
-
 US households become increasingly strained in diverging economy
US households become increasingly strained in diverging economy
-
Four dead men: the cold case that engulfed a Colombian cycling star

-
 Super Bowl stars stake claims for Olympic flag football
Super Bowl stars stake claims for Olympic flag football
-
On a roll, Brazilian cinema seizes its moment

-
 Rising euro, falling inflation in focus at ECB meeting
Rising euro, falling inflation in focus at ECB meeting
-
AI to track icebergs adrift at sea in boon for science

-
 Indigenous Brazilians protest Amazon river dredging for grain exports
Indigenous Brazilians protest Amazon river dredging for grain exports
-
Google's annual revenue tops $400 bn for first time, AI investments rise

-
 Last US-Russia nuclear treaty ends in 'grave moment' for world
Last US-Russia nuclear treaty ends in 'grave moment' for world
-
Man City brush aside Newcastle to reach League Cup final

-
 Guardiola wants permission for Guehi to play in League Cup final
Guardiola wants permission for Guehi to play in League Cup final
-
Boxer Khelif reveals 'hormone treatments' before Paris Olympics

-
 'Bad Boy,' 'Little Pablo' and Mordisco: the men on a US-Colombia hitlist
'Bad Boy,' 'Little Pablo' and Mordisco: the men on a US-Colombia hitlist
-
BHP damages trial over Brazil mine disaster to open in 2027

-
 Dallas deals Davis to Wizards in blockbuster NBA trade: report
Dallas deals Davis to Wizards in blockbuster NBA trade: report
-
Iran-US talks back on, as Trump warns supreme leader

-
 Lens cruise into French Cup quarters, Endrick sends Lyon through
Lens cruise into French Cup quarters, Endrick sends Lyon through
-
No.1 Scheffler excited for Koepka return from LIV Golf

-
 Curling quietly kicks off sports programme at 2026 Winter Olympics
Curling quietly kicks off sports programme at 2026 Winter Olympics
-
Undav pokes Stuttgart past Kiel into German Cup semis

-
 Germany goalkeeper Ter Stegen to undergo surgery
Germany goalkeeper Ter Stegen to undergo surgery
-
Bezos-led Washington Post announces 'painful' job cuts

-
 Iran says US talks are on, as Trump warns supreme leader
Iran says US talks are on, as Trump warns supreme leader
-
Gaza health officials say strikes kill 24 after Israel says officer wounded

-
 Empress's crown dropped in Louvre heist to be fully restored: museum
Empress's crown dropped in Louvre heist to be fully restored: museum
-
UK PM says Mandelson 'lied' about Epstein relations

-
 Shai to miss NBA All-Star Game with abdominal strain
Shai to miss NBA All-Star Game with abdominal strain
-
Trump suggests 'softer touch' needed on immigration

-
 From 'flop' to Super Bowl favorite: Sam Darnold's second act
From 'flop' to Super Bowl favorite: Sam Darnold's second act
-
Man sentenced to life in prison for plotting to kill Trump in 2024

-
 Native Americans on high alert over Minneapolis crackdown
Native Americans on high alert over Minneapolis crackdown
-
Dallas deals Davis to Wizards in blockbuster NBA deal: report

-
 Russia 'no longer bound' by nuclear arms limits as treaty with US ends
Russia 'no longer bound' by nuclear arms limits as treaty with US ends
-
Panama hits back after China warns of 'heavy price' in ports row

-
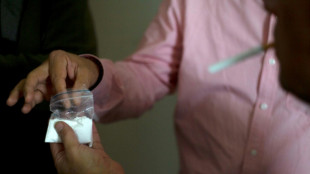 Strike kills guerrillas as US, Colombia agree to target narco bosses
Strike kills guerrillas as US, Colombia agree to target narco bosses
-
Wildfire smoke kills more than 24,000 Americans a year: study

-
 Telegram founder slams Spain PM over under-16s social media ban
Telegram founder slams Spain PM over under-16s social media ban
-
Curling kicks off sports programme at 2026 Winter Olympics

-
 Preventative cholera vaccination resumes as global supply swells: WHO
Preventative cholera vaccination resumes as global supply swells: WHO
-
Wales' Macleod ready for 'physical battle' against England in Six Nations

-
 Xi calls for 'mutual respect' with Trump, hails ties with Putin
Xi calls for 'mutual respect' with Trump, hails ties with Putin
-
'All-time great': Maye's ambitions go beyond record Super Bowl bid

-
 Shadow over Vonn as Shiffrin, Odermatt headline Olympic skiing
Shadow over Vonn as Shiffrin, Odermatt headline Olympic skiing
-
US seeks minerals trade zone in rare Trump move with allies

-
 Ukraine says Abu Dhabi talks with Russia 'substantive and productive'
Ukraine says Abu Dhabi talks with Russia 'substantive and productive'
-
Brazil mine disaster victims in London to 'demand what is owed'

-
 AI-fuelled tech stock selloff rolls on
AI-fuelled tech stock selloff rolls on
-
Russia vows to act 'responsibly' as nuclear pact ends with US

-
 White says time at Toulon has made him a better Scotland player
White says time at Toulon has made him a better Scotland player
-
Washington Post announces 'painful' job cuts


WHO pushes two Ebola treatments found to boost survival rates
The World Health Organization said Friday that two existing treatments dramatically reduced deaths from Ebola and should be given to people of all ages suffering from the often-fatal haemorrhagic disease.
Publishing its first-ever guidelines on which therapeutics to use against Ebola, the UN health agency strongly recommended using two monoclonal antibodies, mAb114, also known as Ansuvimab or Ebanga, and REGN-EB3, or Inmazeb.
Studies had showed that the two treatments significantly "reduced mortality," Janet Diaz, lead of the clinical management unit in the WHO's Health Emergencies programme, told reporters in Geneva.
Depending on the standard of care, she said they could save between 230 and 400 lives for every 1,000 people infected.
In its guidelines, the WHO recommended against using other therapeutics that have been tested for Ebola, including monoclonal antibody ZMapp and antiviral drug remdesivir.
Ebola is an often-fatal viral haemorrhagic fever that was first identified in central Africa in 1976. The disease was named after a river in the Democratic Republic of Congo, then known as Zaire.
The worst epidemic in West Africa between 2013 and 2016 killed more than 11,300 people. The DRC has had more than a dozen epidemics, the deadliest killing 2,280 people in 2020.
Case fatality rates for the disease, which spreads through bodily fluids and causes high fever, vomiting and bleeding, can be as high as 80-90 percent, depending on how quickly it is detected and treated.
The WHO said mAb114 and REGN-EB3 should be given swiftly to anyone who contracts the virus.
In a statement the health agency said that the two had "demonstrated clear benefits" and could be used for everyone infected by Ebola, including older people, pregnant and breastfeeding women, children and newborns.
"Patients should receive recommended neutralising monoclonal antibodies as soon as possible after laboratory confirmation of diagnosis," it said.
The WHO cautioned though that access to both the treatments remained "challenging, especially in resource-poor areas."
"WHO is ready to support countries, manufacturers and partners to improve access to these treatments, and to support national and global efforts to increase affordability," the UN health agency said.
Robert Fowler of the University of Toronto, who co-chaired the guideline development group, hailed how "advances in supportive care and therapeutics over the past decade have revolutionised the treatment of Ebola."
"Ebola virus disease used to be perceived as a near certain killer. However, that is no longer the case," he said in the statement.
Combined with proper support, the two recommended treatments mean "recovery for the vast majority of people," he said.
L.Hussein--SF-PST



