
-
 Sudan 'lost all sources of revenue' in the war: finance minister to AFP
Sudan 'lost all sources of revenue' in the war: finance minister to AFP
-
Freezing rain hampers transport in Central Europe

-
 Nuuk, Copenhagen cautiously mull Greenland independence
Nuuk, Copenhagen cautiously mull Greenland independence
-
'Proving the boys wrong': Teenage racers picked for elite driver programme

-
 Mbappe absent from training as Arbeloa takes charge at Real Madrid
Mbappe absent from training as Arbeloa takes charge at Real Madrid
-
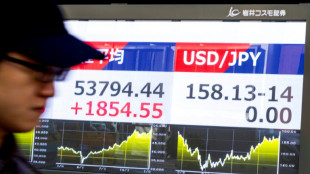
Iran worries push up oil price as world stocks diverge
-
 Volvo Cars pauses battery factory after fruitless partner search
Volvo Cars pauses battery factory after fruitless partner search
-
Social media harms teens, watchdog warns, as France weighs ban

-
 Central bank chiefs voice 'full solidarity' with US Fed, Powell
Central bank chiefs voice 'full solidarity' with US Fed, Powell
-
Greece airspace shutdown exposes badly outdated systems

-
 France climate goals off track as emissions cuts slow again
France climate goals off track as emissions cuts slow again
-
Boeing sells 50 737 MAX jets to leasing group ACG

-
 Freezing rain paralyses transport in Central Europe
Freezing rain paralyses transport in Central Europe
-
Man Utd reach deal to appoint Carrick as interim boss: reports

-
 Trump hits Iran trade partners with tariffs as protest toll soars
Trump hits Iran trade partners with tariffs as protest toll soars
-
Is China a threat to Greenland as Trump argues?

-
 Takaichi says urged S. Korea's Lee to help 'ensure regional stability'
Takaichi says urged S. Korea's Lee to help 'ensure regional stability'
-
South Korean prosecutors set to demand heavy sentence for Yoon

-
 Honduras electoral authorities reject vote recount
Honduras electoral authorities reject vote recount
-
Tractors in Paris to protest EU's trade deal with S. America

-
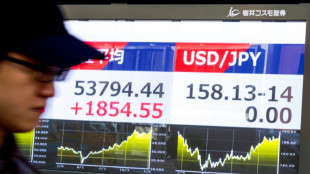 Asian markets rise, Iran worries push up oil
Asian markets rise, Iran worries push up oil
-
Williams loses golden oldie clash in final Australian Open warm-up

-
 Kyrgios stands by decision to skip Australian Open singles
Kyrgios stands by decision to skip Australian Open singles
-
Disaster losses drop in 2025, picture still 'alarming': Munich Re

-
 Williams, 45, loses in first round of final Australian Open warm-up
Williams, 45, loses in first round of final Australian Open warm-up
-
Doncic scores 42 points but Lakers humbled by Kings

-
 'Serious threat': Indonesia legal reform sparks rights challenges
'Serious threat': Indonesia legal reform sparks rights challenges
-
Rodgers misery as Texans rout Steelers to advance in NFL playoffs

-
 Morocco's Bono 'one of best goalkeepers in the world'
Morocco's Bono 'one of best goalkeepers in the world'
-
Salah and Mane meet again with AFCON final place on the line

-
 French museum fare hikes for non-European tourists spark outcry
French museum fare hikes for non-European tourists spark outcry
-
In 'big trouble'? The factors determining Iran's future

-
 Osimhen finds AFCON scoring touch to give Nigeria cutting edge
Osimhen finds AFCON scoring touch to give Nigeria cutting edge
-
Trump announces tariffs on Iran trade partners as protest toll rises

-
 Sabalenka favourite at Australian Open but faces Swiatek, US threats
Sabalenka favourite at Australian Open but faces Swiatek, US threats
-
Gay Australian footballer Cavallo alleges former club was homophobic

-
 Global Sports Brand U.S. Polo Assn. Announced as Official Jersey and Apparel Sponsor for the Legendary Snow Polo World Cup St. Moritz
Global Sports Brand U.S. Polo Assn. Announced as Official Jersey and Apparel Sponsor for the Legendary Snow Polo World Cup St. Moritz
-
Trump has options on Iran, but first must define goal

-
 Paris FC's Ikone stuns PSG to knock out former club from French Cup
Paris FC's Ikone stuns PSG to knock out former club from French Cup
-
Australia's ambassador to US leaving post, marked by Trump rift

-
 Slot angered by 'weird' Szoboszlai error in Liverpool FA Cup win
Slot angered by 'weird' Szoboszlai error in Liverpool FA Cup win
-
Szoboszlai plays hero and villain in Liverpool's FA Cup win

-
 Hawaii's Kilauea volcano puts on spectacular lava display
Hawaii's Kilauea volcano puts on spectacular lava display
-
US stocks at records despite early losses on Fed independence angst

-
 Koepka rejoins PGA Tour under new rules for LIV players
Koepka rejoins PGA Tour under new rules for LIV players
-
Ex-France, Liverpool defender Sakho announces retirement

-
 Jerome Powell: The careful Fed chair standing firm against Trump
Jerome Powell: The careful Fed chair standing firm against Trump
-
France scrum-half Le Garrec likely to miss start of Six Nations

-
 AI helps fuel new era of medical self-testing
AI helps fuel new era of medical self-testing
-
Leaders of Japan and South Korea meet as China flexes muscles


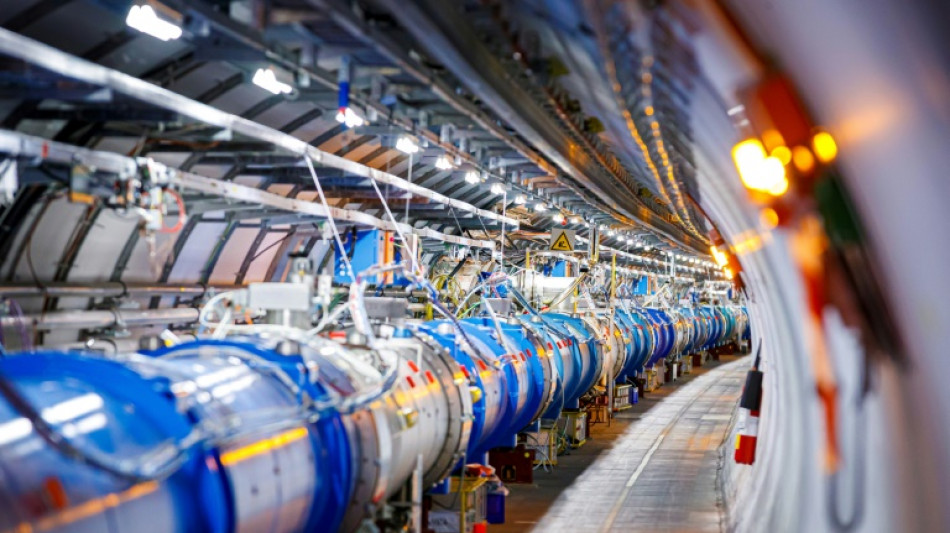
Large Hadron Collider revs up to unprecedented energy level
Ten years after it discovered the Higgs boson, the Large Hadron Collider is about to start smashing protons together at unprecedented energy levels in its quest to reveal more secrets about how the universe works.
The world's largest and most powerful particle collider started back up in April after a three-year break for upgrades in preparation for its third run.
From Tuesday it will run around the clock for nearly four years at a record energy of 13.6 trillion electronvolts, the European Organisation for Nuclear Research (CERN) announced at a press briefing last week.
It will send two beams of protons -- particles in the nucleus of an atom -- in opposite directions at nearly the speed of light around a 27-kilometre (17-mile) ring buried 100 metres under the Swiss-French border.
The resulting collisions will be recorded and analysed by thousands of scientists as part of a raft of experiments, including ATLAS, CMS, ALICE and LHCb, which will use the enhanced power to probe dark matter, dark energy and other fundamental mysteries.
- 1.6 billion collisions a second -
"We aim to be delivering 1.6 billion proton-proton collisions per second" for the ATLAS and CMS experiments, CERN's head of accelerators and technology Mike Lamont said.
This time around the proton beams will be narrowed to less than 10 microns -- a human hair is around 70 microns thick -- to increase the collision rate, he added.
The new energy rate will allow them to further investigate the Higgs boson, which the Large Hadron Collider first observed on July 4, 2012.
The discovery revolutionised physics in part because the boson fit within the Standard Model -- the mainstream theory of all the fundamental particles that make up matter and the forces that govern them.
However several recent findings have raised questions about the Standard Model, and the newly upgraded collider will look at the Higgs boson in more depth.
"The Higgs boson is related to some of the most profound open questions in fundamental physics today," said CERN director-general Fabiola Gianotti, who first announced the boson's discovery a decade ago.
Compared to the collider's first run that discovered the boson, this time around there will be 20 times more collisions.
"This is a significant increase, paving the way for new discoveries," Lamont said.
Joachim Mnich, CERN's head of research and computing, said there was still much more to learn about the boson.
"Is the Higgs boson really a fundamental particle or is it a composite?" he asked.
"Is it the only Higgs-like particle that exists -- or are there others?"
- 'New physics season' -
Past experiments have determined the mass of the Higgs boson, as well as more than 60 composite particles predicted by the Standard Model, such as the tetraquark.
But Gian Giudice, head of CERN's theoretical physics department, said observing particles is only part of the job.
"Particle physics does not simply want to understand the how -- our goal is to understand the why," he said.
Among the Large Hadron Collider's nine experiments is ALICE, which probes the matter that existed in the first 10 microseconds after the Big Bang, and LHCf, which uses the collisions to simulate cosmic rays.
After this run, the collider will come back in 2029 as the High-Luminosity LHC, increasing the number of detectable events by a factor of 10.
Beyond that, the scientists are planning a Future Circular Collider -- a 100-kilometre ring that aims to reach energies of a whopping 100 trillion electronvolts.
But for now, physicists are keenly awaiting results from the Large Hadron Collider's third run.
"A new physics season is starting," CERN said.
I.Yassin--SF-PST




