
-
 Iran says US talks are on, as Trump warns supreme leader
Iran says US talks are on, as Trump warns supreme leader
-
Gaza health officials say strikes kill 24 after Israel says officer wounded

-
 Empress's crown dropped in Louvre heist to be fully restored: museum
Empress's crown dropped in Louvre heist to be fully restored: museum
-
UK PM says Mandelson 'lied' about Epstein relations

-
 Shai to miss NBA All-Star Game with abdominal strain
Shai to miss NBA All-Star Game with abdominal strain
-
Trump suggests 'softer touch' needed on immigration

-
 From 'flop' to Super Bowl favorite: Sam Darnold's second act
From 'flop' to Super Bowl favorite: Sam Darnold's second act
-
Man sentenced to life in prison for plotting to kill Trump in 2024

-
 Native Americans on high alert over Minneapolis crackdown
Native Americans on high alert over Minneapolis crackdown
-
Dallas deals Davis to Wizards in blockbuster NBA deal: report

-
 Russia 'no longer bound' by nuclear arms limits as treaty with US ends
Russia 'no longer bound' by nuclear arms limits as treaty with US ends
-
Panama hits back after China warns of 'heavy price' in ports row

-
 Strike kills guerrillas as US, Colombia agree to target narco bosses
Strike kills guerrillas as US, Colombia agree to target narco bosses
-
Wildfire smoke kills more than 24,000 Americans a year: study

-
 Telegram founder slams Spain PM over under-16s social media ban
Telegram founder slams Spain PM over under-16s social media ban
-
Curling kicks off sports programme at 2026 Winter Olympics

-
 Preventative cholera vaccination resumes as global supply swells: WHO
Preventative cholera vaccination resumes as global supply swells: WHO
-
Wales' Macleod ready for 'physical battle' against England in Six Nations

-
 Xi calls for 'mutual respect' with Trump, hails ties with Putin
Xi calls for 'mutual respect' with Trump, hails ties with Putin
-
'All-time great': Maye's ambitions go beyond record Super Bowl bid

-
 Shadow over Vonn as Shiffrin, Odermatt headline Olympic skiing
Shadow over Vonn as Shiffrin, Odermatt headline Olympic skiing
-
US seeks minerals trade zone in rare Trump move with allies

-
 Ukraine says Abu Dhabi talks with Russia 'substantive and productive'
Ukraine says Abu Dhabi talks with Russia 'substantive and productive'
-
Brazil mine disaster victims in London to 'demand what is owed'

-
 AI-fuelled tech stock selloff rolls on
AI-fuelled tech stock selloff rolls on
-
Russia vows to act 'responsibly' as nuclear pact ends with US

-
 White says time at Toulon has made him a better Scotland player
White says time at Toulon has made him a better Scotland player
-
Washington Post announces 'painful' job cuts

-
 All lights are go for Jalibert, says France's Dupont
All lights are go for Jalibert, says France's Dupont
-
Artist rubs out Meloni church fresco after controversy

-
 Palestinians in Egypt torn on return to a Gaza with 'no future'
Palestinians in Egypt torn on return to a Gaza with 'no future'
-
US removing 700 immigration officers from Minnesota

-
 Who is behind the killing of late ruler Gaddafi's son, and why now?
Who is behind the killing of late ruler Gaddafi's son, and why now?
-
Coach Thioune tasked with saving battling Bremen

-
 Russia vows to act 'responsibly' once nuclear pact with US ends
Russia vows to act 'responsibly' once nuclear pact with US ends
-
Son of Norway's crown princess admits excesses but denies rape

-
 US calls for minerals trade zone in rare move with allies
US calls for minerals trade zone in rare move with allies
-
Vowles dismisses Williams 2026 title hopes as 'not realistic'

-
 'Dinosaur' Glenn chasing skating gold in first Olympics
'Dinosaur' Glenn chasing skating gold in first Olympics
-
Gaza health officials say strikes kill 23 after Israel says shots wounded officer

-
 Italy foils Russian cyberattacks targeting Olympics
Italy foils Russian cyberattacks targeting Olympics
-
Stocks stabilise after Wall St AI-fuelled sell-off

-
 Figure skating favourite Malinin feeling 'the pressure' in Milan
Figure skating favourite Malinin feeling 'the pressure' in Milan
-
Netflix film probes conviction of UK baby killer nurse

-
 Timber hopes League Cup can be catalyst for Arsenal success
Timber hopes League Cup can be catalyst for Arsenal success
-
China calls EU 'discriminatory' over probe into energy giant Goldwind

-
 Sales warning slams Ozempic maker Novo Nordisk's stock
Sales warning slams Ozempic maker Novo Nordisk's stock
-
Can Vonn defy ACL rupture to win Olympic medal?

-
 Breakthrough or prelude to attack? What we know about Iran-US talks
Breakthrough or prelude to attack? What we know about Iran-US talks
-
German far-right MP detained over alleged Belarus sanctions breach


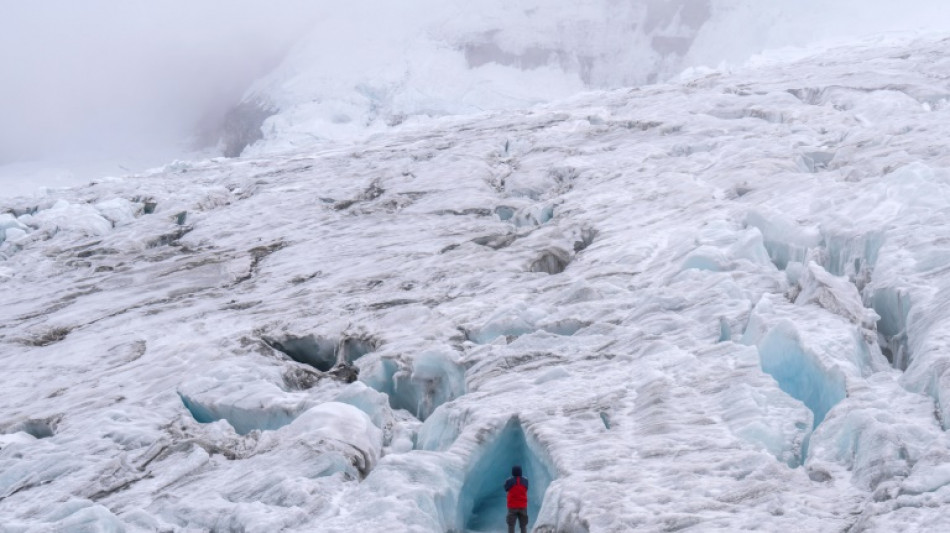
Climate action could save half of world's vanishing glaciers, says study
More than three-quarters of the world's glaciers are set to vanish if climate change continues unchecked, a major new study warned Thursday, fueling sea-level rise and jeopardizing water supplies for billions.
Published in Science, the international analysis provides the clearest picture yet of long-term glacier loss, revealing that every fraction of a degree in global temperature rise significantly worsens the outlook.
It may sound grim, but co-lead author Harry Zekollari, a glaciologist at Vrije Universiteit Brussel and ETH Zurich, told AFP the findings should be seen as a "message of hope."
Under existing climate policies, global temperatures are projected to reach 2.7 degrees Celsius (4.9F) above pre-industrial levels by 2100 -- a pathway that would ultimately erase 76 percent of current glacier mass over the coming centuries.
But if warming is held to the Paris Agreement's 1.5C target, 54 percent of glacial mass could be preserved, according to the study, which combined outputs from eight glacier models to simulate ice loss across a range of future climate scenarios.
"What is really special about this study is we can really show how every tenth of a degree of additional warming matters," co-lead author Lilian Schuster of the University of Innsbruck told AFP.
The paper's release comes as Swiss authorities monitor flood risks following the collapse of the massive Birch Glacier, which destroyed an evacuated village.
While Swiss glaciers have been heavily impacted by climate change, it remains unclear how much the latest disaster was driven by warming versus natural geological forces.
- Cultural and economic importance -
Glaciers are found on every continent except Australia -- from Mount Kilimanjaro to the Austrian Alps and the Karakoram range in Pakistan.
While most are clustered in the polar regions, their presence in mountain ranges across the world makes them vital to local ecosystems, agriculture and human communities.
Vast bodies of snow, ice, rock, and sediment that gain mass in winter and lose it in summer, glaciers formed in the Earth's deep past when conditions were far colder than today.
Their meltwater sustains rivers critical for farming, fisheries, and drinking water.
Their loss can have profound ripple effects, from disrupting tourism economies to eroding cultural heritage.
In recent years, symbolic glacier funerals have been held in Iceland, Switzerland and Mexico.
"The question I always get is, why are you a glaciologist in Belgium?" said Zekollari. "Well -- sea level rise. Glaciers melt everywhere on Earth... and that affects coastal defenses even in places far from mountains."
Around 25 percent of current sea-level rise is attributed to glacier melt.
Even if all fossil fuel use stopped today, the study finds that 39 percent of glacier mass loss is already locked in -- enough to raise sea levels by at least 113 millimeters (4.4 inches).
- Uneven impacts -
One key finding of the study is that some glaciers are far more vulnerable than others -- and the global average obscures drastic regional losses.
Glaciers in the European Alps, the Rockies of the US and Canada, and Iceland are expected to lose nearly all their ice at 2C of warming -- the fallback goal of the Paris accord.
In the central and eastern Himalayas, whose rivers support hundreds of millions of people, only 25 percent of glacier ice would remain at 2C.
By contrast, the west of the range may retain 60 percent of its ice at the same temperature thanks to its wide range of elevations, which allows some glaciers to persist at colder, higher altitudes, said Shuster.
Glacier loss is already affecting communities.
In a related commentary in Science, Cymene Howe and Dominic Boyer of Rice University describe how the retreat of Oregon's Glisan Glacier has imperiled orchards, fisheries, and the cultural heritage of the Indigenous Quinault people.
"Unfortunately we'll lose a lot, but with ambitious targets we can still save many of these glaciers -- which are not only beautiful, but vital for water supply, sea-level regulation, tourism, hydroelectricity, spiritual values, ecology, and more," said Zekollari.
N.Shalabi--SF-PST


