
-
 Floods, landslides kill at least 30 in India's Jammu region
Floods, landslides kill at least 30 in India's Jammu region
-
Former player comes out as bisexual in Australian Rules first

-
 Indian spin great Ashwin calls time on IPL career
Indian spin great Ashwin calls time on IPL career
-
India faces world football ban for second time in three years

-
 Globetrotter Herzog to get special Venice award
Globetrotter Herzog to get special Venice award
-
'Old things work': Argentines giving new life to e-waste

-
 Showtime for Venice Film Festival, with monsters, aliens, Clooney and Roberts
Showtime for Venice Film Festival, with monsters, aliens, Clooney and Roberts
-
Thai woman jailed for 43 years for lese-majeste freed
-
 What is swatting? Shooting hoaxes target campuses across US
What is swatting? Shooting hoaxes target campuses across US
-
Row over Bosnia's Jewish treasure raising funds for Gaza

-
 Police search Australian bush for gunman after two officers killed
Police search Australian bush for gunman after two officers killed
-
NZ rugby player who suffered multiple concussions dies aged 39

-
 Former Australian Rules player comes out as bisexual in first
Former Australian Rules player comes out as bisexual in first
-
French, German, Polish leaders to visit Moldova in show of force in face of Russia

-
 US tariffs on Indian goods double to 50% over Russian oil purchases
US tariffs on Indian goods double to 50% over Russian oil purchases
-
Feudal warlord statue beheaded in Japan

-
 Tokyo logs record 10 days of 35C or more
Tokyo logs record 10 days of 35C or more
-
Sinner, Swiatek romp through at US Open as Gauff struggles

-
 Brazil to face South Korea, Japan in World Cup build-up
Brazil to face South Korea, Japan in World Cup build-up
-
Asian markets diverge with eyes on Nvidia earnings

-
 Osaka out to recapture sparkle at US Open
Osaka out to recapture sparkle at US Open
-
China's rulers push party role before WWII anniversary

-
 Pakistan's monsoon misery: nature's fury, man's mistake
Pakistan's monsoon misery: nature's fury, man's mistake
-
SpaceX answers critics with successful Starship test flight

-
 Nightlife falls silent as Ecuador's narco gangs take charge
Nightlife falls silent as Ecuador's narco gangs take charge
-
Unnamed skeletons? US museum at center of ethical debate

-
 France returns skull of beheaded king to Madagascar
France returns skull of beheaded king to Madagascar
-
SpaceX's Starship megarocket launches on latest test flight

-
 US restaurant chain Cracker Barrel cracks, revives old logo
US restaurant chain Cracker Barrel cracks, revives old logo
-
Brazil's Bolsonaro placed under 24-hour watch ahead of coup trial verdict

-
 Taylor-Travis love story: 5 things to know
Taylor-Travis love story: 5 things to know
-
Sports world congratulates Swift and Kelce on engagement

-
 Wolves inflict more woe on West Ham, Leeds crash out League Cup
Wolves inflict more woe on West Ham, Leeds crash out League Cup
-
Venezuela deploys warships, drones as US destroyers draw near

-
 French political turmoil sends European stocks down, Wall Street edges up
French political turmoil sends European stocks down, Wall Street edges up
-
Sinner, Swiatek romp through at US Open

-
 Meta to back pro-AI candidates in California
Meta to back pro-AI candidates in California
-
Yankees-Giants set for earliest US MLB opener in 2026 schedule

-
 Messi will be game-day decision for Miami in Leagues Cup semis
Messi will be game-day decision for Miami in Leagues Cup semis
-
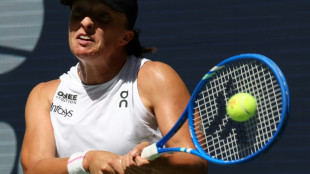
'Swiftie' Swiatek swats Arango, talks Taylor & Travis engagement
-
 New era: Taylor Swift and Travis Kelce announce engagement
New era: Taylor Swift and Travis Kelce announce engagement
-
SpaceX set once more for Starship test flight

-
 Sinner begins US Open defence with quick win
Sinner begins US Open defence with quick win
-
Who is Lisa Cook, the Fed governor Trump seeks to fire?

-
 Masters updates qualifying criteria to add six national opens
Masters updates qualifying criteria to add six national opens
-
New era unlocked: Taylor Swift and Travis Kelce announce engagement

-
 Israeli protesters demand hostage deal as cabinet meets
Israeli protesters demand hostage deal as cabinet meets
-
Trump to seek death penalty for murders in US capital

-
 Taylor Swift and Travis Kelce announce engagement
Taylor Swift and Travis Kelce announce engagement
-
Swiatek swats Arango, Sinner launches US Open defence


Oceans feel the heat from human climate pollution
Oceans have absorbed the vast majority of the warming caused by burning fossil fuels and shielded societies from the full impact of greenhouse gas emissions.
But this crucial ally has developed alarming symptoms of stress -- heatwaves, loss of marine life, rising sea levels, falling oxygen levels and acidification caused by the uptake of excess carbon dioxide.
These effects risk not just the health of the ocean but the entire planet.
- Heating up -
By absorbing more than 90 percent of the excess heat trapped in the atmosphere by greenhouse gases, "oceans are warming faster and faster", said Angelique Melet, an oceanographer at the European Mercator Ocean monitor.
The UN's IPCC climate expert panel has said the rate of ocean warming -- and therefore its heat uptake -- has more than doubled since 1993.
Average sea surface temperatures reached new records in 2023 and 2024.
Despite a respite at the start of 2025, temperatures remain at historic highs, according to data from the Europe Union's Copernicus climate monitor.
The Mediterranean has set a new temperature record in each of the past three years and is one of the basins most affected, along with the North Atlantic and Arctic oceans, said Thibault Guinaldo, of France's CEMS research centre.
Marine heatwaves have doubled in frequency, become longer lasting and more intense, and affect a wider area, the IPCC said in its special oceans report.
Warmer seas can make storms more violent, feeding them with heat and evaporated water.
The heating water can also be devastating for species, especially corals and seagrass beds, which are unable to migrate.
For corals, between 70 percent and 90 percent are expected to be lost this century if the world reaches 1.5 degrees Celsius (2.7 degrees Fahrenheit) of warming compared to pre-industrial levels.
Scientists expect that threshold -- the more ambitious goal of the Paris climate deal -- to be breached in the early 2030s or even before.
- Relentless rise -
When a liquid or gas warms up, it expands and takes up more space.
In the case of the oceans, this thermal expansion combines with the slow but irreversible melting of the world's ice caps and mountain glaciers to lift the world's seas.
The pace at which global oceans are rising has doubled in three decades and if current trends continue it will double again by 2100 to about one centimetre per year, according to recent research.
Around 230 million people worldwide live less than a metre above sea level, vulnerable to increasing threats from floods and storms.
"Ocean warming, like sea-level rise, has become an inescapable process on the scale of our lives, but also over several centuries," said Melet.
"But if we reduce greenhouse gas emissions, we will reduce the rate and magnitude of the damage, and gain time for adaptation".
- More acidity, less oxygen -
The ocean not only stores heat, it has also taken up 20 to 30 percent of all humans' carbon dioxide emissions since the 1980s, according to the IPCC, causing the waters to become more acidic.
Acidification weakens corals and makes it harder for shellfish and the skeletons of crustaceans and certain plankton to calcify.
"Another key indicator is oxygen concentration, which is obviously important for marine life," said Melet.
Oxygen loss is due to a complex set of causes including those linked to warming waters.
- Reduced sea ice -
Combined Arctic and Antarctic sea ice cover -- frozen ocean water that floats on the surface -- plunged to a record low in mid-February, more than a million square miles below the pre-2010 average.
This becomes a vicious circle, with less sea ice allowing more solar energy to reach and warm the water, leading to more ice melting.
This feeds the phenomenon of "polar amplification" that makes global warming faster and more intense at the poles, said Guinaldo.
D.Qudsi--SF-PST
