
-
 Ford steers England to rare win over New Zealand
Ford steers England to rare win over New Zealand
-
Massive march in Brazil marks first big UN climate protest in years

-
 Spain rescues hundreds of exotic animals from unlicensed shelter
Spain rescues hundreds of exotic animals from unlicensed shelter
-
Huge fire sparked by explosions near Argentine capital 'contained'

-
 South Africa defy early red card to beat battling Italy
South Africa defy early red card to beat battling Italy
-
Sinner beats De Minaur to reach ATP Finals title match

-
 Zelensky vows overhaul of Ukraine's scandal-hit energy firms
Zelensky vows overhaul of Ukraine's scandal-hit energy firms
-
South Africa defy early red card to beat Italy

-
 Alex Marquez claims Valencia MotoGP sprint victory
Alex Marquez claims Valencia MotoGP sprint victory
-
McIlroy shares lead with Race to Dubai title in sight

-
 Climate protesters rally in Brazil at COP30 halfway mark
Climate protesters rally in Brazil at COP30 halfway mark
-
Spike Lee gifts pope Knicks jersey as pontiff meets film stars

-
 BBC caught in crossfire of polarised political and media landscape
BBC caught in crossfire of polarised political and media landscape
-
'Happy' Shiffrin dominates in Levi slalom for 102nd World Cup win

-
 Palestinian national team on 'mission' for peace in Spain visit
Palestinian national team on 'mission' for peace in Spain visit
-
Brazilian 'Superman' cheers child cancer patients in Ghana

-
 India close in on win over South Africa after Jadeja heroics
India close in on win over South Africa after Jadeja heroics
-
Huge explosions rock industrial area near Argentina's capital

-
 Bezzecchi takes pole for Valencia sprint and MotoGP
Bezzecchi takes pole for Valencia sprint and MotoGP
-
Dominant Shiffrin leads after first slalom run in Levi

-
 Nine killed in accidental explosion at Indian Kashmir police station
Nine killed in accidental explosion at Indian Kashmir police station
-
Climate protesters to rally at COP30's halfway mark

-
 Fighting South Africa lose Rickelton after India 189 all out
Fighting South Africa lose Rickelton after India 189 all out
-
Harmer leads South Africa fightback as India 189 all out

-
 Prison looms for Brazil's Bolsonaro after court rejects his appeal
Prison looms for Brazil's Bolsonaro after court rejects his appeal
-
EU bows to pressure on loosening AI, privacy rules

-
 India close in on lead despite South African strikes
India close in on lead despite South African strikes
-
Curry's 49 points propel Warriors in 109-108 win over Spurs

-
 NZ boxer Parker denies taking banned substance after failed test
NZ boxer Parker denies taking banned substance after failed test
-
Australia setback as Hazlewood ruled out of 1st Ashes Test

-
 Australia pace spearhead Josh Hazlewood ruled out of 1st Ashes Test
Australia pace spearhead Josh Hazlewood ruled out of 1st Ashes Test
-
UN Security Council to vote Monday on Trump Gaza plan

-
 Japan's Tomono leads after men's short program at Skate America
Japan's Tomono leads after men's short program at Skate America
-
China tells citizens to avoid Japan travel as Taiwan row grows

-
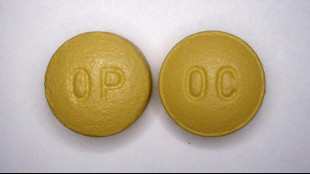 Purdue Pharma to be dissolved as US judge says to approve bankruptcy
Purdue Pharma to be dissolved as US judge says to approve bankruptcy
-
Iran's first woman orchestra conductor inspires

-
 Wood gets all-clear in boost for England
Wood gets all-clear in boost for England
-
Golf's world No. 8 Thomas has back surgery

-
 Rebooted Harlem museum celebrates rise of Black art
Rebooted Harlem museum celebrates rise of Black art
-
'Desperation in the air': immigrant comics skewer Trump crackdown

-
 UN regulator says shipping still wants to decarbonize -- despite US threats
UN regulator says shipping still wants to decarbonize -- despite US threats
-
Grant, Kim share halfway lead in LPGA Annika tournament

-
 Musk's Grokipedia leans on 'questionable' sources, study says
Musk's Grokipedia leans on 'questionable' sources, study says
-
Trump signs order to lower tariffs on beef, coffee, other goods

-
 Croatia qualify for 2026 World Cup, Netherlands close, Germany in limbo
Croatia qualify for 2026 World Cup, Netherlands close, Germany in limbo
-
'Last Chance U' coach dies after shooting: US police

-
 Sinner completes perfect ATP Finals group stage, Auger-Aliassime reaches last four
Sinner completes perfect ATP Finals group stage, Auger-Aliassime reaches last four
-
Woltemade sends Germany past Luxembourg in World Cup qualifier

-
 Croatia qualify for 2026 World Cup with 3-1 win over Faroes
Croatia qualify for 2026 World Cup with 3-1 win over Faroes
-
Kai Trump makes strides but still misses cut in LPGA debut


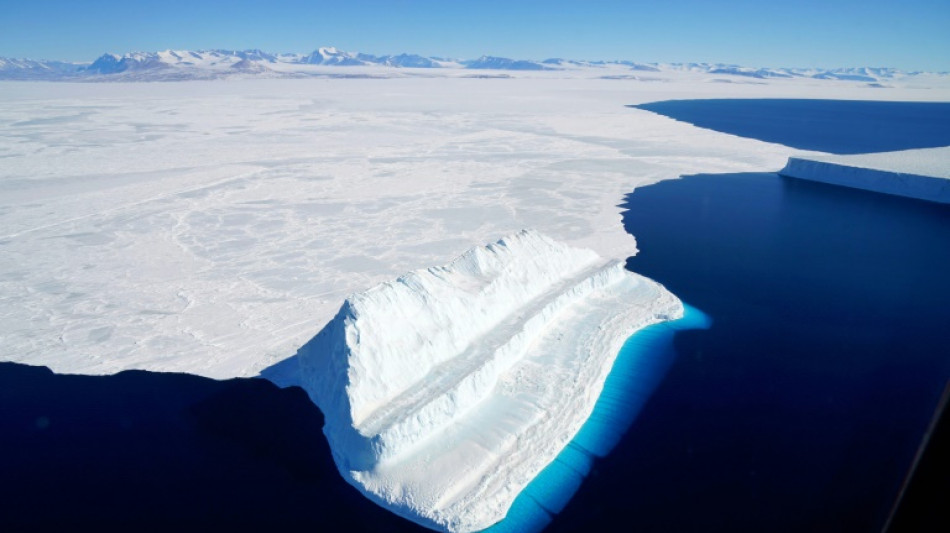
How did life survive 'Snowball Earth'? In ponds, study suggests
Earth has not always been so hospitable to live. During several ice ages, the planet's surface was almost completely frozen over, creating what has been dubbed "Snowball Earth".
Liquid water appears to be the most important ingredient for life on any planet, raising the question: how did anything survive such frosty, brutal times?
A group of scientists said Thursday that they had found an astonishing diversity of micro-organisms in tiny pools of melted ice in Antarctica, suggesting that life could have ridden out Snowball Earth in similar ponds.
During the Cryogenian Period between 635 and 720 million years ago, the average global temperature did not rise above -50 degrees Celsius (-58 Fahrenheit). The climate near the equator at the time resembled modern-day Antarctica.
Yet even in such extreme conditions, life found a way to keep evolving.
Fatima Husain, the lead author of a new study published in Nature Communications, told AFP there was evidence of complex life forms "before and after the Cryogenian in the fossil record".
"There are multiple hypotheses regarding possible places life may have persisted," said Husain, a graduate student at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
Perhaps it found shelter in patches of open ocean, or in deep-sea hydrothermal vents, or under vast sheets of ice.
The tiny melted ice pools that dotted the equator were another proposed refuge.
These ponds could have been oases for eukaryotes, complex organisms that eventually evolved into multicellular life forms that would rise to dominate Earth, including humans.
- Could aliens be hiding in ponds? -
Melted ice ponds still exist today in Antarctica, at the edges of ice sheets.
In 2018, members of a New Zealand research team visited the McMurdo ice shelf in east Antarctica, home to several such pools, which are only a few metres wide and less a metre deep.
The bottom of the ponds are lined with a mat of microbes that have accumulated over the years to form slimy layers.
"These mats can be a few centimetres thick, colourful, and they can be very clearly layered," Husain said.
They are made up of single-celled organisms called cyanobacteria that are known to be able to survive extreme conditions.
But the researchers also found signs indicating there were eukaryotes such as algae or microscopic animals.
This suggests there was surprising diversity in the ponds, which appears to have been influenced by the amount of salt each contained.
"No two ponds were alike," Husain said. "We found diverse assemblages of eukaryotes from all the major groups in all the ponds studied."
"They demonstrate that these unique environments are capable of sheltering diverse assemblages of life, even in close proximity," she added.
This could have implications in the search for extraterrestrial life.
"Studies of life within these special environments on Earth can help inform our understanding of potential habitable environments on icy worlds, including icy moons in our Solar System," Husain said.
Saturn's moon Enceladus and Jupiter's Europa are covered in ice, but scientists increasingly suspect they could be home to simple forms of life, and several space missions have been launched to find out more about them.
H.Nasr--SF-PST


