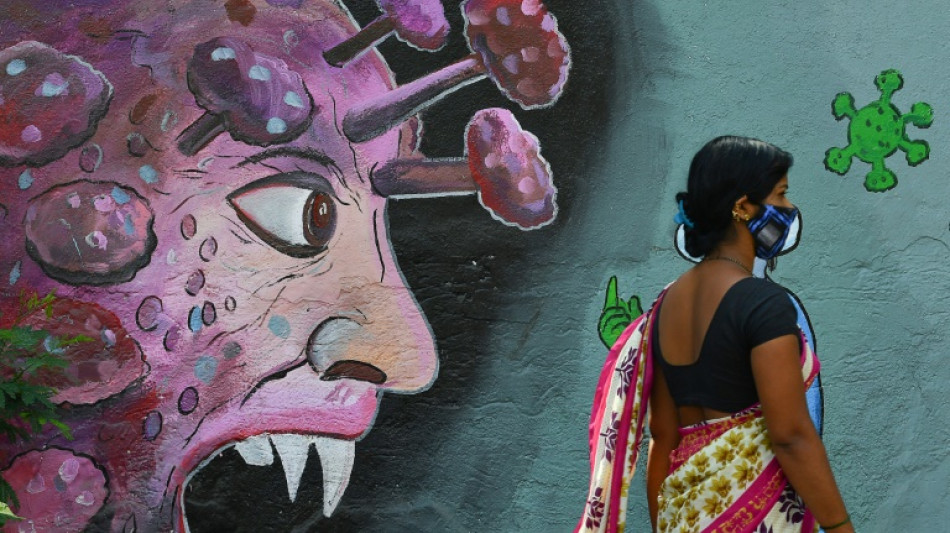
-
 Voter swings raise midterm alarm bells for Trump's Republicans
Voter swings raise midterm alarm bells for Trump's Republicans
-
Australia dodges call for arrest of visiting Israel president

-
 Countries using internet blackouts to boost censorship: Proton
Countries using internet blackouts to boost censorship: Proton
-
Top US news anchor pleads with kidnappers for mom's life

-
 Thailand's pilot PM on course to keep top job
Thailand's pilot PM on course to keep top job
-
The coming end of ISS, symbol of an era of global cooperation

-
 New crew set to launch for ISS after medical evacuation
New crew set to launch for ISS after medical evacuation
-
Family affair: Thailand waning dynasty still election kingmaker

-
 Japan's first woman PM tipped for thumping election win
Japan's first woman PM tipped for thumping election win
-
Stocks in retreat as traders reconsider tech investment

-
 LA officials call for Olympic chief to resign over Epstein file emails
LA officials call for Olympic chief to resign over Epstein file emails
-
Ukraine, Russia, US to start second day of war talks

-
 Fiji football legend returns home to captain first pro club
Fiji football legend returns home to captain first pro club
-
Trump attacks US electoral system with call to 'nationalize' voting

-
 Barry Manilow cancels Las Vegas shows but 'doing great' post-surgery
Barry Manilow cancels Las Vegas shows but 'doing great' post-surgery
-
US households become increasingly strained in diverging economy

-
 Four dead men: the cold case that engulfed a Colombian cycling star
Four dead men: the cold case that engulfed a Colombian cycling star
-
Super Bowl stars stake claims for Olympic flag football

-
 On a roll, Brazilian cinema seizes its moment
On a roll, Brazilian cinema seizes its moment
-
Rising euro, falling inflation in focus at ECB meeting

-
 AI to track icebergs adrift at sea in boon for science
AI to track icebergs adrift at sea in boon for science
-
Indigenous Brazilians protest Amazon river dredging for grain exports

-
 Google's annual revenue tops $400 bn for first time, AI investments rise
Google's annual revenue tops $400 bn for first time, AI investments rise
-
Last US-Russia nuclear treaty ends in 'grave moment' for world

-
 Man City brush aside Newcastle to reach League Cup final
Man City brush aside Newcastle to reach League Cup final
-
Guardiola wants permission for Guehi to play in League Cup final

-
 Boxer Khelif reveals 'hormone treatments' before Paris Olympics
Boxer Khelif reveals 'hormone treatments' before Paris Olympics
-
'Bad Boy,' 'Little Pablo' and Mordisco: the men on a US-Colombia hitlist

-
 BHP damages trial over Brazil mine disaster to open in 2027
BHP damages trial over Brazil mine disaster to open in 2027
-
Dallas deals Davis to Wizards in blockbuster NBA trade: report

-
 Iran-US talks back on, as Trump warns supreme leader
Iran-US talks back on, as Trump warns supreme leader
-
Lens cruise into French Cup quarters, Endrick sends Lyon through

-
 No.1 Scheffler excited for Koepka return from LIV Golf
No.1 Scheffler excited for Koepka return from LIV Golf
-
Curling quietly kicks off sports programme at 2026 Winter Olympics

-
 Undav pokes Stuttgart past Kiel into German Cup semis
Undav pokes Stuttgart past Kiel into German Cup semis
-
Germany goalkeeper Ter Stegen to undergo surgery

-
 Bezos-led Washington Post announces 'painful' job cuts
Bezos-led Washington Post announces 'painful' job cuts
-
Iran says US talks are on, as Trump warns supreme leader

-
 Gaza health officials say strikes kill 24 after Israel says officer wounded
Gaza health officials say strikes kill 24 after Israel says officer wounded
-
Empress's crown dropped in Louvre heist to be fully restored: museum

-
 UK PM says Mandelson 'lied' about Epstein relations
UK PM says Mandelson 'lied' about Epstein relations
-
Shai to miss NBA All-Star Game with abdominal strain

-
 Trump suggests 'softer touch' needed on immigration
Trump suggests 'softer touch' needed on immigration
-
From 'flop' to Super Bowl favorite: Sam Darnold's second act

-
 Man sentenced to life in prison for plotting to kill Trump in 2024
Man sentenced to life in prison for plotting to kill Trump in 2024
-
Native Americans on high alert over Minneapolis crackdown

-
 Dallas deals Davis to Wizards in blockbuster NBA deal: report
Dallas deals Davis to Wizards in blockbuster NBA deal: report
-
Russia 'no longer bound' by nuclear arms limits as treaty with US ends

-
 Panama hits back after China warns of 'heavy price' in ports row
Panama hits back after China warns of 'heavy price' in ports row
-
Strike kills guerrillas as US, Colombia agree to target narco bosses
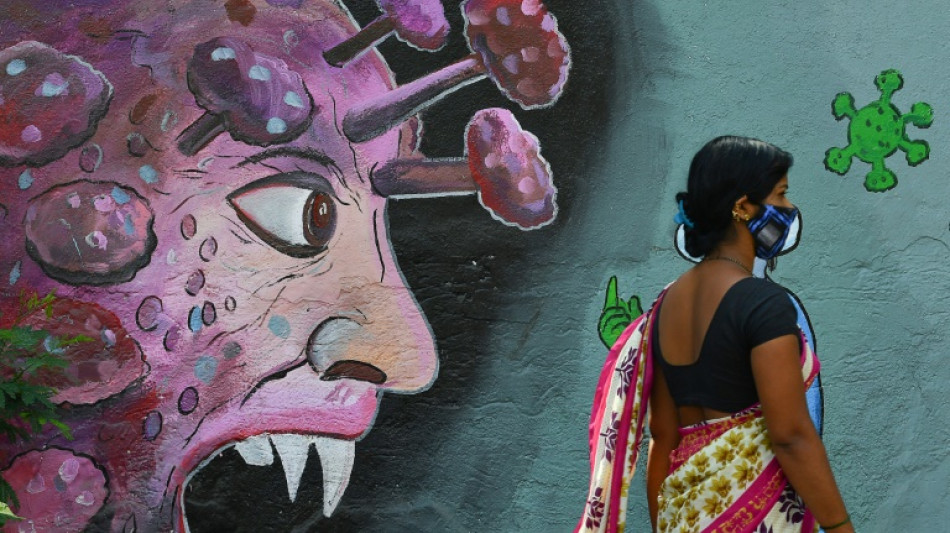
Long Covid remains a mystery, though theories are emerging
Millions of people around the world are believed to suffer from long Covid yet little remains known about the condition -- though research has recently proposed several theories for its cause.
Between 10 to 20 percent of people who contract coronavirus are estimated to have long Covid symptoms -- most commonly fatigue, breathlessness and a lack of mental clarity dubbed brain fog -- months after recovering from the disease.
The US-based Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME) estimates that nearly 145 million people worldwide had at least one of those symptoms in 2020 and 2021.
In Europe alone, 17 million people had a long Covid symptom at least three months after infection during that time, according to IHME modelling for the World Health Organization (WHO) published earlier this month.
These millions "cannot continue to suffer in silence", WHO Europe director Hans Kluge said, calling for the world to act quickly to learn more about the condition.
Researchers have been racing to catch up but the vast array -- and inconsistency -- of symptoms has complicated matters.
More than 200 different symptoms have been ascribed to long Covid so far, according to a University College London study.
- 'Fatigue in the background' -
"There are no symptoms that are truly specific to long Covid but it does have certain characteristics that fluctuate," said Olivier Robineau, the long Covid coordinator at France's Emerging Infectious Diseases research agency.
"Fatigue remains in the background," he told AFP, while the symptoms "seem to be exacerbated after intellectual or physical effort -- and they become less frequent over time".
One thing we do know is that people who had more severe initial cases, including needing to be hospitalised, are more likely to get long Covid, according to the IHME.
Researchers have been pursuing several leads into exactly what could be behind the condition.
A study published in the journal Clinical Infectious Diseases in September found that Covid's infamous spike protein --- the key that lets the virus into the body's cells -- was still present in patients a full year after infection.
This suggests that viral reservoirs may persist in some people, potentially causing inflammation that could lead to long Covid-like symptoms, the researchers said.
If they are right, a test could be developed to identify the spike, potentially leading to one of the great and elusive goals of long Covid research -- a clear way to diagnose the condition.
However, their findings have not been confirmed by other research, and several other causes have been proposed.
- 'Data not very solid yet' -
One leading theory is that tissue damage from severe Covid cases triggers lasting disruption to the immune system.
Another suggests that the initial infection causes tiny blood clots, which could be related to long Covid symptoms.
However "for each of these hypotheses, the data is not very solid yet", Robineau said.
It is most likely that "we are not going to find a single cause to explain long Covid", he added.
"The causes may not be exclusive. They could be linked or even succeed each other in the same individual, or be different in different individuals."
A way to treat the condition also remains elusive.
For the last year, the Hotel-Dieu hospital in Paris has been offering long Covid patients a half-day treatment course.
"They meet an infectious disease specialist, a psychiatrist, then a doctor specialising in sports rehabilitation," said Brigitte Ranque, who runs the protocol dubbed CASPER.
"In the team's experience, a majority of the symptoms can be attributed to functional somatic syndromes," she said. These are a group of chronic disorders such as chronic fatigue and fibromyalgia that have no known cause.
Cognitive behavioural therapy, a psychological approach often used for those syndromes, is used to treat long Covid alongside supervised physical activity, Ranque said.
"The patients are brought back in three months later. The majority of them are better. More than half say they are cured," she told AFP.
"But about 15 percent did not improve at all."
H.Darwish--SF-PST




