-
 Iran says US talks are on, as Trump warns supreme leader
Iran says US talks are on, as Trump warns supreme leader
-
Gaza health officials say strikes kill 24 after Israel says officer wounded

-
 Empress's crown dropped in Louvre heist to be fully restored: museum
Empress's crown dropped in Louvre heist to be fully restored: museum
-
UK PM says Mandelson 'lied' about Epstein relations

-
 Shai to miss NBA All-Star Game with abdominal strain
Shai to miss NBA All-Star Game with abdominal strain
-
Trump suggests 'softer touch' needed on immigration

-
 From 'flop' to Super Bowl favorite: Sam Darnold's second act
From 'flop' to Super Bowl favorite: Sam Darnold's second act
-
Man sentenced to life in prison for plotting to kill Trump in 2024

-
 Native Americans on high alert over Minneapolis crackdown
Native Americans on high alert over Minneapolis crackdown
-
Dallas deals Davis to Wizards in blockbuster NBA deal: report

-
 Russia 'no longer bound' by nuclear arms limits as treaty with US ends
Russia 'no longer bound' by nuclear arms limits as treaty with US ends
-
Panama hits back after China warns of 'heavy price' in ports row

-
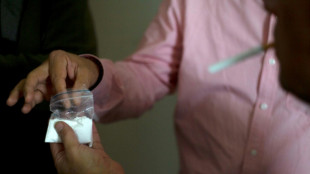 Strike kills guerrillas as US, Colombia agree to target narco bosses
Strike kills guerrillas as US, Colombia agree to target narco bosses
-
Wildfire smoke kills more than 24,000 Americans a year: study

-
 Telegram founder slams Spain PM over under-16s social media ban
Telegram founder slams Spain PM over under-16s social media ban
-
Curling kicks off sports programme at 2026 Winter Olympics

-
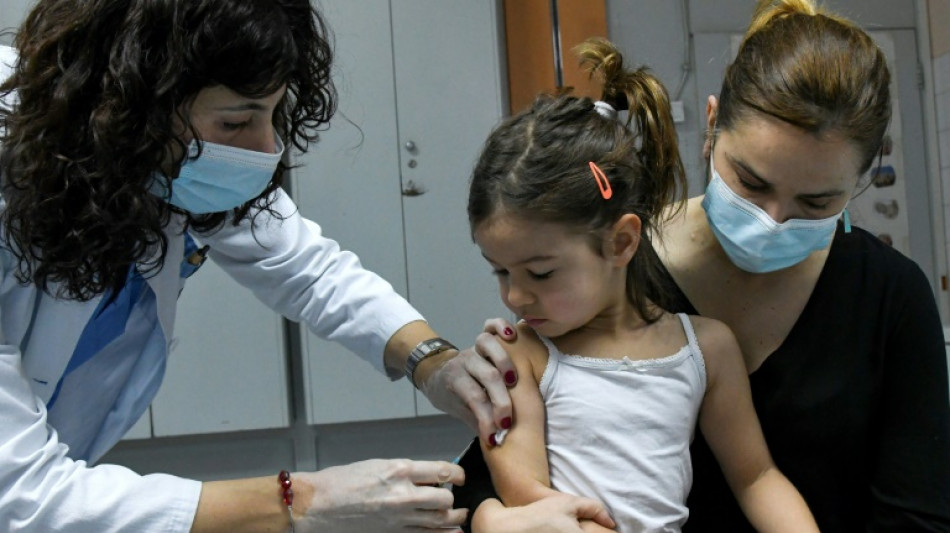
 Preventative cholera vaccination resumes as global supply swells: WHO
Preventative cholera vaccination resumes as global supply swells: WHO
-
Wales' Macleod ready for 'physical battle' against England in Six Nations

-
 Xi calls for 'mutual respect' with Trump, hails ties with Putin
Xi calls for 'mutual respect' with Trump, hails ties with Putin
-
'All-time great': Maye's ambitions go beyond record Super Bowl bid

-
 Shadow over Vonn as Shiffrin, Odermatt headline Olympic skiing
Shadow over Vonn as Shiffrin, Odermatt headline Olympic skiing
-
US seeks minerals trade zone in rare Trump move with allies

-
 Ukraine says Abu Dhabi talks with Russia 'substantive and productive'
Ukraine says Abu Dhabi talks with Russia 'substantive and productive'
-
Brazil mine disaster victims in London to 'demand what is owed'

-
 AI-fuelled tech stock selloff rolls on
AI-fuelled tech stock selloff rolls on
-
Russia vows to act 'responsibly' as nuclear pact ends with US

-
 White says time at Toulon has made him a better Scotland player
White says time at Toulon has made him a better Scotland player
-
Washington Post announces 'painful' job cuts

-
 All lights are go for Jalibert, says France's Dupont
All lights are go for Jalibert, says France's Dupont
-
Artist rubs out Meloni church fresco after controversy

-
 Palestinians in Egypt torn on return to a Gaza with 'no future'
Palestinians in Egypt torn on return to a Gaza with 'no future'
-
US removing 700 immigration officers from Minnesota

-
 Who is behind the killing of late ruler Gaddafi's son, and why now?
Who is behind the killing of late ruler Gaddafi's son, and why now?
-
Coach Thioune tasked with saving battling Bremen

-
 Russia vows to act 'responsibly' once nuclear pact with US ends
Russia vows to act 'responsibly' once nuclear pact with US ends
-
Son of Norway's crown princess admits excesses but denies rape

-
 US calls for minerals trade zone in rare move with allies
US calls for minerals trade zone in rare move with allies
-
Vowles dismisses Williams 2026 title hopes as 'not realistic'

-
 'Dinosaur' Glenn chasing skating gold in first Olympics
'Dinosaur' Glenn chasing skating gold in first Olympics
-
Gaza health officials say strikes kill 23 after Israel says shots wounded officer

-
 Italy foils Russian cyberattacks targeting Olympics
Italy foils Russian cyberattacks targeting Olympics
-
Stocks stabilise after Wall St AI-fuelled sell-off

-
 Figure skating favourite Malinin feeling 'the pressure' in Milan
Figure skating favourite Malinin feeling 'the pressure' in Milan
-
Netflix film probes conviction of UK baby killer nurse

-
 Timber hopes League Cup can be catalyst for Arsenal success
Timber hopes League Cup can be catalyst for Arsenal success
-
China calls EU 'discriminatory' over probe into energy giant Goldwind

-
 Sales warning slams Ozempic maker Novo Nordisk's stock
Sales warning slams Ozempic maker Novo Nordisk's stock
-
Can Vonn defy ACL rupture to win Olympic medal?

-
 Breakthrough or prelude to attack? What we know about Iran-US talks
Breakthrough or prelude to attack? What we know about Iran-US talks
-
German far-right MP detained over alleged Belarus sanctions breach


Covid-19 misinformation bolsters anti-vaccine movement
More parents are questioning the necessity of routine vaccinations for young children. Adults are skipping shots as well, even for vaccines with a long safety record.
The trend comes amid a wave of misinformation and disinformation about Covid-19 and the vaccines that helped to stem pandemic deaths. Politicization of the Covid-19 shots has bolstered the anti-vaccine movement, contributing to the decline in routine immunizations for measles, polio and other dangerous diseases.
"They ask if these are truly necessary, or if we can give them at later times," said Jason Terk, a Texas pediatrician and spokesperson for the American Academy of Pediatrics.
"This is not the majority of parents, but we are seeing a higher number."
The anti-vaccine movement has mushroomed as its messages on social media are amplified by conservative political figures as well as foreign influence operations, whose vaccine disinformation efforts pre-date the pandemic.
With routine immunization rates falling, concerns are growing about a resurgence of diseases which had largely been eradicated in many parts of the world.
In the United States, the percentage of kindergarten children with recommended immunizations fell a percentage point to 94 percent in the 2020-21 school year, representing some 35,000 children unvaccinated.
"I refer to it as the parallel contagion," Terk said. "This seems to have at its origin hesitancy in Covid-19 vaccinations and increasing distrust of vaccines and the bodies we've relied on to keep us healthy and well."
Dramatic changes were seen in some states, especially during the height of the pandemic: researchers found a 47 percent drop in immunization rates in Texas among five-month-olds and a 58 percent decline for 16-month-olds between 2019 and 2020.
The researchers, writing in the scientific journal Vaccine, said the declines resulted from shelter-in-place restrictions and vaccine exemptions, but also to "an aggressive anti-vaccine movement in Texas."
Washington state reported a 13 percent decline in childhood immunization rates in 2021 compared with pre-pandemic levels and Michigan's vaccination rate for toddlers fell last year to 69.9 percent, the lowest in a decade.
- Adults too -
Adult and adolescent inoculation rates have also dropped for vaccines protecting against diseases such as influenza, hepatitis, measles, tetanus and shingles, according to health consultancy Avalere, which analyzes insurer claims.
This has led to an estimated 37 million missed vaccination doses from January 2020 to July 2021 for adults and children ages seven and older, Avalere found.
Declines early in the pandemic can be attributed to shelter-in-place orders and social distancing, but "there is a risk of a bleed-over" of Covid vaccine misinformation, which affects other vaccines which have a longstanding safety record, noted Avalere managing director Jason Hall.
Social media have helped create a coalition that includes true anti-vaccine believers, libertarians and conservative political figures. These segments have been amplified by disinformation actors from Russia and elsewhere, said David Broniatowski, a George Washington University professor and associate director of the school's Institute for Data, Democracy and Politics.
"People have been opposing vaccines for as long as there have been vaccines, but they've gotten more sophisticated over the past 10 years and a lot of that has been because of the ability to organize on social media across boundaries,” said Broniatowski, who researches vaccine disinformation.
He noted that while anti-vaccine activists, libertarians and foreign agents are not necessarily coordinating, "they have found common cause" in opposing vaccine mandates.
"One of the main changes we've seen is a pivot away from focusing on vaccines per se as a health issue to a civil rights and a political issue," he added.
Conspiracy theories have surged during the pandemic, according to a 2021 YouGov poll, which found 28 percent of Americans and significant numbers in other countries say the truth about the harmful effects of vaccines is being "deliberately hidden."
- Foreign actors -
Broniatowski said that foreign disinformation agents "use vaccines as a wedge issue that can mobilize a segment of the population.”
A 2018 paper co-authored by Broniatowski in the American Journal of Public Health found anti-vaccine Twitter activity was amplified by Russian trolls from 2014 to 2017 as part of an effort to promote discord and undermine confidence in the health system.
Research from the Center for European Policy Analysis showed both China and Russia have promoted Covid-19 vaccine misinformation, in part to show that Western governments are incompetent and can't be trusted.
"There's been a concerted effort on the part of these actors to diminish the standing of science because it serves their political purposes," Broniatowski said.
The problem is growing globally as well. A United Nations report last year found 23 million children worldwide missed out on routine immunizations in 2020. In the Americas region, the percentage of fully inoculated children fell to 82 percent from 91 percent in 2016 due to factors including funding shortfalls, vaccine misinformation and instability.
This is likely to create more health risks down the road from diseases which have been mostly contained.
"We had certain thresholds of protection to keep these diseases from being relevant from a public health point of view," Terk said.
"The more people pushing back, the more likely we'll have pockets of vulnerability."
K.AbuTaha--SF-PST



