
-
 M23, DR Congo sign new peace roadmap in Doha
M23, DR Congo sign new peace roadmap in Doha
-
Estevao, Casemiro on target for Brazil in Senegal win

-
 Ford steers England to rare win over New Zealand
Ford steers England to rare win over New Zealand
-
Massive march in Brazil marks first big UN climate protest in years

-
 Spain rescues hundreds of exotic animals from unlicensed shelter
Spain rescues hundreds of exotic animals from unlicensed shelter
-
Huge fire sparked by explosions near Argentine capital 'contained'

-
 South Africa defy early red card to beat battling Italy
South Africa defy early red card to beat battling Italy
-
Sinner beats De Minaur to reach ATP Finals title match

-
 Zelensky vows overhaul of Ukraine's scandal-hit energy firms
Zelensky vows overhaul of Ukraine's scandal-hit energy firms
-
South Africa defy early red card to beat Italy

-
 Alex Marquez claims Valencia MotoGP sprint victory
Alex Marquez claims Valencia MotoGP sprint victory
-
McIlroy shares lead with Race to Dubai title in sight

-
 Climate protesters rally in Brazil at COP30 halfway mark
Climate protesters rally in Brazil at COP30 halfway mark
-
Spike Lee gifts pope Knicks jersey as pontiff meets film stars

-
 BBC caught in crossfire of polarised political and media landscape
BBC caught in crossfire of polarised political and media landscape
-
'Happy' Shiffrin dominates in Levi slalom for 102nd World Cup win

-
 Palestinian national team on 'mission' for peace in Spain visit
Palestinian national team on 'mission' for peace in Spain visit
-
Brazilian 'Superman' cheers child cancer patients in Ghana

-
 India close in on win over South Africa after Jadeja heroics
India close in on win over South Africa after Jadeja heroics
-
Huge explosions rock industrial area near Argentina's capital

-
 Bezzecchi takes pole for Valencia sprint and MotoGP
Bezzecchi takes pole for Valencia sprint and MotoGP
-
Dominant Shiffrin leads after first slalom run in Levi

-
 Nine killed in accidental explosion at Indian Kashmir police station
Nine killed in accidental explosion at Indian Kashmir police station
-
Climate protesters to rally at COP30's halfway mark

-
 Fighting South Africa lose Rickelton after India 189 all out
Fighting South Africa lose Rickelton after India 189 all out
-
Harmer leads South Africa fightback as India 189 all out

-
 Prison looms for Brazil's Bolsonaro after court rejects his appeal
Prison looms for Brazil's Bolsonaro after court rejects his appeal
-
EU bows to pressure on loosening AI, privacy rules

-
 India close in on lead despite South African strikes
India close in on lead despite South African strikes
-
Curry's 49 points propel Warriors in 109-108 win over Spurs

-
 NZ boxer Parker denies taking banned substance after failed test
NZ boxer Parker denies taking banned substance after failed test
-
Australia setback as Hazlewood ruled out of 1st Ashes Test

-
 Australia pace spearhead Josh Hazlewood ruled out of 1st Ashes Test
Australia pace spearhead Josh Hazlewood ruled out of 1st Ashes Test
-
UN Security Council to vote Monday on Trump Gaza plan

-
 Japan's Tomono leads after men's short program at Skate America
Japan's Tomono leads after men's short program at Skate America
-
China tells citizens to avoid Japan travel as Taiwan row grows

-
 Purdue Pharma to be dissolved as US judge says to approve bankruptcy
Purdue Pharma to be dissolved as US judge says to approve bankruptcy
-
Iran's first woman orchestra conductor inspires

-
 Wood gets all-clear in boost for England
Wood gets all-clear in boost for England
-
Golf's world No. 8 Thomas has back surgery

-
 Rebooted Harlem museum celebrates rise of Black art
Rebooted Harlem museum celebrates rise of Black art
-
'Desperation in the air': immigrant comics skewer Trump crackdown

-
 UN regulator says shipping still wants to decarbonize -- despite US threats
UN regulator says shipping still wants to decarbonize -- despite US threats
-
Grant, Kim share halfway lead in LPGA Annika tournament

-
 Musk's Grokipedia leans on 'questionable' sources, study says
Musk's Grokipedia leans on 'questionable' sources, study says
-
Trump signs order to lower tariffs on beef, coffee, other goods

-
 Croatia qualify for 2026 World Cup, Netherlands close, Germany in limbo
Croatia qualify for 2026 World Cup, Netherlands close, Germany in limbo
-
'Last Chance U' coach dies after shooting: US police

-
 Sinner completes perfect ATP Finals group stage, Auger-Aliassime reaches last four
Sinner completes perfect ATP Finals group stage, Auger-Aliassime reaches last four
-
Woltemade sends Germany past Luxembourg in World Cup qualifier


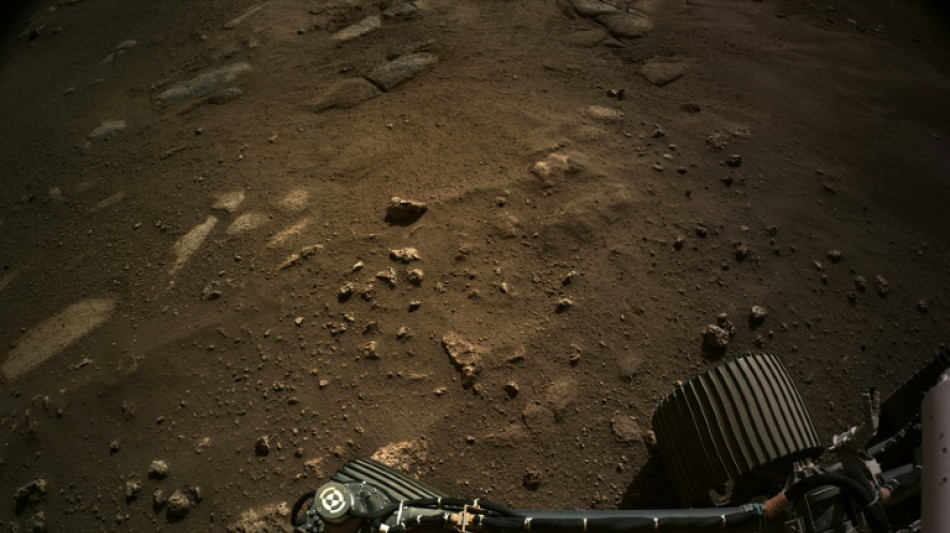
The promise and peril of a crewed Mars mission
A crewed mission to Mars would rank among the most complex and costly undertakings in human history -- and US President Donald Trump has vowed to make it a national priority.
That political momentum, coupled with SpaceX chief Elon Musk's zeal, has breathed new life into a cause long championed by Red Planet advocates -- even as major obstacles remain, including Trump and Musk's latest feud.
- Why go? -
As NASA writes in its Moon to Mars blueprint, "exploration of the cosmos remains a great calling for humanity."
A mission to Mars would pursue scientific objectives like determining whether Mars ever hosted life and charting the evolution of its surface, as well as answering broader space physics questions -- such as the history of the Sun through studying Martian soil.
Geopolitics also looms large, as Trump has pledged to "plant the American flag on the planet Mars and even far beyond," invoking the "unlimited promise of the American dream."
Critics, however, say cuts to NASA's science budget and the cancellation of key projects -- including the return of rock samples collected by the Perseverance rover -- are undermining the research mission.
"The purpose of exploration is not just to go somewhere," Nobel-winning astrophysicist John Mather told AFP. "This is not a tourist thing. This is a fundamental knowledge thing."
- Getting there -
Musk is betting SpaceX's future on Starship, the largest rocket ever built, despite fiery failures in its nine test flights.
He's aiming for an uncrewed launch by late 2026, timed with the next favorable Earth-Mars alignment.
But the timeline is widely seen as optimistic: Starship has yet to land its upper stage or demonstrate in-orbit refueling -- both essential for deep space travel.
Some experts believe the system is fundamentally sound, while others say it's too soon to judge.
"A lot of the pertinent and relevant technical information... is not known to us," Kurt Polzin, chief engineer for NASA's space nuclear propulsion project, told AFP.
He backs Nuclear Thermal Propulsion (NTP), which uses fission to heat hydrogen and generate thrust.
NTP delivers "a lot of power in a very small package," Polzin said, eliminating the need for orbital refueling or fuel production on Mars.
Astronauts would spend seven to nine months in a cramped spacecraft, exposed to intense space radiation beyond Earth's magnetosphere.
Ideas to improve radiation shielding range from passive methods, like using dense materials, to active concepts such as plasma fields that deflect radiation, while drugs are being developed to reduce cell damage.
Without a system to simulate gravity -- such as rotational spin -- crews would also need grueling exercise routines to counteract muscle and bone loss.
Mental health is another concern. Growing plants aboard -- more for morale than sustenance -- has proved beneficial on the ISS.
Communication delays further complicate matters.
On the station, real-time data has helped prevent an average of 1.7 potentially fatal incidents per year, said Erik Antonsen, chair of NASA's human systems risk board -- but such communication will not be possible en route to Mars.
- Life on Mars -
Once on the surface, the uncertainties grow.
Probes and rovers have found hints -- organic molecules, seasonal methane -- but no definitive signs of life. If it ever existed, it likely died out long ago.
Still, Earth's own "extremophiles" offer intriguing clues -- from fungi that harness Chernobyl's radiation for energy, to microbes that survived 500,000 years in frozen stasis.
"If they can survive here in extreme environments, we have every reason to suspect they can be on Mars," said NASA astrobiologist Jennifer Eigenbrode at the recent Humans to the Moon and Mars Summit.
And while NASA has decided nuclear fission will power surface operations, other choices -- from crop selection to habitat design -- remain open.
"Mars has a 24-hour, 39-minute day -- that small difference creates strain, increases stress, and reduces sleep quality," said Phnam Bagley, a space architect who designs for comfort and crew well-being -- critical factors in preventing conflict.
The first trip would be around 500 days on the surface, but long-term colonization raises deeper questions.
For instance, scientists don't yet know whether mammalian embryos can develop in low gravity -- or what childbirth on Mars would entail.
"I think it's really important to take that seriously," said NASA's Antonsen.
"Even if you don't plan on it happening, people are still going to have sex, and somebody might get pregnant. Then it becomes a medical issue."
W.Mansour--SF-PST


