-
 Iran says US talks are on, as Trump warns supreme leader
Iran says US talks are on, as Trump warns supreme leader
-
Gaza health officials say strikes kill 24 after Israel says officer wounded

-
 Empress's crown dropped in Louvre heist to be fully restored: museum
Empress's crown dropped in Louvre heist to be fully restored: museum
-
UK PM says Mandelson 'lied' about Epstein relations

-
 Shai to miss NBA All-Star Game with abdominal strain
Shai to miss NBA All-Star Game with abdominal strain
-
Trump suggests 'softer touch' needed on immigration

-
 From 'flop' to Super Bowl favorite: Sam Darnold's second act
From 'flop' to Super Bowl favorite: Sam Darnold's second act
-
Man sentenced to life in prison for plotting to kill Trump in 2024

-
 Native Americans on high alert over Minneapolis crackdown
Native Americans on high alert over Minneapolis crackdown
-
Dallas deals Davis to Wizards in blockbuster NBA deal: report

-
 Russia 'no longer bound' by nuclear arms limits as treaty with US ends
Russia 'no longer bound' by nuclear arms limits as treaty with US ends
-
Panama hits back after China warns of 'heavy price' in ports row

-
 Strike kills guerrillas as US, Colombia agree to target narco bosses
Strike kills guerrillas as US, Colombia agree to target narco bosses
-
Wildfire smoke kills more than 24,000 Americans a year: study

-
 Telegram founder slams Spain PM over under-16s social media ban
Telegram founder slams Spain PM over under-16s social media ban
-
Curling kicks off sports programme at 2026 Winter Olympics

-
 Preventative cholera vaccination resumes as global supply swells: WHO
Preventative cholera vaccination resumes as global supply swells: WHO
-
Wales' Macleod ready for 'physical battle' against England in Six Nations

-
 Xi calls for 'mutual respect' with Trump, hails ties with Putin
Xi calls for 'mutual respect' with Trump, hails ties with Putin
-
'All-time great': Maye's ambitions go beyond record Super Bowl bid

-
 Shadow over Vonn as Shiffrin, Odermatt headline Olympic skiing
Shadow over Vonn as Shiffrin, Odermatt headline Olympic skiing
-
US seeks minerals trade zone in rare Trump move with allies

-
 Ukraine says Abu Dhabi talks with Russia 'substantive and productive'
Ukraine says Abu Dhabi talks with Russia 'substantive and productive'
-
Brazil mine disaster victims in London to 'demand what is owed'

-
 AI-fuelled tech stock selloff rolls on
AI-fuelled tech stock selloff rolls on
-
Russia vows to act 'responsibly' as nuclear pact ends with US

-
 White says time at Toulon has made him a better Scotland player
White says time at Toulon has made him a better Scotland player
-
Washington Post announces 'painful' job cuts

-
 All lights are go for Jalibert, says France's Dupont
All lights are go for Jalibert, says France's Dupont
-
Artist rubs out Meloni church fresco after controversy

-
 Palestinians in Egypt torn on return to a Gaza with 'no future'
Palestinians in Egypt torn on return to a Gaza with 'no future'
-
US removing 700 immigration officers from Minnesota

-
 Who is behind the killing of late ruler Gaddafi's son, and why now?
Who is behind the killing of late ruler Gaddafi's son, and why now?
-
Coach Thioune tasked with saving battling Bremen

-
 Russia vows to act 'responsibly' once nuclear pact with US ends
Russia vows to act 'responsibly' once nuclear pact with US ends
-
Son of Norway's crown princess admits excesses but denies rape

-
 US calls for minerals trade zone in rare move with allies
US calls for minerals trade zone in rare move with allies
-
Vowles dismisses Williams 2026 title hopes as 'not realistic'

-
 'Dinosaur' Glenn chasing skating gold in first Olympics
'Dinosaur' Glenn chasing skating gold in first Olympics
-
Gaza health officials say strikes kill 23 after Israel says shots wounded officer

-
 Italy foils Russian cyberattacks targeting Olympics
Italy foils Russian cyberattacks targeting Olympics
-
Stocks stabilise after Wall St AI-fuelled sell-off

-
 Figure skating favourite Malinin feeling 'the pressure' in Milan
Figure skating favourite Malinin feeling 'the pressure' in Milan
-
Netflix film probes conviction of UK baby killer nurse

-
 Timber hopes League Cup can be catalyst for Arsenal success
Timber hopes League Cup can be catalyst for Arsenal success
-
China calls EU 'discriminatory' over probe into energy giant Goldwind

-
 Sales warning slams Ozempic maker Novo Nordisk's stock
Sales warning slams Ozempic maker Novo Nordisk's stock
-
Can Vonn defy ACL rupture to win Olympic medal?

-
 Breakthrough or prelude to attack? What we know about Iran-US talks
Breakthrough or prelude to attack? What we know about Iran-US talks
-
German far-right MP detained over alleged Belarus sanctions breach


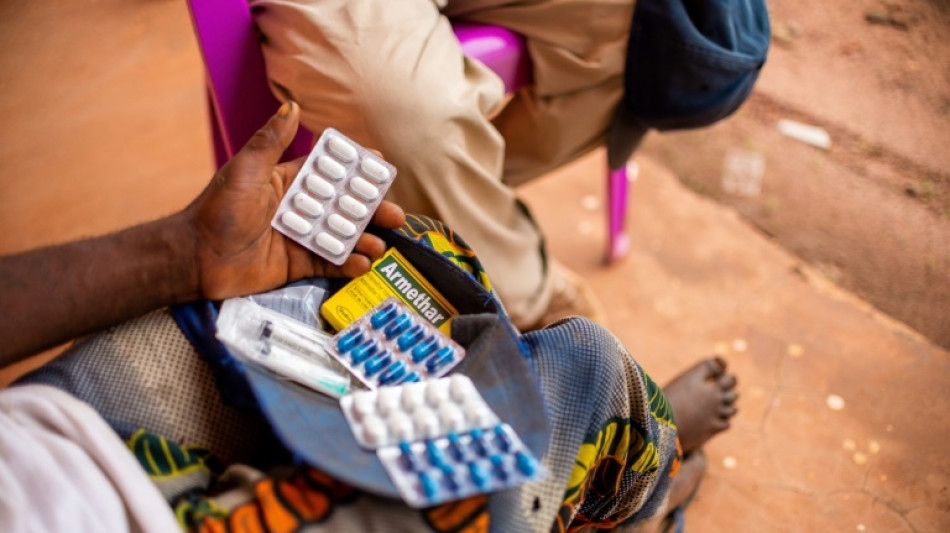
DR Congo drug manufacturing plan sparks safety concerns
Sitting at his desk overlooking a pharmaceutical factory floor on the outskirts of the Congolese capital Kinshasa, Joss Ilunga Dijimba, 52, cracked a jovial smile.
"It's not easy doing business in Congo," he said.
His family was forced to relocate the factory in the 1990s to survive bouts of mass looting. And nowadays, there are onerous taxes, customs duties, and problems retaining talented staff.
His company, which employs about 40 people and produces generics such as paracetamol, is one of a tiny number of drug manufacturers in the Democratic Republic of Congo, an impoverished nation roughly the size of Western Europe.
But a government plan to require hospitals and NGOs to buy more locally produced drugs could soon boost the fledgling pharmaceutical industry -- despite fears in some quarters that safety standards are far below international norms.
Several NGOs, some of which provide medical care in the DRC's conflict-torn east, have requested opt-outs.
At the small Pharmagros plant, behind barbed-wire walls near the Congo river, men in hairnets and white coats formulate medicines with imported precursor using lab equipment in airconditioned rooms.
"Promoting local industry's a good thing," said Dijimba, a University of Texas graduate, insisting that several Congolese firms, including his, maintained high standards.
"It could grow the middle class."
About 73 percent of the DRC's population of 90 million lives on under $1.9 a day, according to the World Bank. Most products in the African country are imported.
- 'At your own peril' -
The Congolese government has designated 35 drug molecules, including paracetamol, that medical facilities will be required to purchase in locally made form.
The government wants to stimulate business without banning imports, said Donatien Kabamb Kabey, the pharmaceuticals director at the DRC's health ministry.
He explained that all the molecules can be replaced with imported equivalents, suggesting that ibuprofen could replace paracetamol, for example.
Although not yet implemented, the policy already appears to be working.
Fifteen new pharma businesses are setting up in the DRC ahead of the new rules, Kabey said, which will add to the existing 24.
The policy was partly designed to encourage factories to return after fleeing the country in the 1990s, he added, when unpaid soldiers went on the rampage towards the end of ex-dictator Mobutu Sese Seko's reign.
But experts warn that Congolese-made medicines face a major challenge: reassuring doctors and patients that they meet regulatory standards.
"When you go to the private sector in Congo, you do it at your own peril," said Ed Vreeke, who runs the Belgium-based independent pharmaceutical auditing firm Quamed.
"They know darn well that the quality they produce is not good."
Vreeke said Congolese regulators had improved, but the country lacked the massive resources needed to properly perform audits, check labels, and inspect the chemical composition of drugs for safety.
Kabey, whose department at the health ministry oversees inspections, said standards had improved "enormously" in recent years, but did not provide further details.
He said the government was establishing a national quality-control lab.
- 'A huge thing' -
Shoddy or falsified medicines kill hundreds of thousands of people every year, according to the World Health Organization, mostly in poor countries.
The DRC's hot and humid climate also poses storage problems.
A 2021 study of both imported and locally produced eye drops sold in Kinshasa, for example, showed that three out of the seven products tested were substandard. The one sample manufactured in the DRC was contaminated.
Outside a pharmacy in Kinshasa's upmarket Gombe district, clutching a bag of medicines, 29-year-old corporate lawyer Joelle Mamputu said she didn't pay attention to where drugs were made but said she had "no prejudice".
However, a 52-year-old public servant named Olivier said there was "quite a difference" between Congolese and foreign drugs.
He added he would buy Congolese drugs were the quality the same.
Despite official assurances, major international NGOs such as Doctors Without Borders (MSF) and Medecins du Monde (MDM) have requested opt-outs from the purchasing requirements, several humanitarian workers said.
MSF declined to comment.
MDM confirmed it had asked for an exemption due to concerns over quality and capacity to meet demand.
"It's a huge thing," said one humanitarian who asked for anonymity, explaining that the new rules will affect all non-governmental organisations, hospitals and pharmacies.
Many aid workers understand the need to promote enterprise, he said, but there are internal disagreements about whether to compromise on quality.
"We need to have high quality standards for everyone, but the reality of the country is that sometimes it's impossible".
B.AbuZeid--SF-PST



