
-
 Bills battle Broncos as Allen eyes Super Bowl
Bills battle Broncos as Allen eyes Super Bowl
-
Magic rally to top Grizzlies in NBA Berlin game

-
 Venezuela's Machado says she 'presented' Trump with Nobel medal
Venezuela's Machado says she 'presented' Trump with Nobel medal
-
Key Colombia guerrilla group backs pact to fight US, commander tells AFP

-
 Chiefs' Mahomes targets NFL 'Week 1' after knee surgery
Chiefs' Mahomes targets NFL 'Week 1' after knee surgery
-
Venezuelan interim leader vows oil sector reform after Maduro ouster

-
 Social media sites block 4.7 million underage accounts in Australia
Social media sites block 4.7 million underage accounts in Australia
-
US court clears Norway's Equinor to resume wind project halted by Trump

-
 Threats to Iran spike 'volatility': UN official
Threats to Iran spike 'volatility': UN official
-
Rabiot and AC Milan give Como French lesson to stay on Inter's heels

-
 US says reached deal with Taiwan to lower tariffs, boost investments
US says reached deal with Taiwan to lower tariffs, boost investments
-
South Korea's ex-leader Yoon faces first court verdict over martial law chaos

-
 'Gigantic explosion', fire in Dutch city of Utrecht, four hurt
'Gigantic explosion', fire in Dutch city of Utrecht, four hurt
-
Twenty-six charged in latest basketball gambling scandal

-
 Venezuela's Machado meets Trump for 'positive' talks despite snub
Venezuela's Machado meets Trump for 'positive' talks despite snub
-
NBA Europe 'must respect tradition', says commissioner Silver

-
 Thieves steal Pokemon cards in armed robbery at US store
Thieves steal Pokemon cards in armed robbery at US store
-
French Olympic champion Papadakis claims she was under partner's 'control'

-
 Fury over Grok sexualized images despite new restrictions
Fury over Grok sexualized images despite new restrictions
-
US says Iran halts executions as Gulf allies pull Trump back from strike

-
 Frank says Spurs taking 'small steps' in right direction
Frank says Spurs taking 'small steps' in right direction
-
Syrian activist Sarah Mardini acquitted of migrant trafficking in Greece

-
 Goldman Sachs' profits jump on hot merger market
Goldman Sachs' profits jump on hot merger market
-
Platini says Infantino has become 'more of an autocrat'

-
 Scottish Borders, Lake District to grace 2027 Tour de France
Scottish Borders, Lake District to grace 2027 Tour de France
-
Venezuela's sidelined Machado arrives at White House for Trump talks

-
 French mother superior bullied nuns at Paris order: inquiry
French mother superior bullied nuns at Paris order: inquiry
-
Cuba pays tribute to soldiers killed in Maduro capture

-
 UK politician joins hard-right Reform just hours after Tories sack him
UK politician joins hard-right Reform just hours after Tories sack him
-
'Gigantic explosion', fire in Dutch city, four hurt

-
 French mother superior bullied nuns at Paris convent - inquiry
French mother superior bullied nuns at Paris convent - inquiry
-
Deprived of heating, Kyiv enters survival mode to beat big freeze

-
 Oil prices slump after Trump eases concerns over Iran
Oil prices slump after Trump eases concerns over Iran
-
French mother superior bullied nuns in Montmartre: report

-
 Rosenior refuses to back Sanchez as Chelsea number one
Rosenior refuses to back Sanchez as Chelsea number one
-
Harry due to testify to UK court next week in last tabloid case

-
 Trump threatens to invoke Insurrection Act over Minnesota protests
Trump threatens to invoke Insurrection Act over Minnesota protests
-
Niger faces dilemma over uranium shipment stuck at airport

-
 UN chief attacks world leaders putting cooperation on 'deathwatch'
UN chief attacks world leaders putting cooperation on 'deathwatch'
-
Morocco and Senegal prepare for final showdown but Salah's AFCON dream fades

-
 Polls close in Uganda after delays, internet blackout
Polls close in Uganda after delays, internet blackout
-
Forced confession fears as Iran chief justice interrogates protesters

-
 Al-Attiyah closes on sixth Dakar Rally as Ekstrom wins 11th stage
Al-Attiyah closes on sixth Dakar Rally as Ekstrom wins 11th stage
-
Luis Enrique has no doubts about PSG's title credentials

-
 England off-spinner Bashir signs for Derbyshire after Ashes exile
England off-spinner Bashir signs for Derbyshire after Ashes exile
-
Trump convinced 'to give Iran a chance' after threats over protest crackdown

-
 European military mission in Greenland as US aim 'remains intact'
European military mission in Greenland as US aim 'remains intact'
-
UK's Hockney warns moving Bayeux Tapestry would be 'madness'

-
 Senior UK opposition politican sacked over 'plot' to join hard-right party
Senior UK opposition politican sacked over 'plot' to join hard-right party
-
Syrians flee Kurdish-controlled area near Aleppo


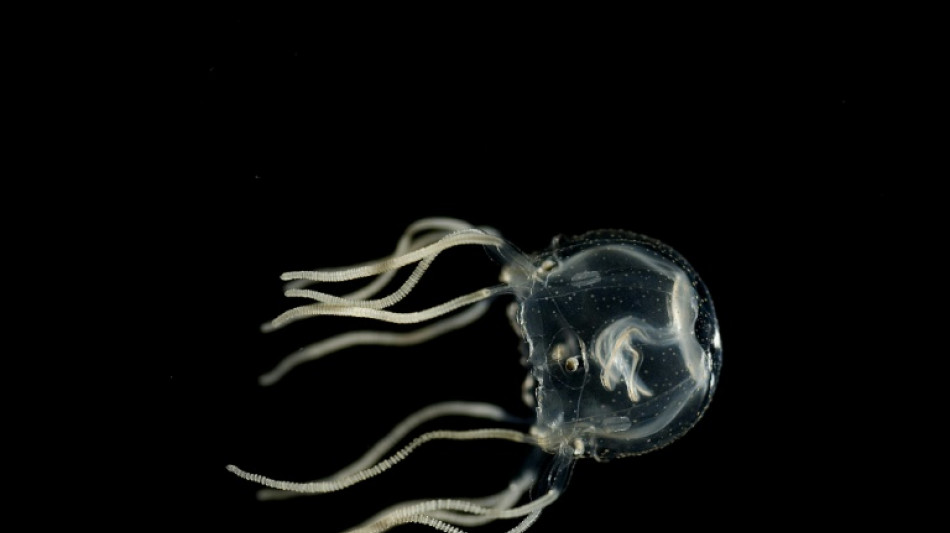
No brain, no problem: Tiny jellyfish can learn from experience
Caribbean box jellyfish are barely a centimetre long and have no brain.
But these gelatinous, fingernail-sized creatures are capable of learning from visual cues to avoid swimming into obstacles -- a cognitive ability never before seen in animals with such a primitive nervous system, researchers said on Friday.
Their performance of what is called "associative learning" is comparable to far more advanced animals such as fruit flies or mice, which have the notable benefit of having a brain, the researchers said.
The Caribbean box jellyfish, or Tripedalia cystophora, is known to be able to navigate through murky water and a maze of submerged mangrove roots.
These scenarios throw up plenty of dangers that could damage the jellyfish's fragile gelatinous membrane which envelops its bell-shaped body.
But they avoid harm thanks to four visual sensory centres called rhopalia, each of which has lens-shaped eyes and around a thousand neurons.
For comparison, fruit flies are packing 200,000 neurons in their tiny brains.
Cnidarians -- the animal group which includes jellyfish, sea anemones and coral -- are brainless, instead getting by with a "dispersed" central nervous system.
Despite this considerable disadvantage, the Caribbean box jellyfish responds to what is called "operant conditioning," according to the study in the journal Current Biology.
This means they can be trained to "predict a future problem and try to avoid it," said Anders Garm, a marine biologist at the University of Copenhagen and the study's lead author.
Garm told AFP that this capacity is "more complex than classical conditioning," which is best known for Russian neurologist Ivan Pavlov's experiments showing that dogs cannot help but salivate when they see their food bowl.
- 'Very intriguing' -
To test the jellyfish, the researchers put them in a small, water-filled tank with stripes of varying darkness on the glass walls to represent mangrove roots.
After a few bumps into the walls, the jellyfish quickly learned to move through the parts of the enclosures where the bars were least visible.
If the bars were made more prominent, the jellyfish never hit the walls, remaining safely in the centre of the tank. However this was not ideal for scrounging around for food.
If the stripes were removed entirely, the jellyfish constantly ran into the walls of the tank.
"If you separate the two stimuli, there is no learning," Garm concluded.
The jellyfish learned their lesson in between three to six tries, "which is basically the same amount of trials for what we would normally consider an advanced animal, like a fruit fly, a crab or even a mouse," he said.
They said their research supports the theory that even animals with a very small number of neurons are capable of learning.
That such a simple organism is able to achieve this feat "points to the very intriguing fact that this may be a fundamental property of nerve systems," Garm said.
Cnidarians are a "sister group" to the animal group that includes most other animals -- including humans.
Garm suggested that some 500 million years ago, a common ancestor of the two groups could have developed a nervous system that was already able to learn by association.
N.Awad--SF-PST




