
-
 Freeski star Gu says injuries hit confidence as she targets Olympic treble
Freeski star Gu says injuries hit confidence as she targets Olympic treble
-
UK police search properties in Mandelson probe

-
 Bompastor extends contract as Chelsea Women's boss despite slump
Bompastor extends contract as Chelsea Women's boss despite slump
-
Milan-Cortina Winter Olympics open with glittering ceremony

-
 A French yoga teacher's 'hell' in a Venezuelan jail
A French yoga teacher's 'hell' in a Venezuelan jail
-
England's Underhill taking nothing for granted against Wales

-
 Fans cheer for absent Ronaldo as Saudi row deepens
Fans cheer for absent Ronaldo as Saudi row deepens
-
Violence-ridden Haiti in limbo as transitional council wraps up

-
 Hundreds protest in Milan ahead of Winter Olympics
Hundreds protest in Milan ahead of Winter Olympics
-
Suspect in murder of Colombian footballer Escobar killed in Mexico

-
 Colombia's Rodriguez signs with MLS Minnesota United
Colombia's Rodriguez signs with MLS Minnesota United
-
Wainwright says England game still 'huge occasion' despite Welsh woes

-
 WADA shrugs off USA withholding dues
WADA shrugs off USA withholding dues
-
France detects Russia-linked Epstein smear attempt against Macron

-
 Winter Olympics to open with star-studded ceremony
Winter Olympics to open with star-studded ceremony
-
Trump posts, then deletes, racist clip of Obamas as monkeys

-
 Danone expands recall of infant formula batches in Europe
Danone expands recall of infant formula batches in Europe
-
Trump deletes racist video post of Obamas as monkeys

-
 Colombia's Rodriguez signs with MLS side Minnesota United
Colombia's Rodriguez signs with MLS side Minnesota United
-
UK police probing Mandelson after Epstein revelations search properties

-
 Russian drone hits Ukrainian animal shelter
Russian drone hits Ukrainian animal shelter
-
US says new nuclear deal should include China, accuses Beijing of secret tests

-
 French cycling hope Seixas dreaming of Tour de France debut
French cycling hope Seixas dreaming of Tour de France debut
-
France detects Russia-linked Epstein smear attempt against Macron: govt source

-
 EU nations back chemical recycling for plastic bottles
EU nations back chemical recycling for plastic bottles
-
Terror at Friday prayers: witnesses describe blast rocking Islamabad mosque

-
 Iran expects more US talks after 'positive atmosphere' in Oman
Iran expects more US talks after 'positive atmosphere' in Oman
-
US says 'key participant' in 2012 attack on Benghazi mission arrested

-
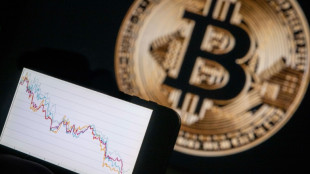 Why bitcoin is losing its luster after stratospheric rise
Why bitcoin is losing its luster after stratospheric rise
-
Arteta apologises to Rosenior after disrespect row

-
 Terror at Friday prayers: witness describes 'extremely powerful' blast in Islamabad
Terror at Friday prayers: witness describes 'extremely powerful' blast in Islamabad
-
Winter Olympics men's downhill: Three things to watch

-
 Ice dancers Chock and Bates shine as US lead Japan in team event
Ice dancers Chock and Bates shine as US lead Japan in team event
-
Stellantis takes massive hit on 'overestimation' of EV demand

-
 Stocks rebound though tech stocks still suffer
Stocks rebound though tech stocks still suffer
-
Spanish PM urges caution as fresh rain heads for flood zone

-
 Iran says to hold more talks with US despite Trump military threats
Iran says to hold more talks with US despite Trump military threats
-
Russia accuses Kyiv of gun attack on army general in Moscow

-
 Cambodia reveals damage to UNESCO-listed temple after Thailand clashes
Cambodia reveals damage to UNESCO-listed temple after Thailand clashes
-
Norway crown princess 'deeply regrets' Epstein friendship

-
 Italy set for Winter Olympics opening ceremony as Vonn passes test
Italy set for Winter Olympics opening ceremony as Vonn passes test
-
England's Jacks says players back under-fire skipper Brook '100 percent'

-
 Carrick relishing Frank reunion as Man Utd host Spurs
Carrick relishing Frank reunion as Man Utd host Spurs
-
Farrell keeps the faith in Irish still being at rugby's top table

-
 Meloni, Vance hail 'shared values' amid pre-Olympic protests
Meloni, Vance hail 'shared values' amid pre-Olympic protests
-
Olympic freestyle champion Gremaud says passion for skiing carried her through dark times

-
 US urges new three-way nuclear deal with Russia and China
US urges new three-way nuclear deal with Russia and China
-
Indonesia landslide death toll rises to 74

-
 Hemetsberger a 'happy psychopath' after final downhill training
Hemetsberger a 'happy psychopath' after final downhill training
-
Suicide blast at Islamabad mosque kills at least 31, wounds over 130


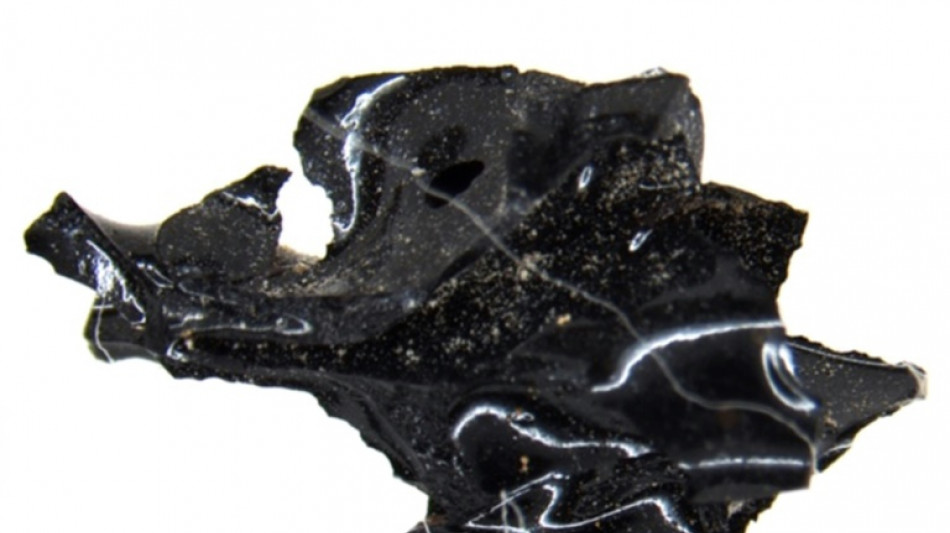
How did this man's brain turn to glass? Scientists have a theory
A young man was lying in his bed when a viciously hot cloud of ash swept down from the erupting Mount Vesuvius and turned his brain to glass almost 2,000 years ago.
That is the theory Italian scientists proposed on Thursday to explain the strange case of the ancient Roman's brain, which they said is the only human tissue ever known to have naturally turned to glass.
This unique brain could rewrite the story of one of history's most famous natural disasters -- and help protect people against this little-understood phenomenon during future volcanic eruptions, the scientists suggested.
When Mount Vesuvius -- near the modern-day Italian city of Naples -- erupted in 79 AD, the cities of Pompeii and Herculaneum were buried in a fast-moving blanket of rock and ash called a pyroclastic flow.
Thousands of bodies have been discovered at the sites effectively frozen in time, offering a glimpse into the daily life of ancient Rome.
In the 1960s, the charred remains of a man aged roughly 20 were found on a wooden bed in a Herculaneum building dedicated to worshipping the Roman Emperor Augustus.
Italian anthropologist Pier Paolo Petrone, a co-author of a new study, noticed something strange in 2018.
"I saw that something was shimmery in the shattered skull," he told AFP in 2020.
What was left of the man's brain had been transformed into fragments of shiny black glass.
- 'Amazing, truly unexpected' -
These "chips" are up to a centimetre wide, volcanologist Guido Giordano, the lead author of the new study in Scientific Reports, told AFP.
When the scientists studied the glass using an electron microscope, they discovered an "amazing, truly unexpected thing," he said.
Complex networks of neurons, axons and other identifiable parts of the man's brain and spinal cord were preserved in the glass, according to the study.
How this happened is something of a mystery.
Glass occurs rarely in nature because it requires extremely hot temperatures to cool very rapidly, leaving no time for crystallisation. It is usually caused by meteorites, lightning or lava.
This is even more unlikely to happen to human tissues, because they are mostly made out of water.
The Roman's brain being preserved in glass is the "only such occurrence on Earth" ever documented for human or animal tissue, the study said.
The scientists determined that the brain must have been exposed to temperatures soaring above 510 degrees Celsius (950 Fahrenheit).
That is hotter than the pyroclastic flow that buried the city, which topped out at around 465C.
Then the brain needed to rapidly cool down -- and all this had to happen before the flow arrived.
The "only possible scenario" was that an ash cloud emitted by Vesuvius delivered an initial hot blast before quickly dissipating, the study said.
This theory is supported by a thin layer of ash that settled in the city shortly before it was smothered.
This would mean the people of Herculaneum were actually killed by the ash cloud -- not the pyroclastic flow as had long been thought.
- 'Poorly-studied' threat -
Giordano hoped the research would lead to more awareness about the threat posed by these hot ash clouds, which remain "very poorly studied" because they leave little trace behind.
French volcanologists Katia and Maurice Krafft, the subjects of the Oscar-nominated 2022 documentary "Fire of Love", were killed by such an ash cloud, Giordano said.
And some of the 215 people killed during the 2018 eruption of Guatemala's Fuego volcano were also victims of this phenomenon, he added.
"There is a window of survivability" for these hot blasts, he emphasised, adding that fitting houses near volcanoes to withstand high heat could help.
But why did the man with the glass brain uniquely suffer this fate?
Unlike Pompeii, Herculaneum had some time to respond to the eruption. All the other bodies discovered there were clearly trying to flee into the Mediterranean Sea.
However the man, who is thought to have been the guardian of the Collegium building, stayed in bed in the middle of town, so was the first hit.
"Maybe he was drunk," Giordano joked, adding that we will likely never know the truth.
M.AlAhmad--SF-PST



