
-
 Scandic Trust Group strengthens sales network with First Idea Consultant
Scandic Trust Group strengthens sales network with First Idea Consultant
-
No end to Sudan fighting despite RSF paramilitaries backing truce plan

-
 US officials, NGOs cry foul as Washington snubs UN rights review
US officials, NGOs cry foul as Washington snubs UN rights review
-
Injured teen medal hope Tabanelli risks missing home Winter Olympics

-
 Bellingham, Foden recalled to England squad for World Cup qualifiers
Bellingham, Foden recalled to England squad for World Cup qualifiers
-
Tanzania rights group condemns 'reprisal killings' of civilians

-
 Slot urges patience as Isak returns to training with Liverpool
Slot urges patience as Isak returns to training with Liverpool
-
Rees-Zammit set for Wales return with bench role against Argentina

-
 China's new aircraft carrier enters service in key move to modernise fleet
China's new aircraft carrier enters service in key move to modernise fleet
-
Operation Cloudburst: Dutch train for 'water bomb' floods

-
 Leaders turn up the heat on fossil fuels at Amazon climate summit
Leaders turn up the heat on fossil fuels at Amazon climate summit
-
US travel woes mount as govt shutdown prompts flight cuts

-
 North Korea fires unidentified ballistic missile: Seoul military
North Korea fires unidentified ballistic missile: Seoul military
-
West Bank's ancient olive tree a 'symbol of Palestinian endurance'

-
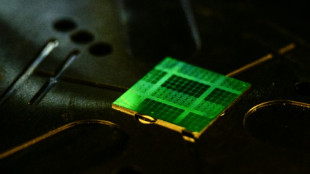 Global tech tensions overshadow Web Summit's AI and robots
Global tech tensions overshadow Web Summit's AI and robots
-
Green shines as Suns thump Clippers 115-102

-
 Japan to screen #MeToo film months after Oscar nomination
Japan to screen #MeToo film months after Oscar nomination
-
Erasmus relishing 'brutal' France re-match on Paris return

-
 Rejuvenated Vlahovic taking the reins for Juve ahead of Turin derby
Rejuvenated Vlahovic taking the reins for Juve ahead of Turin derby
-
'Well-oiled' Leipzig humming along in Bayern's slipstream

-
 Bangladesh cricket probes sexual harassment claims
Bangladesh cricket probes sexual harassment claims
-
NFL-best Broncos edge Raiders to win seventh in a row

-
 Deadly Typhoon Kalmaegi ravages Vietnam, Philippines
Deadly Typhoon Kalmaegi ravages Vietnam, Philippines
-
Three killed in new US strike on alleged drug boat, toll at 70

-
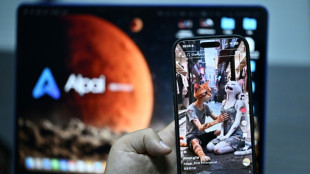 Chinese microdrama creators turn to AI despite job loss concerns
Chinese microdrama creators turn to AI despite job loss concerns
-
Trump hails Central Asia's 'unbelievable potential' at summit

-
 Kolya, the Ukrainian teen preparing for frontline battle
Kolya, the Ukrainian teen preparing for frontline battle
-
Big leap in quest to get to bottom of climate ice mystery

-
 Markets drop as valuations and US jobs, rates spook investors
Markets drop as valuations and US jobs, rates spook investors
-
'Soap opera on cocaine': how vertical dramas flipped Hollywood

-
 Under pressure? EU states on edge over migrant burden-sharing
Under pressure? EU states on edge over migrant burden-sharing
-
US influencers falsely associate Mamdani with extremist group

-
 Hungary's Orban to meet Trump in face of Russia oil sanctions
Hungary's Orban to meet Trump in face of Russia oil sanctions
-
US facing travel chaos as flights cut due to govt shutdown

-
 Liverpool and Man City renew rivalry as they try to narrow Arsenal gap
Liverpool and Man City renew rivalry as they try to narrow Arsenal gap
-
UK's Andrew asked to testify over Epstein as he formally loses titles

-
 Local hero: 'DC sandwich guy' found not guilty of assaulting officer with sub
Local hero: 'DC sandwich guy' found not guilty of assaulting officer with sub
-
Dead famous: Paris puts heritage graves up for grabs

-
 UK grandmother on Indonesia death row flies home
UK grandmother on Indonesia death row flies home
-
Former NFL star Brown extradited from Dubai to face trial in shooting - police

-
 Chile presidential hopeful vows to expel 'criminal' migrants to El Salvador
Chile presidential hopeful vows to expel 'criminal' migrants to El Salvador
-
Trump event paused in Oval Office when guest faints

-
 NFL Colts add Sauce to recipe while Patriots confront Baker
NFL Colts add Sauce to recipe while Patriots confront Baker
-
Home owned by Miami Heat coach Spoelstra damaged by fire

-
 Tesla shareholders approve Musk's $1 trillion pay package
Tesla shareholders approve Musk's $1 trillion pay package
-
World leaders launch fund to save forests, get first $5 bn

-
 Villa edge Maccabi Tel Aviv in fraught Europa League match
Villa edge Maccabi Tel Aviv in fraught Europa League match
-
Protests as Villa beat Maccabi Tel Aviv under tight security

-
 US Supreme Court backs Trump admin's passport gender policy
US Supreme Court backs Trump admin's passport gender policy
-
Japan boss Jones backs Farrell to revive Ireland's fortunes


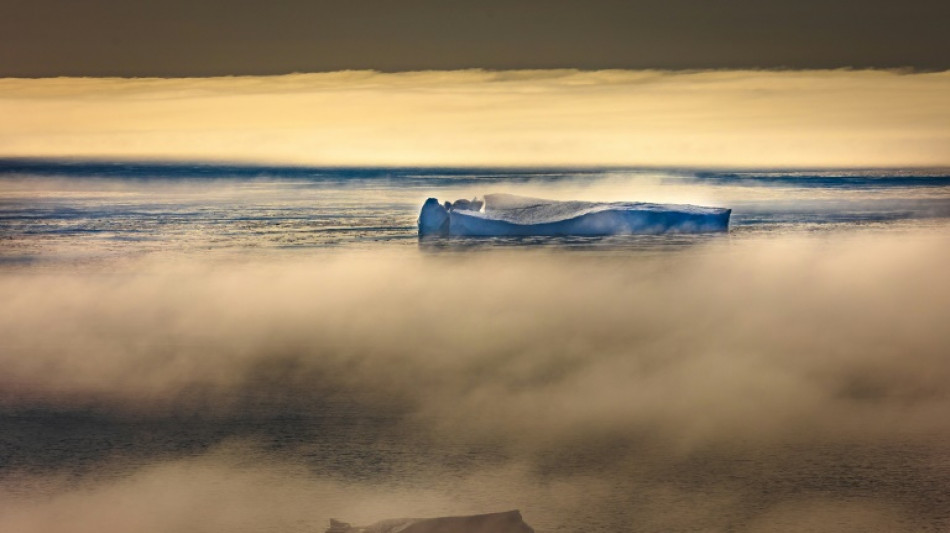
Arctic could be ice-free a decade earlier than thought
The Arctic Ocean's ice cap will disappear in summer as soon as the 2030s and a decade earlier than thought, no matter how aggressively humanity draws down the carbon pollution that drives global warming, scientists said Tuesday.
Even capping global warming at 1.5 degrees Celsius in line with the Paris climate treaty will not prevent the north pole's vast expanse of floating ice from melting away in September, they reported in Nature Communications.
"It is too late to still protect the Arctic summer sea ice as a landscape and as a habitat," co-author Dirk Notz, a professor at the University of Hamburg's Institute of Oceanography, told AFP.
"This will be the first major component of our climate system that we lose because of our emission of greenhouse gases."
Decreased ice cover has serious impacts over time on weather, people and ecosystems -- not just within the region, but globally.
"It can accelerate global warming by melting permafrost laden with greenhouse gases, and sea level rise by melting the Greenland ice sheet," lead author Seung-Ki Min, a researcher at Pohang University of Science and Technology in South Korea, told AFP.
Greenland's kilometres-thick blanket of ice contains enough frozen water to lift oceans six metres.
By contrast, melting sea ice has no discernible impact on sea levels because the ice is already in ocean water, like ice cubes in a glass.
But it does feed into a vicious circle of warming.
- Three times faster -
About 90 percent of the Sun's energy that hits white sea ice is reflected back into space.
But when sunlight hits dark, unfrozen ocean water instead, nearly the same amount of that energy is absorbed by the ocean and spread across the globe.
Both the North and South Pole regions have warmed by three degrees Celsius compared to late 19th-century levels, nearly three times the global average.
An ice-free September in the 2030s "is a decade faster than in recent projections of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC)", the UN's science advisory body, said Min.
In its landmark 2021 report, the IPCC forecast with "high confidence" that the Arctic Ocean would become virtually ice-free at least once by mid-century, and even then only under more extreme greenhouse gas emissions scenarios.
The new study -- which draws from observational data covering the period 1979-2019 to adjust the IPCC models -- finds that threshold will most likely be crossed in the 2040s.
Min and his colleagues also calculated that human activity was responsible for up to 90 percent of the ice cap's shrinking, with only minor impacts from natural factors such as solar and volcanic activity.
The record minimum sea ice extent in the Arctic -- 3.4 million square kilometres (1.3 million square miles) -- occurred in 2012, with the second- and third-lowest ice-covered areas in 2020 and 2019, respectively.
Scientists describe the Arctic Ocean as "ice-free" if the area covered by ice is less than one million square kilometres, about seven percent of the ocean's total area.
Sea ice in Antarctica, meanwhile, dropped to 1.92 million square kilometres in February -- the lowest level on record and almost one million square kilometres below the 1991-2020 mean.
A.AbuSaada--SF-PST



