
-
 US households become increasingly strained in diverging economy
US households become increasingly strained in diverging economy
-
Four dead men: the cold case that engulfed a Colombian cycling star

-
 Super Bowl stars stake claims for Olympic flag football
Super Bowl stars stake claims for Olympic flag football
-
On a roll, Brazilian cinema seizes its moment

-
 Rising euro, falling inflation in focus at ECB meeting
Rising euro, falling inflation in focus at ECB meeting
-
AI to track icebergs adrift at sea in boon for science

-
 Indigenous Brazilians protest Amazon river dredging for grain exports
Indigenous Brazilians protest Amazon river dredging for grain exports
-
Google's annual revenue tops $400 bn for first time, AI investments rise

-
 Last US-Russia nuclear treaty ends in 'grave moment' for world
Last US-Russia nuclear treaty ends in 'grave moment' for world
-
Man City brush aside Newcastle to reach League Cup final

-
 Guardiola wants permission for Guehi to play in League Cup final
Guardiola wants permission for Guehi to play in League Cup final
-
Boxer Khelif reveals 'hormone treatments' before Paris Olympics

-
 'Bad Boy,' 'Little Pablo' and Mordisco: the men on a US-Colombia hitlist
'Bad Boy,' 'Little Pablo' and Mordisco: the men on a US-Colombia hitlist
-
BHP damages trial over Brazil mine disaster to open in 2027

-
 Dallas deals Davis to Wizards in blockbuster NBA trade: report
Dallas deals Davis to Wizards in blockbuster NBA trade: report
-
Iran-US talks back on, as Trump warns supreme leader

-
 Lens cruise into French Cup quarters, Endrick sends Lyon through
Lens cruise into French Cup quarters, Endrick sends Lyon through
-
No.1 Scheffler excited for Koepka return from LIV Golf

-
 Curling quietly kicks off sports programme at 2026 Winter Olympics
Curling quietly kicks off sports programme at 2026 Winter Olympics
-
Undav pokes Stuttgart past Kiel into German Cup semis

-
 Germany goalkeeper Ter Stegen to undergo surgery
Germany goalkeeper Ter Stegen to undergo surgery
-
Bezos-led Washington Post announces 'painful' job cuts

-
 Iran says US talks are on, as Trump warns supreme leader
Iran says US talks are on, as Trump warns supreme leader
-
Gaza health officials say strikes kill 24 after Israel says officer wounded

-
 Empress's crown dropped in Louvre heist to be fully restored: museum
Empress's crown dropped in Louvre heist to be fully restored: museum
-
UK PM says Mandelson 'lied' about Epstein relations

-
 Shai to miss NBA All-Star Game with abdominal strain
Shai to miss NBA All-Star Game with abdominal strain
-
Trump suggests 'softer touch' needed on immigration

-
 From 'flop' to Super Bowl favorite: Sam Darnold's second act
From 'flop' to Super Bowl favorite: Sam Darnold's second act
-
Man sentenced to life in prison for plotting to kill Trump in 2024

-
 Native Americans on high alert over Minneapolis crackdown
Native Americans on high alert over Minneapolis crackdown
-
Dallas deals Davis to Wizards in blockbuster NBA deal: report

-
 Russia 'no longer bound' by nuclear arms limits as treaty with US ends
Russia 'no longer bound' by nuclear arms limits as treaty with US ends
-
Panama hits back after China warns of 'heavy price' in ports row

-
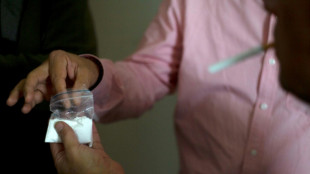 Strike kills guerrillas as US, Colombia agree to target narco bosses
Strike kills guerrillas as US, Colombia agree to target narco bosses
-
Wildfire smoke kills more than 24,000 Americans a year: study

-
 Telegram founder slams Spain PM over under-16s social media ban
Telegram founder slams Spain PM over under-16s social media ban
-
Curling kicks off sports programme at 2026 Winter Olympics

-
 Preventative cholera vaccination resumes as global supply swells: WHO
Preventative cholera vaccination resumes as global supply swells: WHO
-
Wales' Macleod ready for 'physical battle' against England in Six Nations

-
 Xi calls for 'mutual respect' with Trump, hails ties with Putin
Xi calls for 'mutual respect' with Trump, hails ties with Putin
-
'All-time great': Maye's ambitions go beyond record Super Bowl bid

-
 Shadow over Vonn as Shiffrin, Odermatt headline Olympic skiing
Shadow over Vonn as Shiffrin, Odermatt headline Olympic skiing
-
US seeks minerals trade zone in rare Trump move with allies

-
 Ukraine says Abu Dhabi talks with Russia 'substantive and productive'
Ukraine says Abu Dhabi talks with Russia 'substantive and productive'
-
Brazil mine disaster victims in London to 'demand what is owed'

-
 AI-fuelled tech stock selloff rolls on
AI-fuelled tech stock selloff rolls on
-
Russia vows to act 'responsibly' as nuclear pact ends with US

-
 White says time at Toulon has made him a better Scotland player
White says time at Toulon has made him a better Scotland player
-
Washington Post announces 'painful' job cuts


Clouds changing as world warms, adding to climate uncertainty
People have always studied the skies to predict the weather, but recently scientists have noticed that clouds are changing on a global scale -- posing one of the greatest challenges to understanding our warming world.
Some clouds are rising higher into the atmosphere, where they trap more heat. Others are reflecting less sunlight, or shrinking and allowing more solar energy to reach Earth's surface.
Scientists know this is affecting the climate, because the vital role that clouds play in warming and cooling the planet is well understood.
Recent research has shown that clouds -- or rather, a lack of them -- helped drive a stunning surge in record-breaking global heat over the last two years.
What is less certain is how clouds might evolve as the world warms. Will they have a dampening effect on global warming, or amplify it? And if so, by how much?
"That's why clouds are the greatest challenge. Figuring them out is -- and has been -- the big roadblock," said Bjorn Stevens from the Max Planck Institute for Meteorology in Germany, who has written extensively on the subject.
Cloud behaviour is notoriously complex to predict and remains a great unknown for scientists trying to accurately forecast future levels of climate change.
Changes in clouds could mean that, even with the same amount of heat-trapping greenhouse gas emissions, "we could get much more warming or much less warming", said Robin Hogan, principal scientist at the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts.
"That's a big scientific uncertainty," he told AFP.
With satellites and supercomputers, scientists are improving cloud modelling and slowly filling in the missing pieces of the puzzle.
- Vicious cycle -
Part of the difficulty is that clouds are not uniform -- they act differently depending on their type, structure and altitude.
Fluffy, low-hanging clouds generally have a cooling influence. They are big and bright, blocking and bouncing back incoming sunlight.
Higher, streaky ones have a warming effect, letting sunlight trickle through and absorbing heat reflected back from Earth.
In recent decades, scientists have observed a growing imbalance between the amount of energy arriving, rather than leaving Earth, hinting at cloud changes.
As the climate has warmed, certain clouds have drifted higher into the atmosphere where they have a stronger greenhouse effect, said Hogan.
"That actually amplifies the warming," he said.
This is growing evidence that lower clouds are also changing, with recent studies pointing to a marked decline of this cooling layer.
Less reflective cloud exposes more of Earth's surface to sunlight and boosts warming in a "vicious feedback cycle", said climate scientist Richard Allan from the University of Reading.
In March, Allan co-authored a study in the journal Environmental Research Letters that found dimmer and less extensive low-lying clouds drove a doubling of Earth's energy balance in the past 20 years, and contributed to record ocean warmth in 2023.
A study in December, published in the journal Science, also identified a sharp drop in low-lying cloudiness as a likely culprit for that exceptional warming.
Stevens said scientists generally agreed that Earth had become less cloudy -- but there are a number of theories about the causes.
"Clouds are changing. And the question is how much of that change is natural variability -- just decadal fluctuations in cloudiness -- and how much of that is forced from the warming," he said.
- No smoking gun -
Another theory is that decades-long global efforts to improve air quality are altering the formation, properties and lifespan of clouds in ways that are not yet fully understood.
Clouds form around aerosols -- tiny airborne particles like desert dust and sea salt carried on the wind, or pollution from human activity like burning fossil fuels.
Aerosols not only help clouds take shape, but can make them more reflective.
Recent research has suggested that clean air policies -- particularly a global shift to low-sulphur shipping fuel in 2020 -- reduced cloud cover and brightness, inadvertently pushing up warming.
Allan said aerosols were one factor, but it was likely lower clouds were also "melting away" as the climate warmed.
"My feeling is there's a combination of things. It's never one simple smoking gun," he said.
New tools are chipping away at the uncertainty.
Last May, European and Japanese space agencies launched EarthCARE, a revolutionary satellite capable of capturing unprecedented detail of inner cloud workings.
In orbit it joins PACE -- a cutting-edge NASA satellite also studying aerosols, clouds and climate -- that lifted off just three months earlier.
Other recent innovations, including in machine learning, were helping "bridge the gap" in cloud understanding, said Kara Lamb, a research scientist and aerosols expert at Columbia University.
"We are seeing progress over time," she told AFP.
E.Qaddoumi--SF-PST

