
-
 Japan's Kimura soars to Olympic gold in snowboard big air final
Japan's Kimura soars to Olympic gold in snowboard big air final
-
Vail's golden comets Vonn and Shiffrin inspire those who follow

-
 Veteran French politician loses culture post over Epstein links
Veteran French politician loses culture post over Epstein links
-
Japan's Kimura wins Olympic snowboard big air gold

-
 Arteta backs confident Gyokeres to hit 'highest level'
Arteta backs confident Gyokeres to hit 'highest level'
-
Hojlund the hero as Napoli snatch late win at Genoa

-
 England's Arundell 'frustrated' despite hat-trick in Wales romp
England's Arundell 'frustrated' despite hat-trick in Wales romp
-
Lollobrigida skates to first Italian gold of Winter Olympics on her birthday

-
 Arundell hat-trick inspires England thrashing of Wales in Six Nations opener
Arundell hat-trick inspires England thrashing of Wales in Six Nations opener
-
Chile's climate summit chief to lead plastic pollution treaty talks

-
 Rosenior hails 'unstoppable' Palmer after treble tames Wolves
Rosenior hails 'unstoppable' Palmer after treble tames Wolves
-
French ex-minister offers resignation from Paris cultural hub over Epstein links

-
 New NBA dunk contest champ assured and shooting stars return
New NBA dunk contest champ assured and shooting stars return
-
Shiffrin says will use lessons learnt from Beijing flop at 2026 Games

-
 Takaichi tipped for big win as Japan votes
Takaichi tipped for big win as Japan votes
-
Lens return top of Ligue 1 with win over Rennes

-
 Shiffrin learning from Beijing lessons ahead of Milan-Cortina bow
Shiffrin learning from Beijing lessons ahead of Milan-Cortina bow
-
Demonstrators in Berlin call for fall of Iran's Islamic republic

-
 'Free the mountains!": clashes at Milan protest over Winter Olympics
'Free the mountains!": clashes at Milan protest over Winter Olympics
-
Townsend accepts pressure will mount on him after Italy defeat

-
 BMW iX3 new style and design
BMW iX3 new style and design
-
Suryakumar's 84 leads India to opening win over USA in T20 World Cup

-
 Lollobrigida skates to first Italian gold of Milan-Cortina Games
Lollobrigida skates to first Italian gold of Milan-Cortina Games
-
Barca beat Mallorca to extend Liga lead

-
 Gyokeres lifts Arsenal nine clear as Man Utd pile pressure on Frank
Gyokeres lifts Arsenal nine clear as Man Utd pile pressure on Frank
-
Late Guirassy winner for Dortmund trims Bayern's lead atop Bundesliga

-
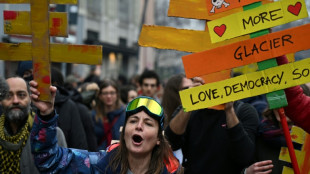 'Free the mountains!": protest in Milan over Winter Olympics
'Free the mountains!": protest in Milan over Winter Olympics
-
Gyokeres double helps Arsenal stretch Premier League lead

-
 New Skoda Epiq: modern with range
New Skoda Epiq: modern with range
-
Six Nations misery for Townsend as Italy beat sorry Scotland

-
 Spain, Portugal face fresh storms, torrential rain
Spain, Portugal face fresh storms, torrential rain
-
Opinions of Zuckerberg hang over social media addiction trial jury selection

-
 Over 2,200 IS detainees transferred to Iraq from Syria: Iraqi official
Over 2,200 IS detainees transferred to Iraq from Syria: Iraqi official
-
Norway's Ruud tops Olympic men's freeski slopestyle qualifying

-
 Czech qualifier Bejlek claims first title in Abu Dhabi
Czech qualifier Bejlek claims first title in Abu Dhabi
-
French duo reach Shanghai, completing year-and-a-half walk

-
 Australian snowboarder James eyes elusive Olympic gold
Australian snowboarder James eyes elusive Olympic gold
-
Sequins and snow: Eva Adamczykova makes Olympic return

-
 Vonn set for Olympic medal bid after successful downhill training
Vonn set for Olympic medal bid after successful downhill training
-
Shepherd takes hat-trick as West Indies beat Scotland in T20 World Cup

-
 Sausages will sell after thrill-seeker Von Allmen wins Olympic downhill
Sausages will sell after thrill-seeker Von Allmen wins Olympic downhill
-
Swiss racer Von Allmen wins first gold of Winter Olympics

-
 'Wake up': Mum sparks comeback after scare for freeski star Gu
'Wake up': Mum sparks comeback after scare for freeski star Gu
-
Von Allmen wins men's Olympic downhill gold, first of Games

-
 First medals up for grabs at Winter Olympics
First medals up for grabs at Winter Olympics
-
Afghanistan captain Khan harbours dream of playing in Kabul

-
 Lindsey Vonn completes second Winter Olympics downhill training run
Lindsey Vonn completes second Winter Olympics downhill training run
-
Freeski star Gu survives major scare in Olympic slopestyle

-
 Iran FM looks to more nuclear talks, but warns US
Iran FM looks to more nuclear talks, but warns US
-
Hetmyer's six-hitting steers West Indies to 182-5 against Scotland


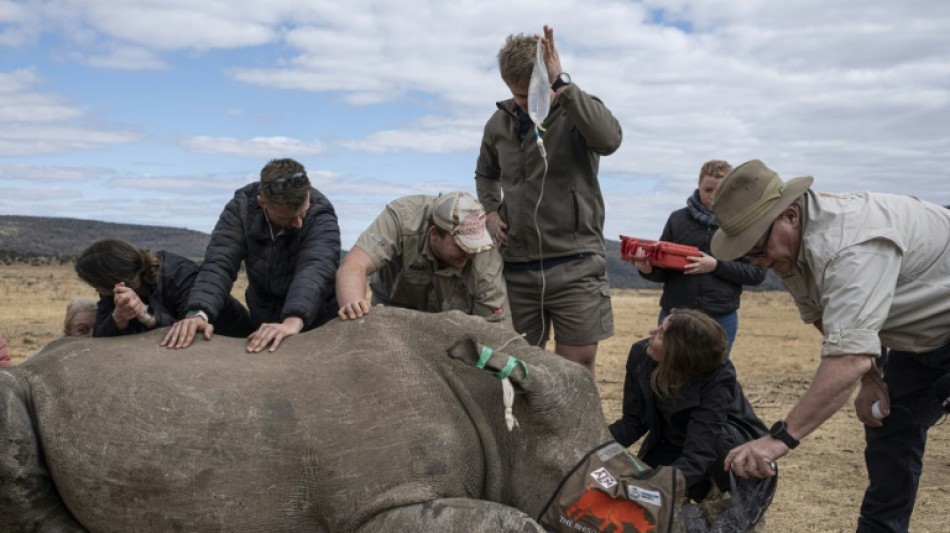
First radioactive rhino horns to curb poaching in S.Africa
South African scientists on Tuesday injected radioactive material into live rhino horns to make them easier to detect at border posts in a pioneering project aimed at curbing poaching.
The country is home to a large majority of the world's rhinos and as such is a hotspot for poaching driven by demand from Asia, where horns are used in traditional medicine for their supposed therapeutic effect.
At the Limpopo rhino orphanage in the Waterberg area, in the country's northeast, a few of the thick-skinned herbivores grazed in the low savannah.
James Larkin, director of the University of the Witwatersrand's radiation and health physics unit who spearheaded the initiative, told AFP he had put "two tiny little radioactive chips in the horn" as he administered the radioisotopes on one of the large animals' horns.
The radioactive material would "render the horn useless... essentially poisonous for human consumption" added Nithaya Chetty, professor and dean of science at the same university.
The dusty rhino, put to sleep and crouched on the ground, did not feel any pain, Larkin said.
The radioactive material's dose was so low it would not impact the animal's health or the environment in any way, he said.
In February the environment ministry said that, despite government efforts to tackle the illicit trade, 499 of the giant mammals were killed in 2023, mostly in state-run parks. This represents an 11 percent increase over the 2022 figures.
Twenty live rhinos in total would be part of the pilot Rhisotope project whereby they would be administered a dose "strong enough to set off detectors that are installed globally" at international border posts originally installed "to prevent nuclear terrorism", a pleased Larkin said, sporting a green hat and a khaki shirt.
Border agents often have handheld radiation detectors which can detect contraband in addition to thousands of radiation detectors installed at ports and airports, the scientists said.
-'Best idea'-
Rhino horns are highly sought after on black markets, where the price by weight rivals that of gold and cocaine.
According to Arrie Van Deventer, the orphanage's founder, dehorning the rhino and poisoning the horns have failed to deter poachers.
"Maybe this is the thing that will stop poaching", the tall, slim-built conservationist said. "This is the best idea I've ever heard".
Wildebeest, warthogs and giraffe roamed the vast conservation area as more than a dozen team members performed the delicate process on another rhino.
Larkin meticulously drilled a small hole into the horn, hammered in the radioisotope, then finished off by spraying 11,000 microdots all over the horn.
About 15,000 rhinos live in the southern African nation, according to an estimate by the international Rhino foundation.
The last phase of the project would be the animal's aftercare following "proper scientific protocol and ethical protocol", said the project's COO, a bubbly Jessica Babich.
The team would then take follow-up blood samples to ensure the rhinos were effectively protected.
The material would last five years on the horn, which was cheaper than dehorning every 18 months, Larkin said.
R.AbuNasser--SF-PST




