
-
 US households become increasingly strained in diverging economy
US households become increasingly strained in diverging economy
-
Four dead men: the cold case that engulfed a Colombian cycling star

-
 Super Bowl stars stake claims for Olympic flag football
Super Bowl stars stake claims for Olympic flag football
-
On a roll, Brazilian cinema seizes its moment

-
 Rising euro, falling inflation in focus at ECB meeting
Rising euro, falling inflation in focus at ECB meeting
-
AI to track icebergs adrift at sea in boon for science

-
 Indigenous Brazilians protest Amazon river dredging for grain exports
Indigenous Brazilians protest Amazon river dredging for grain exports
-
Google's annual revenue tops $400 bn for first time, AI investments rise

-
 Last US-Russia nuclear treaty ends in 'grave moment' for world
Last US-Russia nuclear treaty ends in 'grave moment' for world
-
Man City brush aside Newcastle to reach League Cup final

-
 Guardiola wants permission for Guehi to play in League Cup final
Guardiola wants permission for Guehi to play in League Cup final
-
Boxer Khelif reveals 'hormone treatments' before Paris Olympics

-
 'Bad Boy,' 'Little Pablo' and Mordisco: the men on a US-Colombia hitlist
'Bad Boy,' 'Little Pablo' and Mordisco: the men on a US-Colombia hitlist
-
BHP damages trial over Brazil mine disaster to open in 2027

-
 Dallas deals Davis to Wizards in blockbuster NBA trade: report
Dallas deals Davis to Wizards in blockbuster NBA trade: report
-
Iran-US talks back on, as Trump warns supreme leader

-
 Lens cruise into French Cup quarters, Endrick sends Lyon through
Lens cruise into French Cup quarters, Endrick sends Lyon through
-
No.1 Scheffler excited for Koepka return from LIV Golf

-
 Curling quietly kicks off sports programme at 2026 Winter Olympics
Curling quietly kicks off sports programme at 2026 Winter Olympics
-
Undav pokes Stuttgart past Kiel into German Cup semis

-
 Germany goalkeeper Ter Stegen to undergo surgery
Germany goalkeeper Ter Stegen to undergo surgery
-
Bezos-led Washington Post announces 'painful' job cuts

-
 Iran says US talks are on, as Trump warns supreme leader
Iran says US talks are on, as Trump warns supreme leader
-
Gaza health officials say strikes kill 24 after Israel says officer wounded

-
 Empress's crown dropped in Louvre heist to be fully restored: museum
Empress's crown dropped in Louvre heist to be fully restored: museum
-
UK PM says Mandelson 'lied' about Epstein relations

-
 Shai to miss NBA All-Star Game with abdominal strain
Shai to miss NBA All-Star Game with abdominal strain
-
Trump suggests 'softer touch' needed on immigration

-
 From 'flop' to Super Bowl favorite: Sam Darnold's second act
From 'flop' to Super Bowl favorite: Sam Darnold's second act
-
Man sentenced to life in prison for plotting to kill Trump in 2024

-
 Native Americans on high alert over Minneapolis crackdown
Native Americans on high alert over Minneapolis crackdown
-
Dallas deals Davis to Wizards in blockbuster NBA deal: report

-
 Russia 'no longer bound' by nuclear arms limits as treaty with US ends
Russia 'no longer bound' by nuclear arms limits as treaty with US ends
-
Panama hits back after China warns of 'heavy price' in ports row

-
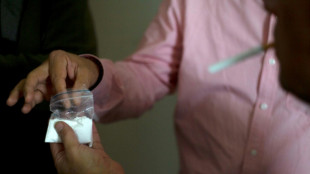 Strike kills guerrillas as US, Colombia agree to target narco bosses
Strike kills guerrillas as US, Colombia agree to target narco bosses
-
Wildfire smoke kills more than 24,000 Americans a year: study

-
 Telegram founder slams Spain PM over under-16s social media ban
Telegram founder slams Spain PM over under-16s social media ban
-
Curling kicks off sports programme at 2026 Winter Olympics

-
 Preventative cholera vaccination resumes as global supply swells: WHO
Preventative cholera vaccination resumes as global supply swells: WHO
-
Wales' Macleod ready for 'physical battle' against England in Six Nations

-
 Xi calls for 'mutual respect' with Trump, hails ties with Putin
Xi calls for 'mutual respect' with Trump, hails ties with Putin
-
'All-time great': Maye's ambitions go beyond record Super Bowl bid

-
 Shadow over Vonn as Shiffrin, Odermatt headline Olympic skiing
Shadow over Vonn as Shiffrin, Odermatt headline Olympic skiing
-
US seeks minerals trade zone in rare Trump move with allies

-
 Ukraine says Abu Dhabi talks with Russia 'substantive and productive'
Ukraine says Abu Dhabi talks with Russia 'substantive and productive'
-
Brazil mine disaster victims in London to 'demand what is owed'

-
 AI-fuelled tech stock selloff rolls on
AI-fuelled tech stock selloff rolls on
-
Russia vows to act 'responsibly' as nuclear pact ends with US

-
 White says time at Toulon has made him a better Scotland player
White says time at Toulon has made him a better Scotland player
-
Washington Post announces 'painful' job cuts


Climate deniers use past heat records to sow doubt online
With Europe gripped by successive heatwaves, climate-change deniers are spreading scepticism by publishing data on social media on extreme temperatures allegedly recorded decades ago to imply scientists are exaggerating global warming.
But experts say the figures cited from the past are often incorrect or taken out of context -- and even if accurate do not change the fact that heatwaves are becoming more frequent and intense.
The posts typically include heat records from almanacs or newspaper reports from the past, arguing that they are similar to the record highs set during this year's heatwaves in Europe.
One post that has gone viral on Facebook includes a screen grab of a brief article published in the New York Times on June 23, 1935, which said the mercury had hit 127 degrees Fahrenheit (52.7 degrees Celsius) in Zaragoza, in northeastern Spain, the day before.
That temperature is much higher than the record for the highest temperature in Spain of 47.6 degrees Celsius recorded on August 14, 2021 by national weather office Aemet at the La Rambla meteorological station in the southern province of Cordoba.
Contacted by AFP Fact Check, Aemet spokesman Ruben del Campo said the highest temperature recorded in Zaragoza that day in 1935 was just 39 degrees Celsius.
"The figure of over 52 degrees in incorrect. It is not a figure that is in our climate database, and in fact, there is no log of a temperature above 50 degrees Celsius," he said.
And "even if the figure was correct, which I stress it is not, that is not proof that climate changes does not exist", he added.
- 'Warmer now' -
Spanish daily newspaper La Vanguardia in 1935 also reported that temperatures had hit the low 50s in Zaragoza but explained that the measurement was taken "in the sun".
Scientists recommend a series of strict criteria to ensure an accurate temperature reading.
"Sensors must be protected from the sun and the rain, and the temperature inside the weather station must be the same as what it is outside," said Aemet meteorologists Ricardo Torrijo.
Another post that has gone viral on Facebook, Telegram and Twitter since last June shows a front page of Spanish weekly magazine El Espanol from August 1957 with the headline: "The hottest summer of the century".
It referred to a reading of a temperature of 50 degrees Celsius in central Spain, which was also taken in the sun.
Isabel Cacho, a climate expert at the University of Barcelona, said that "in the hypothetical case" that the mercury soared above 50 degrees Celsius, "this would not be an argument to question that it is warmer now".
- 'Not change trend' -
Climate scientists overwhelmingly agree that carbon emissions from humans burning fossil fuels are heating the planet, raising the risk, length and severity of heatwaves and other extreme weather events.
"These figures of high temperatures (in the past) do not discredit the existence of climate change," said Jose Luis Garcia, a climate change expert at Greenpeace in Spain.
"They are unrelated. One thing is one-off temperature data and another very different thing is the tendency towards an increase in the average temperature."
Pedro Zorrilla, a Spanish expert in climate change, said the "anomaly" of a very high temperature recorded in 1935 would have a "very small effect" on average temperatures.
"It does not change the trend," he added.
Records show heatwaves are occurring with greater frequency in the Iberian Peninsula, said Mariano Barriendos, a geography and history professor at the University of Barcelona.
"It is relatively usual for a hot air mass to enter the peninsula from the Sahara Desert. What is worrying is that heatwaves are happening more often," he said.
X.Habash--SF-PST



