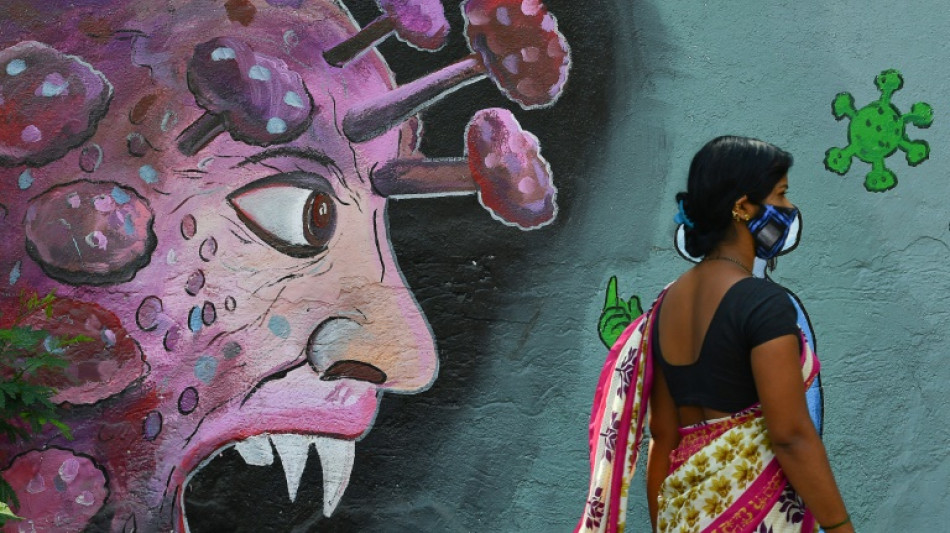
-
 Ukraine, Russia, US start second day of war talks
Ukraine, Russia, US start second day of war talks
-
Nepal's youth lead the charge in the upcoming election

-
 Sony hikes forecasts even as PlayStation falters
Sony hikes forecasts even as PlayStation falters
-
Rijksmuseum puts the spotlight on Roman poet's epic

-
 Trump fuels EU push to cut cord with US tech
Trump fuels EU push to cut cord with US tech
-
Fearless talent: Five young players to watch at the T20 World Cup

-
 India favourites as T20 World Cup to begin after chaotic build-up
India favourites as T20 World Cup to begin after chaotic build-up
-
Voter swings raise midterm alarm bells for Trump's Republicans

-
 Australia dodges call for arrest of visiting Israel president
Australia dodges call for arrest of visiting Israel president
-
Countries using internet blackouts to boost censorship: Proton

-
 Top US news anchor pleads with kidnappers for mom's life
Top US news anchor pleads with kidnappers for mom's life
-
Thailand's pilot PM on course to keep top job

-
 The coming end of ISS, symbol of an era of global cooperation
The coming end of ISS, symbol of an era of global cooperation
-
New crew set to launch for ISS after medical evacuation

-
 Family affair: Thailand waning dynasty still election kingmaker
Family affair: Thailand waning dynasty still election kingmaker
-
Japan's first woman PM tipped for thumping election win

-
 Stocks in retreat as traders reconsider tech investment
Stocks in retreat as traders reconsider tech investment
-
LA officials call for Olympic chief to resign over Epstein file emails

-
 Ukraine, Russia, US to start second day of war talks
Ukraine, Russia, US to start second day of war talks
-
Fiji football legend returns home to captain first pro club

-
 Trump attacks US electoral system with call to 'nationalize' voting
Trump attacks US electoral system with call to 'nationalize' voting
-
Barry Manilow cancels Las Vegas shows but 'doing great' post-surgery

-
 US households become increasingly strained in diverging economy
US households become increasingly strained in diverging economy
-
Four dead men: the cold case that engulfed a Colombian cycling star

-
 Super Bowl stars stake claims for Olympic flag football
Super Bowl stars stake claims for Olympic flag football
-
On a roll, Brazilian cinema seizes its moment

-
 Rising euro, falling inflation in focus at ECB meeting
Rising euro, falling inflation in focus at ECB meeting
-
AI to track icebergs adrift at sea in boon for science

-
 Indigenous Brazilians protest Amazon river dredging for grain exports
Indigenous Brazilians protest Amazon river dredging for grain exports
-
Google's annual revenue tops $400 bn for first time, AI investments rise

-
 Last US-Russia nuclear treaty ends in 'grave moment' for world
Last US-Russia nuclear treaty ends in 'grave moment' for world
-
Man City brush aside Newcastle to reach League Cup final

-
 Guardiola wants permission for Guehi to play in League Cup final
Guardiola wants permission for Guehi to play in League Cup final
-
Boxer Khelif reveals 'hormone treatments' before Paris Olympics

-
 'Bad Boy,' 'Little Pablo' and Mordisco: the men on a US-Colombia hitlist
'Bad Boy,' 'Little Pablo' and Mordisco: the men on a US-Colombia hitlist
-
BHP damages trial over Brazil mine disaster to open in 2027

-
 Dallas deals Davis to Wizards in blockbuster NBA trade: report
Dallas deals Davis to Wizards in blockbuster NBA trade: report
-
Iran-US talks back on, as Trump warns supreme leader

-
 Lens cruise into French Cup quarters, Endrick sends Lyon through
Lens cruise into French Cup quarters, Endrick sends Lyon through
-
No.1 Scheffler excited for Koepka return from LIV Golf

-
 Curling quietly kicks off sports programme at 2026 Winter Olympics
Curling quietly kicks off sports programme at 2026 Winter Olympics
-
Undav pokes Stuttgart past Kiel into German Cup semis

-
 Germany goalkeeper Ter Stegen to undergo surgery
Germany goalkeeper Ter Stegen to undergo surgery
-
Bezos-led Washington Post announces 'painful' job cuts

-
 Iran says US talks are on, as Trump warns supreme leader
Iran says US talks are on, as Trump warns supreme leader
-
Gaza health officials say strikes kill 24 after Israel says officer wounded

-
 Empress's crown dropped in Louvre heist to be fully restored: museum
Empress's crown dropped in Louvre heist to be fully restored: museum
-
UK PM says Mandelson 'lied' about Epstein relations

-
 Shai to miss NBA All-Star Game with abdominal strain
Shai to miss NBA All-Star Game with abdominal strain
-
Trump suggests 'softer touch' needed on immigration

Researchers start to find clues on the trail of long Covid
Tens of millions of people across the world are thought to suffer from long Covid, but four years after the pandemic was declared this elusive condition still cannot be tested for -- let alone treated.
However research could be finally starting to find early clues on the trail of long Covid, raising hopes of future breakthroughs that may also illuminate other stubbornly ambiguous chronic syndromes.
Long Covid is the name given to a wide variety of symptoms still being suffered by people weeks and months after they first contracted the SARS-CoV-2 virus.
The most common are fatigue, shortness of breath, muscle pain and brain fog.
One notable study released last month showed there were significant differences in the proteins of the blood of more than 110 long Covid patients.
Onur Boyman, a Swiss researcher and senior author of the Science study, told AFP he believes this is a "central puzzle piece" in what keeps Covid raging for so long in the bodies of some people.
Part of the body's immune system called the complement system, which normally fights off infection by killing infected cells, remains active in people with long Covid, continuing to attack healthy targets and causing tissue damage, the researchers said.
Boyman said that when people recovered from long Covid, their complement system also improved, suggesting a strong link between the two.
"It shows that long Covid is a disease and you can actually measure it," Boyman said, adding the team hopes this could lead to a future test.
Researchers not involved in the study cautioned that this complement system "dysregulation" could not explain all the different ways that long Covid seems to attack patients.
Still, it is "great to see papers coming out now showing signals which might start to explain long Covid", said Claire Steves, professor of ageing and health at King's College London.
- 'Every aspect of my life' -
Lucia, a US-based long Covid sufferer who preferred not to give her last name, told AFP that "studies like these bring us a lot closer to understanding" the condition.
She pointed to another recent paper which found damage and fewer mitochondria in the muscles of long Covid patients, which could indicate why many patients become exhausted after even a small amount of exercise.
For Lucia, long Covid turned climbing up the stairs to her apartment into a daily battle.
When she first caught Covid in March 2020, Lucia said she could not have imagined how the condition would "affect every aspect of my life -- including socially and financially".
Lucia, a member of the Patient-Led Research Collaborative, emphasised that people with long Covid do not only have to deal with their many health issues.
They also have "to contend with disbelief or dismissal from the medical community or from within their social circles", she said.
The importance of supporting patients was highlighted by a BMJ study this week, which found that group rehab improved the quality of life of long Covid patients.
- Why has it been so hard? -
Ziyad Al-Aly, a clinical epidemiologist at Washington University in St Louis, said long Covid has been so elusive because it is a "multi-system disease".
"Our minds are trained to think about diseases based on organ systems" such as heart or lung disease, he told AFP.
But understanding the mechanisms behind long Covid could more broadly answer "why and how acute infections cause chronic disease", he said.
This means solving the mystery of long Covid may bolster the fight against other conditions such as chronic fatigue syndrome or lingering symptoms after influenza, increasingly referred to as "long flu".
While the true number of long Covid sufferers is difficult to determine, the World Health Organization says it could be between 10-20 percent of all people who have contracted the disease.
Research from the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has suggested that the percentage of people who get long Covid has decreased as new coronavirus variants have become less severe.
Vaccination against Covid has been shown to significantly reduce the chance that people will get long Covid, emphasising the importance of booster shots, researchers say.
Q.Bulbul--SF-PST




