
-
 Colour and caution as banned kite-flying festival returns to Pakistan
Colour and caution as banned kite-flying festival returns to Pakistan
-
England cling on to beat Nepal in last-ball thriller

-
 UK foreign office to review pay-off to Epstein-linked US envoy
UK foreign office to review pay-off to Epstein-linked US envoy
-
England's Arundell eager to learn from Springbok star Kolbe

-
 Czech snowboard great Ledecka fails in bid for third straight Olympic gold
Czech snowboard great Ledecka fails in bid for third straight Olympic gold
-
Expectation, then stunned silence as Vonn crashes out of Olympics

-
 Storm-battered Portugal votes in presidential election run-off
Storm-battered Portugal votes in presidential election run-off
-
Breezy Johnson wins Olympic downhill gold, Vonn crashes out

-
 Vonn's Olympic dream cut short by downhill crash
Vonn's Olympic dream cut short by downhill crash
-
French police arrest five over crypto-linked magistrate kidnapping

-
 Late Jacks flurry propels England to 184-7 against Nepal
Late Jacks flurry propels England to 184-7 against Nepal
-
Vonn crashes out of Winter Olympics, ending medal dream

-
 All-new Ioniq 3 coming in 2026
All-new Ioniq 3 coming in 2026
-
Takaichi wins big in Japan election, media projections show

-
 New Twingo e-tech is at the starting line
New Twingo e-tech is at the starting line
-
New Ypsilon and Ypsilon hf

-
 The Cupra Raval will be launched in 2026
The Cupra Raval will be launched in 2026
-
New id.Polo comes electric

-
 Iran defies US threats to insist on right to enrich uranium
Iran defies US threats to insist on right to enrich uranium
-
Seifert powers New Zealand to their record T20 World Cup chase

-
 Naib's fifty lifts Afghanistan to 182-6 against New Zealand
Naib's fifty lifts Afghanistan to 182-6 against New Zealand
-
Paul Thomas Anderson wins top director prize for 'One Battle After Another'

-
 De Beers sale drags in diamond doldrums
De Beers sale drags in diamond doldrums
-
NFL embraces fashion as league seeks new audiences

-
 What's at stake for Indian agriculture in Trump's trade deal?
What's at stake for Indian agriculture in Trump's trade deal?
-
Real Madrid can wait - Siraj's dream night after late T20 call-up

-
 Castle's monster night fuels Spurs, Rockets rally to beat Thunder
Castle's monster night fuels Spurs, Rockets rally to beat Thunder
-
Japan votes in snow-hit snap polls as Takaichi eyes strong mandate

-
 Pakistan's capital picks concrete over trees, angering residents
Pakistan's capital picks concrete over trees, angering residents
-
Berlin's crumbling 'Russian houses' trapped in bureaucratic limbo

-
 Neglected killer: kala-azar disease surges in Kenya
Neglected killer: kala-azar disease surges in Kenya
-
Super Bowl set for Patriots-Seahawks showdown as politics swirl

-
 Sengun shines as Rockets rally to beat NBA champion Thunder
Sengun shines as Rockets rally to beat NBA champion Thunder
-
Matsuyama grabs PGA Phoenix Open lead with Hisatsune one back

-
 Washington Post CEO out after sweeping job cuts
Washington Post CEO out after sweeping job cuts
-
Haiti's transitional council hands power to PM

-
 N. Korea to hold party congress in February, first since 2021
N. Korea to hold party congress in February, first since 2021
-
Thailand votes after three leaders in two years

-
 Swiss joy as Von Allmen wins first gold of Winter Olympics
Swiss joy as Von Allmen wins first gold of Winter Olympics
-
George backs England to 'kick on' after Six Nations rout of Wales

-
 Malinin upstaged as Japan keep pressure on USA in skating team event
Malinin upstaged as Japan keep pressure on USA in skating team event
-
Japan's Kimura soars to Olympic gold in snowboard big air final

-
 Vail's golden comets Vonn and Shiffrin inspire those who follow
Vail's golden comets Vonn and Shiffrin inspire those who follow
-
Veteran French politician loses culture post over Epstein links

-
 Japan's Kimura wins Olympic snowboard big air gold
Japan's Kimura wins Olympic snowboard big air gold
-
Arteta backs confident Gyokeres to hit 'highest level'

-
 Hojlund the hero as Napoli snatch late win at Genoa
Hojlund the hero as Napoli snatch late win at Genoa
-
England's Arundell 'frustrated' despite hat-trick in Wales romp

-
 Lollobrigida skates to first Italian gold of Winter Olympics on her birthday
Lollobrigida skates to first Italian gold of Winter Olympics on her birthday
-
Arundell hat-trick inspires England thrashing of Wales in Six Nations opener


Covid lessons learned? UN summit mulls plan for healthy planet, and humans
The Covid-19 and Ebola outbreaks brought into stark relief the harms that can come to humans if we interfere too much with nature, placing ourselves in contact with animals carrying unknown pathogens.
At the COP16 biodiversity summit in Cali, Colombia, experts and activists have urged world leaders world to learn the lessons from the estimated seven million lives lost to Covid, and thousands more due to Ebola.
It is up to governments to act, and there is no time to waste.
The IPBES intergovernmental science and policy body on biodiversity has already warned that "future pandemics will emerge more often, spread more rapidly, do more damage to the world economy and kill more people than Covid-19" unless humankind changes course.
At the UN summit in Cali, delegates are working on a "biodiversity and health action plan" proposed for adoption by the 196 member nations of the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD).
It includes commitments to limit harmful agriculture and forestry, reduce the use of pesticides, fertilizers and other chemicals damaging to nature, and reduce the use of antibiotics in farm animals.
The plan is voluntary, however, and parties remain stuck on a few details.
Agreement, WWF wildlife policy manager Colman O’Criodain told AFP, "may be at the expense of watered down language on some issues, such as intensive agriculture and use of antimicrobials" -- which affect biotech and agribusiness, both big money-spinners.
For Sue Lieberman, vice president of the Wildlife Conservation Society pushing for the plan's adoption, "we need to change our relationship with nature if we want to prevent more epidemics and pandemics."
- 'When, not if' -
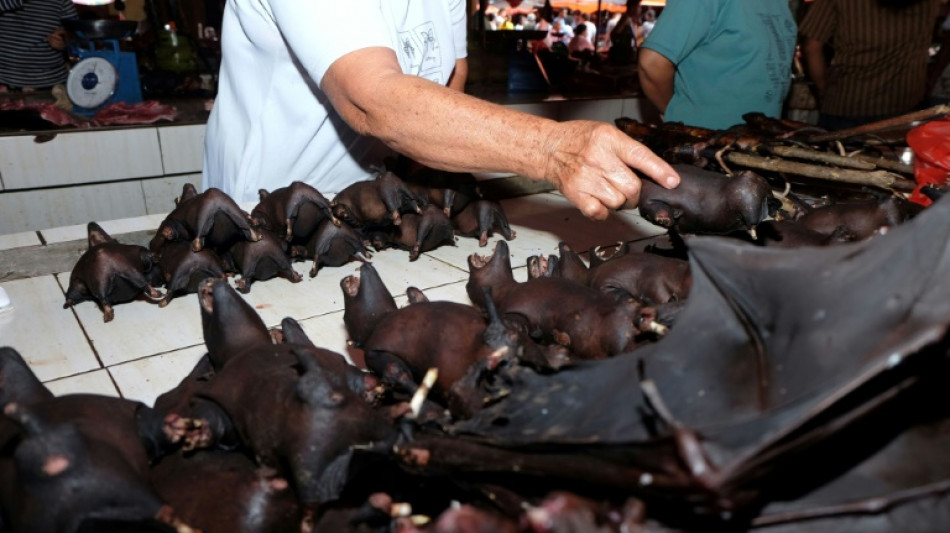
So-called zoonotic diseases spread between animals and people, as can happen when humans encroach into formerly virgin forests, or transport and trade wild animals for their meat.
Covid-19, for example, is believed by many scientists to have emerged at the Wuhan wet market in China, where wild animal meat was illegally sold for consumption.
Ebola, an often fatal hemorrhagic fever that has killed some 15,000 people in Africa, is believed to have its natural host in a bat, which can spread the virus to humans directly or via other animals.
"Deforestation, intensive agriculture, wildlife trade and exploitation are the primary drivers of biodiversity loss and zoonotic disease," Adeline Lerambert of the Born Free wildlife NGO told AFP.
WWF's O'Criodain added: "The further humans and their livestock penetrate into what were intact, undisturbed areas of high biodiversity, the more likely they are to encounter new strains of viruses, especially because viruses are constantly mutating."
The 2020 IPBES report had called for a "transformative change in the global approach to dealing with infectious diseases."
"Covid-19 is at least the sixth global health pandemic since the Great Influenza Pandemic of 1918, and although it has its origins in microbes carried by animals, like all pandemics its emergence has been entirely driven by human activities," it said.
The report estimated that some 1.7 million currently "undiscovered" viruses exist in mammals and birds -- of which up to 827,000 could have the ability to infect people.
As measures to prevent "the spillover of new diseases," the IPBES advocates for expanding protection of natural areas and reducing the unsustainable exploitation of resources.
Will the COP16 action plan be up to the task?
For Lieberman of the Wildlife Conservation Society, it is not ideal that the plan is voluntary, meaning "there's no consequences if a government says: 'never mind, we'll ignore it.' It's up to each country".
But she is hopeful that fear of a repeat of Covid-19 will inspire action nevertheless.
"If nothing is done, if nothing changes, there will be another pandemic. The question is when, not if," Lieberman warned.
T.Samara--SF-PST




