspenders and hats or caps, The women and girls wear long dresses, with their hair pulled back in tight braids or buns.
The community, which speaks a German dialect but whose leaders speak passable Spanish, has little contact with the outside world, relying on tractors and horse-drawn carriages as its main modes of transport.
After 10 years of peaceful coexistence with their Indigenous neighbors, the settlement came under attack last July.
Braun said he was sitting with other men outside a barn when a group of Shipibo-Konibo appeared out of nowhere.
"They came with arrows and machetes. They said you have one or two hours to leave," the 39-year-old recalled, adding that they set fire to property.
No one was injured in the standoff but the charred remains of a shed and a barn and zinc roofs were visible through the long grass.
Ancon admitted that his community's Indigenous guard had chased the Mennonites but "without resorting to violence."
- A fraction of the damage -
A lawyer for the Shipibo-Konibo, Linda Vigo, accused the settlers of hiring contractors to clear forest, "and when it's all cleared, the Mennonites come in with their tractors, flatten everything, and then you go in afterwards and find it all cultivated."
Pedro Favaron, a specialist on Indigenous peoples at the Pontifical Catholic University of Peru, acknowledged that the Mennonite farming model failed to meet "environmental expectations."
But he argued that the land they bought from mixed-race settlers in Masisea "was already degraded."
The independent Monitoring of the Andes Amazon Program, which tracks deforestation and fires, estimates the area cleared by Mennonites in Peru since 2017 at 8,660 hectares.
It's a tiny fraction of the 3 million hectares of forest lost over the past three decades in the Andean country, mainly due to fires, illegal mining and deforestation by other groups.
Standing in the middle of a verdant rice field, Klassen assured: "We love the countryside... We don't want to destroy everything."
O.Farraj--SF-PST


