
-
 Rennie, Joseph lead running to become next All Blacks coach
Rennie, Joseph lead running to become next All Blacks coach
-
Asian stock markets mixed as traders weigh US data, await jobs

-
 Australian Olympic snowboarder airlifted to hospital with broken neck
Australian Olympic snowboarder airlifted to hospital with broken neck
-
Moderna says US refusing to review mRNA-based flu shot
-
 Instagram boss to testify at social media addiction trial
Instagram boss to testify at social media addiction trial
-
'Artists of steel': Japanese swords forge new fanbase

-
 New York model, carved in a basement, goes on display
New York model, carved in a basement, goes on display
-
Noisy humans harm birds and affect breeding success: study

-
 More American women holding multiple jobs as high costs sting
More American women holding multiple jobs as high costs sting
-
Charcoal or solar panels? A tale of two Cubas

-
 Several wounded in clashes at Albania opposition rally
Several wounded in clashes at Albania opposition rally
-
Chelsea's draw with Leeds 'bitter pill' for Rosenior

-
 'On autopilot': US skate star Malinin nears more Olympic gold
'On autopilot': US skate star Malinin nears more Olympic gold
-
Carrick frustrated by Man Utd's lack of sharpness in West Ham draw

-
 Frank confident of keeping Spurs job despite Newcastle defeat
Frank confident of keeping Spurs job despite Newcastle defeat
-
James's All-NBA streak ends as Lakers rule superstar out of Spurs clash

-
 Anti-Khamenei slogans in Tehran on eve of revolution anniversary: social media footage
Anti-Khamenei slogans in Tehran on eve of revolution anniversary: social media footage
-
YouTube says it is not social media in landmark addiction trial

-
 Colombian senator kidnapped, president targeted in election run-up
Colombian senator kidnapped, president targeted in election run-up
-
Britney Spears sells rights to her music catalog: US media

-
 West Ham end Man Utd's winning run, Spurs sink to 16th
West Ham end Man Utd's winning run, Spurs sink to 16th
-
US skate star Malinin leads after short programme in Olympics

-
 Man Utd's Sesko strikes late to rescue West Ham draw
Man Utd's Sesko strikes late to rescue West Ham draw
-
Shiffrin flops at Winter Olympics as helmet row grows

-
 Celtics' Tatum practices with G League team but injury return uncertain
Celtics' Tatum practices with G League team but injury return uncertain
-
Gisele Pelicot publishes memoirs after rape trial ordeal

-
 Newcastle beat sorry Spurs to leave Frank on the brink
Newcastle beat sorry Spurs to leave Frank on the brink
-
'Outrage' as LGBTQ Pride flag removed from Stonewall monument

-
 Chappell Roan leaves agency headed by embattled 2028 Olympic chief
Chappell Roan leaves agency headed by embattled 2028 Olympic chief
-
Venezuelan authorities move Machado ally to house arrest

-
 YouTube rejects addiction claims in landmark social media trial
YouTube rejects addiction claims in landmark social media trial
-
Google turns to century-long debt to build AI

-
 'I felt guided by them': US skater Naumov remembers parents at Olympics
'I felt guided by them': US skater Naumov remembers parents at Olympics
-
Till death do us bark: Brazilian state lets pets be buried with owners

-
 Ukrainian athlete vows to wear banned helmet at Winter Olympics
Ukrainian athlete vows to wear banned helmet at Winter Olympics
-
'Confident' Pakistan ready for India blockbuster after USA win

-
 Latam-GPT: a Latin American AI to combat US-centric bias
Latam-GPT: a Latin American AI to combat US-centric bias
-
Gauff dumped out of Qatar Open, Swiatek, Rybakina through

-
 Paris officers accused of beating black producer to stand trial in November
Paris officers accused of beating black producer to stand trial in November
-
Istanbul bars rock bands accused of 'satanism'

-
 Olympic bronze medal biathlete confesses affair on live TV
Olympic bronze medal biathlete confesses affair on live TV
-
US commerce chief admits Epstein Island lunch but denies closer ties

-
 Mayor of Ecuador's biggest city arrested for money laundering
Mayor of Ecuador's biggest city arrested for money laundering
-
Farhan, spinners lead Pakistan to easy USA win in T20 World Cup

-
 Stocks mixed as muted US retail sales spur caution
Stocks mixed as muted US retail sales spur caution
-
Macron wants more EU joint borrowing: Could it happen?

-
 Shiffrin flops at Winter Olympics as helmet row simmers
Shiffrin flops at Winter Olympics as helmet row simmers
-
No excuses for Shiffrin after Olympic team combined flop

-
 Starmer says UK govt 'united', pressing on amid Epstein fallout
Starmer says UK govt 'united', pressing on amid Epstein fallout
-
Pool on wheels brings swim lessons to rural France


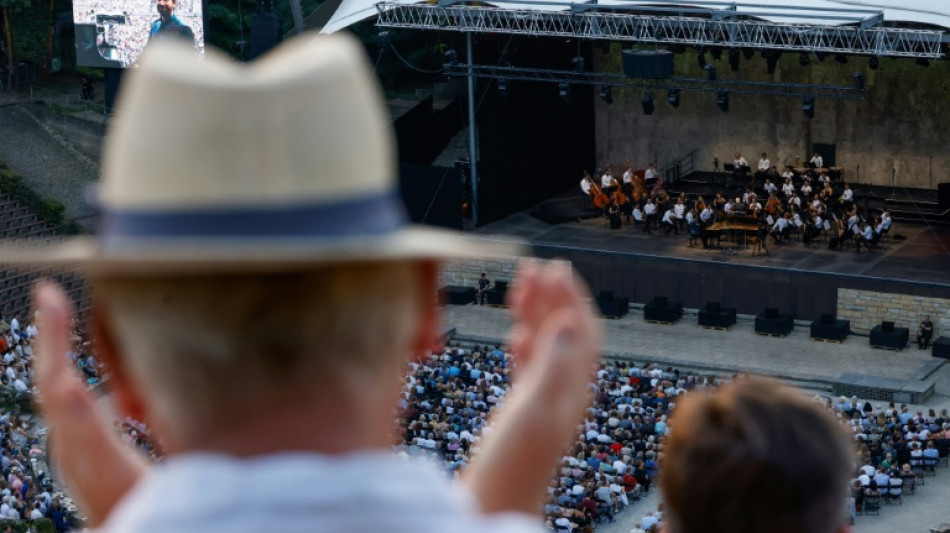
In tune: Classical concert-goers' hearts, breathing synchronize
People who listen to music together often report feeling a powerful connection to each other as a result of their collective experience.
A new study published in the journal Scientific Reports on Thursday now finds that physical responses -- including heart rate, breathing and the electrical conductivity of skin -- synchronize between audience members at classical concerts.
Individuals who rated more highly for personality traits such as openness were more likely to synchronize, while those with neurotic dispositions were less likely to align.
"When we talk about very abstract things such as aesthetic experiences, how you respond to art and to music, the body is always involved there," Wolfgang Tschacher, a psychologist at the University of Bern who led the research as part of the Experimental Concert Research project, told AFP.
This theory is known as "embodied cognition" -- the idea that the mind is not only connected to the body but that the body influences the mind -- which, while arguably intuitive to lay people, has been controversial in scientific circles.
To investigate, Tschacher and colleagues observed 132 audience members across three classical concerts.
All three played the same string quintet pieces: Ludwig van Beethoven's "Op. 104 in C minor," Johannes Brahms' "Op. 111 in G major," and "Epitaphs" by the contemporary composer Brett Dean.
The authors used overhead cameras and wearable sensors to monitor the participants, who filled in questionnaires about their personalities before the concert, and whether they enjoyed the performance and what their mood was afterward.
Overall, they found statistically significant synchronization on several measures -- people's hearts beat faster or slower during the same musical passages, as did their levels of "skin conductance."
Skin conductance is closely related to the body's flight or fight response. When it's high it indicates a state of arousal and can be linked to goosebumps on the skin; when it's low we are in a state of relaxation.
The cameras even caught alignment of body movements, which the authors wrote "appears noteworthy, as the audiences of all concerts were seated in dimmed lighting" and spread out due to the pandemic.
However, though people's breathing rates aligned, they did not actually inhale and exhale in unison.
- The power of music -
As one might expect, people whose personality types indicated "openness to new experiences" and "agreeableness" were more disposed towards synchronizing with others.
Those who rated highly for neuroticism, "a person who tends towards fearful behavior, warding off things, being more depressed," in Tschacher's words, were less likely to synchronize -- but so too were extroverts, which might seem counterintuitive.
"Extroverted people are very social, they tend to intermingle with people, they want to be in power, and they want to have a certain self-value," he said, adding he had seen this result in previous research too. While extroverts are outgoing, they focus less on the music.
For Tschacher, the findings are more evidence in favor of the "embodied cognition" theory and also help explain why public parades or military marches help build cohesion between participants.
And he expects the effects would be "even stronger" in other musical genres.
"There are additional reasons that people will synchronize in pop concerts, people move, they dance, and that's that is synchronized by the music and that would give even clearer results," he said.
W.Mansour--SF-PST


