
-
 Carrick given Manchester derby baptism of fire, Frank in the firing line
Carrick given Manchester derby baptism of fire, Frank in the firing line
-
Trump announces 'board of peace' formed for Gaza

-
 Sam Darnold: the 'old soul' QB tipped to win Super Bowl
Sam Darnold: the 'old soul' QB tipped to win Super Bowl
-
One year on, it's all about Trump. But for how long?

-
 Australian snowboarder Brockhoff quits ahead of Winter Olympics
Australian snowboarder Brockhoff quits ahead of Winter Olympics
-
Bills battle Broncos as Allen eyes Super Bowl

-
 Magic rally to top Grizzlies in NBA Berlin game
Magic rally to top Grizzlies in NBA Berlin game
-
Venezuela's Machado says she 'presented' Trump with Nobel medal

-
 Key Colombia guerrilla group backs pact to fight US, commander tells AFP
Key Colombia guerrilla group backs pact to fight US, commander tells AFP
-
Chiefs' Mahomes targets NFL 'Week 1' after knee surgery

-
 Venezuelan interim leader vows oil sector reform after Maduro ouster
Venezuelan interim leader vows oil sector reform after Maduro ouster
-
Social media sites block 4.7 million underage accounts in Australia

-
 US court clears Norway's Equinor to resume wind project halted by Trump
US court clears Norway's Equinor to resume wind project halted by Trump
-
Threats to Iran spike 'volatility': UN official

-
 Rabiot and AC Milan give Como French lesson to stay on Inter's heels
Rabiot and AC Milan give Como French lesson to stay on Inter's heels
-
US says reached deal with Taiwan to lower tariffs, boost investments

-
 South Korea's ex-leader Yoon faces first court verdict over martial law chaos
South Korea's ex-leader Yoon faces first court verdict over martial law chaos
-
'Gigantic explosion', fire in Dutch city of Utrecht, four hurt

-
 Twenty-six charged in latest basketball gambling scandal
Twenty-six charged in latest basketball gambling scandal
-
Venezuela's Machado meets Trump for 'positive' talks despite snub
-
 NBA Europe 'must respect tradition', says commissioner Silver
NBA Europe 'must respect tradition', says commissioner Silver
-
Thieves steal Pokemon cards in armed robbery at US store

-
 French Olympic champion Papadakis claims she was under partner's 'control'
French Olympic champion Papadakis claims she was under partner's 'control'
-
Fury over Grok sexualized images despite new restrictions

-
 US says Iran halts executions as Gulf allies pull Trump back from strike
US says Iran halts executions as Gulf allies pull Trump back from strike
-
Frank says Spurs taking 'small steps' in right direction

-
 Syrian activist Sarah Mardini acquitted of migrant trafficking in Greece
Syrian activist Sarah Mardini acquitted of migrant trafficking in Greece
-
Goldman Sachs' profits jump on hot merger market

-
 Platini says Infantino has become 'more of an autocrat'
Platini says Infantino has become 'more of an autocrat'
-
Scottish Borders, Lake District to grace 2027 Tour de France

-
 Venezuela's sidelined Machado arrives at White House for Trump talks
Venezuela's sidelined Machado arrives at White House for Trump talks
-
French mother superior bullied nuns at Paris order: inquiry

-
 Cuba pays tribute to soldiers killed in Maduro capture
Cuba pays tribute to soldiers killed in Maduro capture
-
UK politician joins hard-right Reform just hours after Tories sack him

-
 'Gigantic explosion', fire in Dutch city, four hurt
'Gigantic explosion', fire in Dutch city, four hurt
-
French mother superior bullied nuns at Paris convent - inquiry

-
 Deprived of heating, Kyiv enters survival mode to beat big freeze
Deprived of heating, Kyiv enters survival mode to beat big freeze
-
Oil prices slump after Trump eases concerns over Iran

-
 French mother superior bullied nuns in Montmartre: report
French mother superior bullied nuns in Montmartre: report
-
Rosenior refuses to back Sanchez as Chelsea number one

-
 Harry due to testify to UK court next week in last tabloid case
Harry due to testify to UK court next week in last tabloid case
-
Trump threatens to invoke Insurrection Act over Minnesota protests

-
 Niger faces dilemma over uranium shipment stuck at airport
Niger faces dilemma over uranium shipment stuck at airport
-
UN chief attacks world leaders putting cooperation on 'deathwatch'

-
 Morocco and Senegal prepare for final showdown but Salah's AFCON dream fades
Morocco and Senegal prepare for final showdown but Salah's AFCON dream fades
-
Polls close in Uganda after delays, internet blackout

-
 Forced confession fears as Iran chief justice interrogates protesters
Forced confession fears as Iran chief justice interrogates protesters
-
Al-Attiyah closes on sixth Dakar Rally as Ekstrom wins 11th stage

-
 Luis Enrique has no doubts about PSG's title credentials
Luis Enrique has no doubts about PSG's title credentials
-
England off-spinner Bashir signs for Derbyshire after Ashes exile


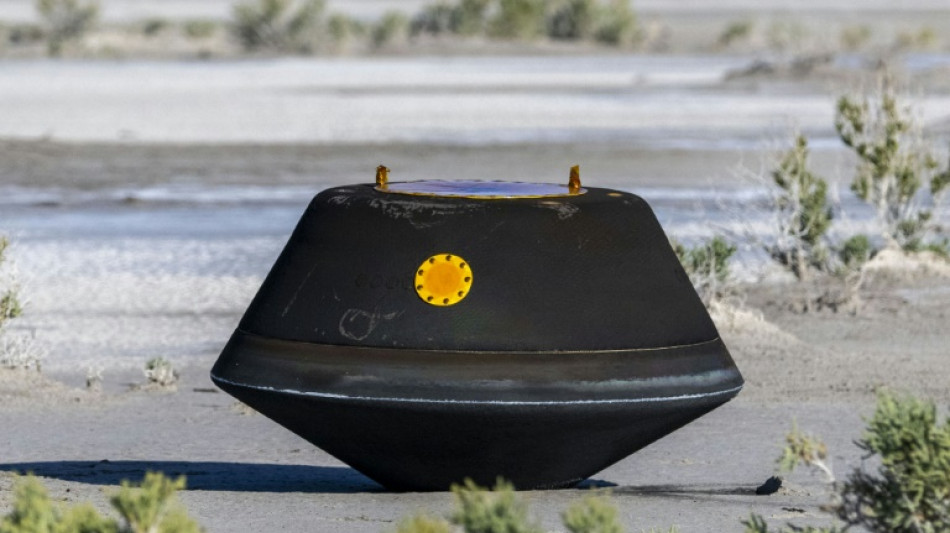
NASA asteroid sample contains life-critical water and carbon
A sample collected from the 4.5-billion-year-old asteroid Bennu contains abundant water and carbon, both vital materials for the formation of our planet, NASA revealed on Wednesday.
The finding offers yet more evidence for the theory that the foundations for life on Earth were seeded from outer space.
"The first analysis shows samples that contain abundant water in the form of hydrated clay minerals," Bill Nelson said in a press event.
"This is the biggest carbon rich asteroid sample ever returned to Earth," he said, with the carbon contained in the form of both minerals and organic molecules.
The OSIRIS-REx mission collected rock and dust from Bennu in 2020, and a capsule containing the precious cargo successfully returned to Earth a little over two weeks ago, landing in the Utah desert.
It is now being painstakingly analyzed in a specialized clean room at NASA's Johnson Space Center in Houston.
OSIRIS-REx wasn't the first mission to rendezvous with an asteroid and bring back samples for study -- Japan succeeded in the feat twice, returning bits of space pebbles in 2010 and 2020.
But the substantial amount of material -- an estimated 250 grams (half a pound) -- as opposed to the 5.4 grams returned by Japan's Hayabusa2 -- is a key difference.
NASA chose Bennu because they think similar asteroids could have delivered organic building blocks to Earth along with water through collisions billions of years ago.
Bennu's orbit, which intersects that of our planet, also made the roundtrip journey easier than going to the Asteroid Belt, which lies between Mars and Jupiter.
Researchers have so far focused their efforts not on the main sample itself but on "bonus particles," described as black dust and debris coating the sample collector.
Back in October 2020, when OSIRIS-REx probe shot nitrogen gas at Bennu to collect its sample, a flap meant to seal it got wedged open with a piece of rock, allowing some of the finer material to flow out of the collector without escaping altogether.
"The very best 'problem' to have is that there is so much material, it's taking longer than we expected to collect it," said deputy OSIRIS-REx curation lead Christopher Snead, in a statement.
An inspection of the remainder of the sample will follow later.
It's thought that Bennu formed from pieces of a larger asteroid in the asteroid belt, following a massive collision between one and two billion years ago.
Data gathered by the spacecraft revealed the particles making up its exterior were so loosely packed that if a person were to step onto the surface, they might sink in, much like stepping into a pit of plastic balls.
In addition to scientific insights, better understanding of Bennu's composition could prove useful if humanity ever needs to steer it away.
While it has no chance of hitting Earth through the mid 2100s, the chances rise to around 1 in 1750 between then and the year 2300, NASA says.
K.Hassan--SF-PST




