
-
 Sudan 'lost all sources of revenue' in the war: finance minister to AFP
Sudan 'lost all sources of revenue' in the war: finance minister to AFP
-
Freezing rain hampers transport in Central Europe

-
 Nuuk, Copenhagen cautiously mull Greenland independence
Nuuk, Copenhagen cautiously mull Greenland independence
-
'Proving the boys wrong': Teenage racers picked for elite driver programme

-
 Mbappe absent from training as Arbeloa takes charge at Real Madrid
Mbappe absent from training as Arbeloa takes charge at Real Madrid
-
Iran worries push up oil price as world stocks diverge
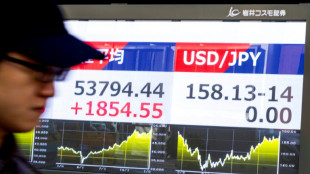
-
 Volvo Cars pauses battery factory after fruitless partner search
Volvo Cars pauses battery factory after fruitless partner search
-
Social media harms teens, watchdog warns, as France weighs ban

-
 Central bank chiefs voice 'full solidarity' with US Fed, Powell
Central bank chiefs voice 'full solidarity' with US Fed, Powell
-
Greece airspace shutdown exposes badly outdated systems

-
 France climate goals off track as emissions cuts slow again
France climate goals off track as emissions cuts slow again
-
Boeing sells 50 737 MAX jets to leasing group ACG

-
 Freezing rain paralyses transport in Central Europe
Freezing rain paralyses transport in Central Europe
-
Man Utd reach deal to appoint Carrick as interim boss: reports

-
 Trump hits Iran trade partners with tariffs as protest toll soars
Trump hits Iran trade partners with tariffs as protest toll soars
-
Is China a threat to Greenland as Trump argues?

-
 Takaichi says urged S. Korea's Lee to help 'ensure regional stability'
Takaichi says urged S. Korea's Lee to help 'ensure regional stability'
-
South Korean prosecutors set to demand heavy sentence for Yoon

-
 Honduras electoral authorities reject vote recount
Honduras electoral authorities reject vote recount
-
Tractors in Paris to protest EU's trade deal with S. America

-
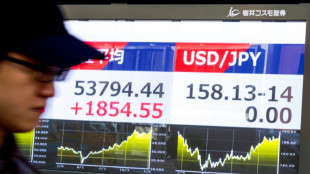 Asian markets rise, Iran worries push up oil
Asian markets rise, Iran worries push up oil
-
Williams loses golden oldie clash in final Australian Open warm-up

-
 Kyrgios stands by decision to skip Australian Open singles
Kyrgios stands by decision to skip Australian Open singles
-
Disaster losses drop in 2025, picture still 'alarming': Munich Re

-
 Williams, 45, loses in first round of final Australian Open warm-up
Williams, 45, loses in first round of final Australian Open warm-up
-
Doncic scores 42 points but Lakers humbled by Kings

-
 'Serious threat': Indonesia legal reform sparks rights challenges
'Serious threat': Indonesia legal reform sparks rights challenges
-
Rodgers misery as Texans rout Steelers to advance in NFL playoffs

-
 Morocco's Bono 'one of best goalkeepers in the world'
Morocco's Bono 'one of best goalkeepers in the world'
-
Salah and Mane meet again with AFCON final place on the line

-
 French museum fare hikes for non-European tourists spark outcry
French museum fare hikes for non-European tourists spark outcry
-
In 'big trouble'? The factors determining Iran's future

-
 Osimhen finds AFCON scoring touch to give Nigeria cutting edge
Osimhen finds AFCON scoring touch to give Nigeria cutting edge
-
Trump announces tariffs on Iran trade partners as protest toll rises

-
 Sabalenka favourite at Australian Open but faces Swiatek, US threats
Sabalenka favourite at Australian Open but faces Swiatek, US threats
-
Gay Australian footballer Cavallo alleges former club was homophobic

-
 Global Sports Brand U.S. Polo Assn. Announced as Official Jersey and Apparel Sponsor for the Legendary Snow Polo World Cup St. Moritz
Global Sports Brand U.S. Polo Assn. Announced as Official Jersey and Apparel Sponsor for the Legendary Snow Polo World Cup St. Moritz
-
Trump has options on Iran, but first must define goal

-
 Paris FC's Ikone stuns PSG to knock out former club from French Cup
Paris FC's Ikone stuns PSG to knock out former club from French Cup
-
Australia's ambassador to US leaving post, marked by Trump rift

-
 Slot angered by 'weird' Szoboszlai error in Liverpool FA Cup win
Slot angered by 'weird' Szoboszlai error in Liverpool FA Cup win
-
Szoboszlai plays hero and villain in Liverpool's FA Cup win

-
 Hawaii's Kilauea volcano puts on spectacular lava display
Hawaii's Kilauea volcano puts on spectacular lava display
-
US stocks at records despite early losses on Fed independence angst

-
 Koepka rejoins PGA Tour under new rules for LIV players
Koepka rejoins PGA Tour under new rules for LIV players
-
Ex-France, Liverpool defender Sakho announces retirement

-
 Jerome Powell: The careful Fed chair standing firm against Trump
Jerome Powell: The careful Fed chair standing firm against Trump
-
France scrum-half Le Garrec likely to miss start of Six Nations

-
 AI helps fuel new era of medical self-testing
AI helps fuel new era of medical self-testing
-
Leaders of Japan and South Korea meet as China flexes muscles


Friends at first sniff: People drawn to others who smell like them
It's often said that people who click right away share "chemistry."
This expression could be true in the literal sense, according to a new study published in the journal Science Advances on Friday, which finds people with similar body odors are more likely to hit it off as friends.
"Nonhuman terrestrial mammals constantly sniff themselves and each other and, based on this, decide who is friend or foe," wrote a group of researchers led by Inbal Ravreby at Weizmann Institute of Science in Israel.
Since people seek friends who are similar to themselves, the team hypothesized that humans may smell themselves and others to subconsciously estimate body odor similarity and judge their compatibility.
To find out, they set about collecting samples from pairs of same-sex, non-romantic friends who described themselves as having clicked at first sight, that is to say "where a sense of friendship was formed before extensive biographical information was exchanged," according to the paper.
After an extensive recruitment effort, they found 20 pairs, half of whom were male, and the other half female, all aged between 22 and 39 years old.
In order to prevent contamination or outside factors influencing their samples, all participants had to follow a strict protocol that included avoiding pungent foods and sleeping away from their partner and pets in a clean cotton T-shirt that was provided to them.
The T-shirts were collected in ziplock bags and tested with an electronic nose -- a device equipped with sensors to analyze chemical composition. The researchers found that the odor signatures of "click friends" were statistically more closely matched than odors between non-friends.
To assess whether the eNose results accurately mirrored human perception, the team recruited human smellers and devised a set of tests to check the validity of their result.
In one of these tests, for example, the human smellers were presented with three odors: two from a pair of click friends, and one outlier. They successfully identified the pairs and rejected the outlier.
- Smell predicted friendships too -
These results seemed to confirm the hypothesis that similar smells might spur friendship, but an alternative explanation was that people who are friends spend a lot of time together and so have similar body-odor shaping experiences, such as where they live and what they eat.
To disentangle these two possibilities, the team devised another test to see whether smell could be a successful predictor in whether two people who've never met go on to click.
They recruited 17 strangers and had them all interact with one another in a test called the "Mirror Game" -- standing half a meter apart so they could subconsciously smell each other, they were asked to mimic each other's hand movements for two minutes, without talking to each other.
Chemical similarity in their odors, as tested by the eNose, successfully predicted mutual clicks in 77 percent of cases, and predicted 68 percent of cases where both sides said they did not click.
What's more, the closer people's smell was, the more they reported liking each other, understanding one another, and feeling greater chemistry between themselves.
Together, the study's results "converged to suggest that human same-sex nonromantic click friends smell more similar to each other than expected by chance," the team concluded.
Humans, unlike other terrestrial mammals, use complex language to interact, and so it's possible the effects of smell in lab settings were amplified compared to how important they may have been in real life, the team wrote.
"Nevertheless, we think our results imply that we may also be more like other terrestrial mammals in this respect than we typically appreciate."
M.Qasim--SF-PST




