
-
 Liverpool's Slot says 'no issue to resolve' with Salah after outburst
Liverpool's Slot says 'no issue to resolve' with Salah after outburst
-
'Stop the slaughter': French farmers block roads over cow disease cull

-
 Stormers see off La Rochelle, Sale stun Clermont in Champions Cup
Stormers see off La Rochelle, Sale stun Clermont in Champions Cup
-
Maresca hails Palmer as Chelsea return to winning ways against Everton

-
 Hungarian protesters demand Orban quits over abuse cases
Hungarian protesters demand Orban quits over abuse cases
-
Belarus frees protest leader Kolesnikova, Nobel winner Bialiatski

-
 Salah sets up goal on return to Liverpool action
Salah sets up goal on return to Liverpool action
-
Palmer strikes as Chelsea return to winning ways against Everton

-
 Pogacar targets Tour de France Paris-Roubaix and Milan-San Remo in 2026
Pogacar targets Tour de France Paris-Roubaix and Milan-San Remo in 2026
-
Salah back in action for Liverpool after outburst

-
 Atletico recover Liga momentum with battling win over Valencia
Atletico recover Liga momentum with battling win over Valencia
-
Meillard leads 'perfect' Swiss sweep in Val d'Isere giant slalom

-
 Salah on Liverpool bench for Brighton match
Salah on Liverpool bench for Brighton match
-
Meillard leads Swiss sweep in Val d'Isere giant slalom

-
 Indonesia flood death toll passes 1,000 as authorities ramp up aid
Indonesia flood death toll passes 1,000 as authorities ramp up aid
-
Cambodia shuts Thailand border crossings over deadly fighting

-
 First urban cable car unveiled outside Paris
First urban cable car unveiled outside Paris
-
Vonn second behind Aicher in World Cup downhill at St Moritz

-
 Aicher pips Vonn to downhill win at St Moritz
Aicher pips Vonn to downhill win at St Moritz
-
Thailand says 4 soldiers killed in Cambodia conflict, denies Trump truce claim

-
 Fans vandalise India stadium after Messi's abrupt exit
Fans vandalise India stadium after Messi's abrupt exit
-
Women sommeliers are cracking male-dominated wine world open

-
 Exhibition of Franco-Chinese print master Zao Wou-Ki opens in Hong Kong
Exhibition of Franco-Chinese print master Zao Wou-Ki opens in Hong Kong
-
Myanmar junta denies killing civilians in hospital strike

-
 Why SpaceX IPO plan is generating so much buzz
Why SpaceX IPO plan is generating so much buzz
-
Thailand continues Cambodia strikes despite Trump truce calls

-
 US envoy to meet Zelensky, Europe leaders in Berlin this weekend
US envoy to meet Zelensky, Europe leaders in Berlin this weekend
-
North Korea acknowledges its troops cleared mines for Russia

-
 US unseals warrant for tanker seized off Venezuelan coast
US unseals warrant for tanker seized off Venezuelan coast
-
Cambodia says Thailand still bombing hours after Trump truce call

-
 Machado urges pressure so Maduro understands 'he has to go'
Machado urges pressure so Maduro understands 'he has to go'
-
Leinster stutter before beating Leicester in Champions Cup

-
 World stocks mostly slide, consolidating Fed-fuelled gains
World stocks mostly slide, consolidating Fed-fuelled gains
-
Crypto firm Tether bids for Juventus, is quickly rebuffed

-
 Union sink second-placed Leipzig to climb in Bundesliga
Union sink second-placed Leipzig to climb in Bundesliga
-
US Treasury lifts sanctions on Brazil Supreme Court justice

-
 UK king shares 'good news' that cancer treatment will be reduced in 2026
UK king shares 'good news' that cancer treatment will be reduced in 2026
-
Wembanyama expected to return for Spurs in NBA Cup clash with Thunder

-
 Five takeaways from Luigi Mangione evidence hearings
Five takeaways from Luigi Mangione evidence hearings
-
UK's king shares 'good news' that cancer treatment will be reduced in 2026

-
 Steelers' Watt undergoes surgery to repair collapsed lung
Steelers' Watt undergoes surgery to repair collapsed lung
-
Iran detains Nobel-prize winner in 'brutal' arrest

-
 NBA Cup goes from 'outside the box' idea to smash hit
NBA Cup goes from 'outside the box' idea to smash hit
-
UK health service battles 'super flu' outbreak

-
 Can Venezuela survive US targeting its oil tankers?
Can Venezuela survive US targeting its oil tankers?
-
Democrats release new cache of Epstein photos

-
 Colombia's ELN guerrillas place communities in lockdown citing Trump 'intervention' threats
Colombia's ELN guerrillas place communities in lockdown citing Trump 'intervention' threats
-
'Don't use them': Tanning beds triple skin cancer risk, study finds
-
 Nancy aims to restore Celtic faith with Scottish League Cup final win
Nancy aims to restore Celtic faith with Scottish League Cup final win
-
Argentina fly-half Albornoz signs for Toulon until 2030


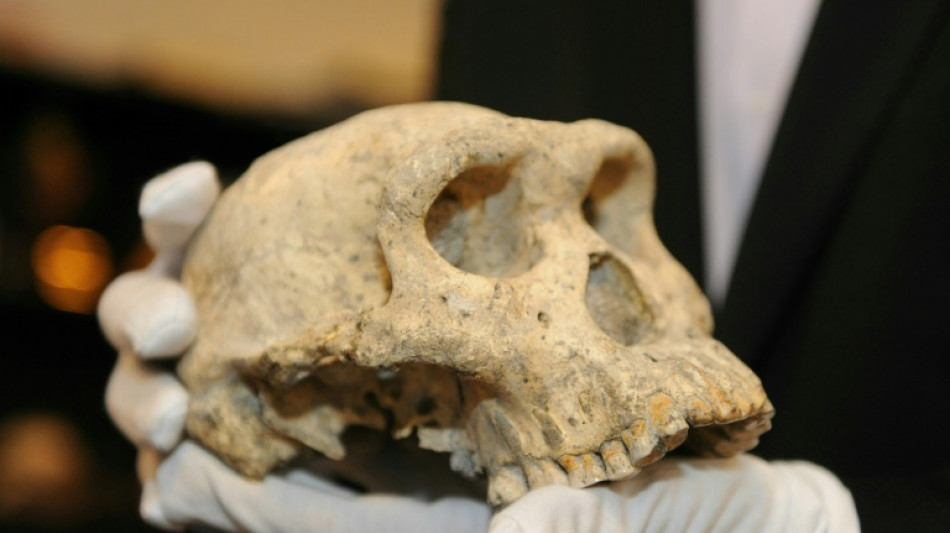
Meet 'Pink', the new face of human evolution in Europe
Western Europe has a new oldest face: the facial bones of an adult nicknamed "Pink" discovered in Spain are from a potential new member of the human family who lived more than 1.1 million years ago, scientists said Wednesday.
Until now, the oldest-known human species in Western Europe was the slender-faced Homo antecessor, dating back around 850,000 years.
But research published in the journal Nature "introduces a new actor in the history of human evolution in Europe", lead study author Rosa Huguet of Spain's University of Rovira i Virgili told a press conference.
The fossilised upper jawbone and partial cheekbone of Pink were discovered at the Atapuerca archaeological site in northern Spain in 2022.
Since then, a team of Spanish scientists have been working to find out more about Pink, whose nickname is a reference to prog rock band Pink Floyd.
The bones were excavated from a layer of silt and red mud 16 metres (52 feet) deep at a site known as Sima del Elefante -- or "elephant pit".
They were found less than 250 metres from where the fossils of Western Europe's previous oldest human, Homo antecessor, were discovered nearly two decades ago.
But the title of oldest human in all of Europe is still held by the Dmanisi people -- also called Homo georgicus -- who lived up to 1.8 million years ago in what is now Georgia.
They were the first members of the human family, or hominins, known to have made it to Europe from Africa, the cradle of humanity.
We modern Homo sapiens first showed up in Africa around 300,000 years ago -- and took our time getting to Europe.
- Face value -
The Spanish researchers used 3D imaging techniques to flesh out Pink's full face.
Homo antecessor had a "very modern" face which is "vertical and flat" similar to our own, said Maria Martinon-Torres, director of Spain's National Research Center on Human Evolution.
But Pink's face is more "projected forward and more robust," the study co-author added.
This means it bears some similarities to the face of Homo erectus -- but not enough that the scientists could confirm that Pink was a member of this important human ancestor.
So the scientists made up a new name for the possible species that Pink could belong to: Homo "affinis" erectus.
"This is the most honest proposal we can make with the evidence we have," Martinon-Torres said.
From just a few face bones, the researchers could not determine Pink's age or gender.
But by analysing small stone tools and animals bones found at the site, they were able to get an idea of the environment Pink lived in.
It was a humid forest landscape, roamed by horses, ancient cattle, monkeys and even some hippos.
The area was a wildlife corridor with plenty of water, making it an "ideal" place for our ancient relatives to settle, Huguet said.
- What happened to them? -
The new discovery supports the hypothesis that early humans settled Europe going from east to west at least 1.4 million years ago, according to the Spanish researchers.
If Pink is a representative of a previously unknown human species, it could have been a bridge between the Dmanisi hominins and Homo antecessors, they added.
But this raises another question: what became of these people?
Spanish paleoanthropologist Jose Maria Bermudez de Castro felt that Pink's people likely did not survive a severe human "bottleneck" nearly 900,000 years ago thought to have been caused by global cooling.
"I think that Homo affinis erectus probably disappeared," the study co-author said.
Future research will aim to shed light on these mysteries. The Spanish team has not yet reached the bottom of the elephant pit -- nor other sites around it.
Q.Najjar--SF-PST



