
-
 Liverpool's Slot says 'no issue to resolve' with Salah after outburst
Liverpool's Slot says 'no issue to resolve' with Salah after outburst
-
'Stop the slaughter': French farmers block roads over cow disease cull

-
 Stormers see off La Rochelle, Sale stun Clermont in Champions Cup
Stormers see off La Rochelle, Sale stun Clermont in Champions Cup
-
Maresca hails Palmer as Chelsea return to winning ways against Everton

-
 Hungarian protesters demand Orban quits over abuse cases
Hungarian protesters demand Orban quits over abuse cases
-
Belarus frees protest leader Kolesnikova, Nobel winner Bialiatski

-
 Salah sets up goal on return to Liverpool action
Salah sets up goal on return to Liverpool action
-
Palmer strikes as Chelsea return to winning ways against Everton

-
 Pogacar targets Tour de France Paris-Roubaix and Milan-San Remo in 2026
Pogacar targets Tour de France Paris-Roubaix and Milan-San Remo in 2026
-
Salah back in action for Liverpool after outburst

-
 Atletico recover Liga momentum with battling win over Valencia
Atletico recover Liga momentum with battling win over Valencia
-
Meillard leads 'perfect' Swiss sweep in Val d'Isere giant slalom

-
 Salah on Liverpool bench for Brighton match
Salah on Liverpool bench for Brighton match
-
Meillard leads Swiss sweep in Val d'Isere giant slalom

-
 Indonesia flood death toll passes 1,000 as authorities ramp up aid
Indonesia flood death toll passes 1,000 as authorities ramp up aid
-
Cambodia shuts Thailand border crossings over deadly fighting

-
 First urban cable car unveiled outside Paris
First urban cable car unveiled outside Paris
-
Vonn second behind Aicher in World Cup downhill at St Moritz

-
 Aicher pips Vonn to downhill win at St Moritz
Aicher pips Vonn to downhill win at St Moritz
-
Thailand says 4 soldiers killed in Cambodia conflict, denies Trump truce claim

-
 Fans vandalise India stadium after Messi's abrupt exit
Fans vandalise India stadium after Messi's abrupt exit
-
Women sommeliers are cracking male-dominated wine world open

-
 Exhibition of Franco-Chinese print master Zao Wou-Ki opens in Hong Kong
Exhibition of Franco-Chinese print master Zao Wou-Ki opens in Hong Kong
-
Myanmar junta denies killing civilians in hospital strike

-
 Why SpaceX IPO plan is generating so much buzz
Why SpaceX IPO plan is generating so much buzz
-
Thailand continues Cambodia strikes despite Trump truce calls

-
 US envoy to meet Zelensky, Europe leaders in Berlin this weekend
US envoy to meet Zelensky, Europe leaders in Berlin this weekend
-
North Korea acknowledges its troops cleared mines for Russia

-
 US unseals warrant for tanker seized off Venezuelan coast
US unseals warrant for tanker seized off Venezuelan coast
-
Cambodia says Thailand still bombing hours after Trump truce call

-
 Machado urges pressure so Maduro understands 'he has to go'
Machado urges pressure so Maduro understands 'he has to go'
-
Leinster stutter before beating Leicester in Champions Cup

-
 World stocks mostly slide, consolidating Fed-fuelled gains
World stocks mostly slide, consolidating Fed-fuelled gains
-
Crypto firm Tether bids for Juventus, is quickly rebuffed

-
 Union sink second-placed Leipzig to climb in Bundesliga
Union sink second-placed Leipzig to climb in Bundesliga
-
US Treasury lifts sanctions on Brazil Supreme Court justice

-
 UK king shares 'good news' that cancer treatment will be reduced in 2026
UK king shares 'good news' that cancer treatment will be reduced in 2026
-
Wembanyama expected to return for Spurs in NBA Cup clash with Thunder

-
 Five takeaways from Luigi Mangione evidence hearings
Five takeaways from Luigi Mangione evidence hearings
-
UK's king shares 'good news' that cancer treatment will be reduced in 2026

-
 Steelers' Watt undergoes surgery to repair collapsed lung
Steelers' Watt undergoes surgery to repair collapsed lung
-
Iran detains Nobel-prize winner in 'brutal' arrest

-
 NBA Cup goes from 'outside the box' idea to smash hit
NBA Cup goes from 'outside the box' idea to smash hit
-
UK health service battles 'super flu' outbreak

-
 Can Venezuela survive US targeting its oil tankers?
Can Venezuela survive US targeting its oil tankers?
-
Democrats release new cache of Epstein photos

-
 Colombia's ELN guerrillas place communities in lockdown citing Trump 'intervention' threats
Colombia's ELN guerrillas place communities in lockdown citing Trump 'intervention' threats
-
'Don't use them': Tanning beds triple skin cancer risk, study finds
-
 Nancy aims to restore Celtic faith with Scottish League Cup final win
Nancy aims to restore Celtic faith with Scottish League Cup final win
-
Argentina fly-half Albornoz signs for Toulon until 2030


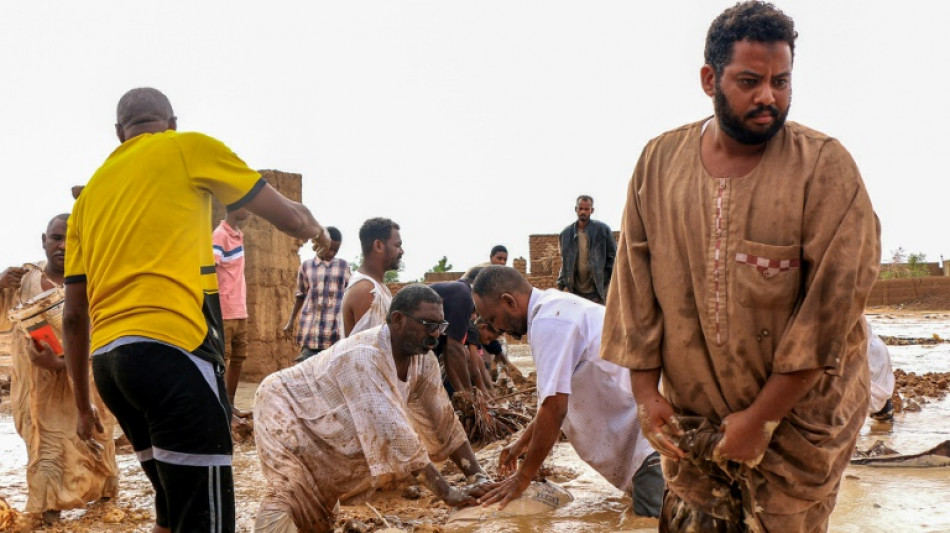
Climate change worsened deadly Africa floods, scientists say
Human-caused climate change worsened floods that have killed hundreds of people and displaced millions in Cameroon, Chad, Niger, Nigeria and Sudan this year, according to a study published on Wednesday.
The intense rainy season has unleashed a humanitarian crisis across large areas of the Sahel region bordering the Sahara desert.
A new analysis by the World Weather Attribution (WWA) network of scientists found warming driven by the use of fossil fuels had exacerbated the flooding in Sudan.
The researchers also said climate change would have made this year's torrential rains around five to 20 percent more intense across the Niger and Lake Chad basins, citing a previous WWA study of similar floods in 2022.
"This is only going to keep getting worse if we keep burning fossil fuels," said Clair Barnes from the Centre for Environmental Policy at Imperial College London.
Speaking at a briefing ahead of the study's publication, she said such downpours "could happen every year" if global temperatures increase to two degrees Celsius (35.6 Fahrenheit) above pre-industrial levels.
"It's pretty serious," she said.
- Downpours and storms -
Global warming is not just about rising temperatures -- the extra heat trapped in the atmosphere and seas has knock-on effects and can result in more intense downpours and storms.
The researchers said there was a clear link between the extreme rainfall and a warming planet.
In the study, they focused on war-torn Sudan, where millions of displaced people have been uprooted by conflict and driven into flood-prone areas.
The scientists used modelling to compare weather patterns in our world and one without human-induced warming, and found that month-long spells of intense rainfall in parts of Sudan had become heavier and more likely due to climate change.
At the current 1.3 degrees Celsius of warming, they said similar periods of rainfall are expected to occur on average about once every three years, and have become about 10 percent heavier due to climate change.
- 'Incredibly concerning' -
"These results are incredibly concerning," said Izidine Pinto, one of the study's authors and a researcher at the Royal Netherlands Meteorological Institute.
He warned that "with every fraction of a degree of warming, the risk of extreme floods will keep increasing", and called for the UN's COP29 climate summit to "accelerate the transition away from fossil fuels" when it meets in Azerbaijan next month.
Joyce Kimutai, a researcher at Imperial's Centre for Environmental Policy, said the floods underscored the need for a loss and damage fund for nations devastated by climate change.
A key meeting ahead of COP29 earlier this month ended with countries making little progress over how to finance a deal for poorer nations.
"Africa has contributed a tiny amount of carbon emissions globally, but is being hit the hardest by extreme weather," Kimutai said.
The role of climate change in the floods was compounded by other human-made problems, the researchers said, and they called for better maintenance of dams and investment in early warning systems.
H.Darwish--SF-PST




