
-
 US Supreme Court allows third country deportations to resume
US Supreme Court allows third country deportations to resume
-
Oil prices tumble as markets shrug off Iranian rebuttal to US

-
 Rishabh Pant: India's unorthodox hero with 'method to his madness'
Rishabh Pant: India's unorthodox hero with 'method to his madness'
-
PSG ease past Seattle Sounders and into Club World Cup last 16

-
 Atletico win in vain as Botafogo advance at Club World Cup
Atletico win in vain as Botafogo advance at Club World Cup
-
Osaka, Azarenka advance on grass at Bad Homburg

-
 Haliburton latest NBA star with severe injury in playoffs
Haliburton latest NBA star with severe injury in playoffs
-
Trump wants quick win in Iran, but goal remains elusive

-
 Iran attacks US base in Qatar, Trump says time to make peace
Iran attacks US base in Qatar, Trump says time to make peace
-
Kasatkina falls, Fonseca secures first win on grass at Eastbourne

-
 Iran attacks US base in Qatar in retaliation for strikes on nuclear sites
Iran attacks US base in Qatar in retaliation for strikes on nuclear sites
-
Club World Cup prize money does not mean more pressure: Chelsea boss Maresca

-
 Leeds sign Slovenia defender Bijol from Udinese
Leeds sign Slovenia defender Bijol from Udinese
-
E.coli can turn plastic into painkillers, chemists discover

-
 Bluff and last-minute orders: Trump's path to Iran decision
Bluff and last-minute orders: Trump's path to Iran decision
-
US strikes on Iran open rift in Trump's support base

-
 Indiana's Haliburton has torn right Achilles tendon: reports
Indiana's Haliburton has torn right Achilles tendon: reports
-
England rally after Pant heroics to set up thrilling finish to India opener

-
 US hit by first extreme heat wave of the year
US hit by first extreme heat wave of the year
-
Holders Thailand among seven set for LPGA International Crown

-
 England set 371 to win India series opener after Pant heroics
England set 371 to win India series opener after Pant heroics
-
UK and Ukraine agree to deepen ties as Zelensky meets Starmer

-
 New York state to build nuclear power plant
New York state to build nuclear power plant
-
Syria announces arrests over Damascus church attack

-
 Bradley eyes playing captain role at Ryder Cup after win
Bradley eyes playing captain role at Ryder Cup after win
-
US existing home sales little-changed on sluggish market

-
 Top US court takes case of Rastafarian whose hair was cut in prison
Top US court takes case of Rastafarian whose hair was cut in prison
-
Greece declares emergency on Chios over wildfires

-
 Embattled Thai PM reshuffles cabinet as crisis rages
Embattled Thai PM reshuffles cabinet as crisis rages
-
Killer whales spotted grooming each other with seaweed

-
 Where is Iran's uranium? Questions abound after US strikes
Where is Iran's uranium? Questions abound after US strikes
-
EU approves MotoGP takeover by F1 owner Liberty Media

-
 Duplantis says vaulting 6.40m is within the 'realm of possibility'
Duplantis says vaulting 6.40m is within the 'realm of possibility'
-
Pant piles on agony for England with record-breaking century

-
 NATO to take 'quantum leap' with 5% summit pledge: Rutte
NATO to take 'quantum leap' with 5% summit pledge: Rutte
-
Textor sells Crystal Palace stake to boost hopes of European competition

-
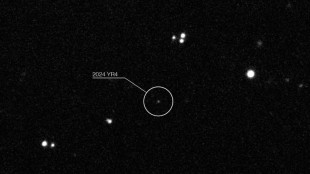 Earth's satellites at risk if asteroid smashes into Moon: study
Earth's satellites at risk if asteroid smashes into Moon: study
-
Syria president vows those involved in church attack will face justice

-
 Russian barrage kills 10 in Kyiv, including 11-year-old girl
Russian barrage kills 10 in Kyiv, including 11-year-old girl
-
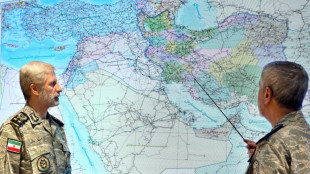
Military bases or vital waterway: Iran weighs response to US strikes
-
 Italian sculptor Arnaldo Pomodoro dies aged nearly 99
Italian sculptor Arnaldo Pomodoro dies aged nearly 99
-
Rahul and Pant build India lead against England

-
 UK probes maternity services after scandals
UK probes maternity services after scandals
-
Asian countries most vulnerable to Strait of Hormuz blockade

-
 Anger as Kanye West to perform in Slovakia after Hitler song
Anger as Kanye West to perform in Slovakia after Hitler song
-
Israel targets Iran Guards, Tehran prison in fresh wave of strikes

-
 Star-packed, Covid-shaped 'Death Stranding 2' drops this week
Star-packed, Covid-shaped 'Death Stranding 2' drops this week
-
IOC is in 'best of hands', says Bach as he hands over to Coventry

-
 Oil prices seesaw as investors await Iran response to US strikes
Oil prices seesaw as investors await Iran response to US strikes
-
Beijing issues weather warning for hottest days of year


E.coli can turn plastic into painkillers, chemists discover
Scientists have found a way to use the bacteria E.Coli to convert plastic waste into a popular painkiller, a study said Monday, though outside experts doubted the technique would make a dent in the fight against plastic pollution.
Paracetamol, which is one of the most commonly used drugs worldwide, is made from the derivatives of fossil fuels, often by Asia-based subcontractors using cheap, polluting methods that contribute to climate change.
The world is also facing an escalating crisis of plastic pollution, with countries set for another bruising round of negotiations in August in the hope of sealing an international treaty to reduce plastic waste.
The British team of researchers behind the new study sought to find a solution to the two problems by roping in a third -- E.coli, which is normally known for making people sick when they eat contaminated food.
First the chemists used a molecule derived from PET plastic, which is used in bottles and many other plastic products the world over, to spark a chemical reaction in a strain of E.coli.
This created a molecule they called PABA, according to the Nature Chemistry study, which was partly funded by drug firm AstraZeneca.
By genetically modifying the bacteria, the chemists were able to transform their molecule into acetaminophen, also known as paracetamol.
"This work demonstrates that PET plastic isn't just waste or a material destined to become more plastic -- it can be transformed by microorganisms into valuable new products, including those with potential for treating disease," lead study Stephen Wallace said in a statement.
Singaporean researchers not involved in the study praised how it combined synthetic and biological chemistry.
But "several practical considerations remain" to take this idea beyond the proof-of-concept stage, they wrote in a linked commentary in the journal Nature Chemistry.
The chemical reaction produces only a limited amount of PABA molecules, which "may be insufficient for industrial applications", they wrote.
Melissa Valliant, communications director of the Beyond Plastics project of Bennington College in the United States, expressed scepticism.
"A new 'plastic-eating bacteria' pops up in the news every few months and has been doing so for years," she told AFP.
"These discoveries never scale up to anything significant enough to tackle the massive plastic pollution problem."
This "crisis needs to be stopped at the source," she added, which means "companies and policymakers must reduce the amount of plastic being produced and used in the first place".
Q.Jaber--SF-PST
