
-
 Rallies across US after woman shot and killed by immigration agent
Rallies across US after woman shot and killed by immigration agent
-
Egypt dump out holders Ivory Coast as Nigeria set up AFCON semi with Morocco

-
 Rosenior salutes 'outstanding' start to Chelsea reign
Rosenior salutes 'outstanding' start to Chelsea reign
-
Maduro loyalists stage modest rally as Venezuelan govt courts US

-
 Byrne late penalty fires Leinster into Champions Cup last 16 after 'ding-dong' battle
Byrne late penalty fires Leinster into Champions Cup last 16 after 'ding-dong' battle
-
Rosenior makes flying start as Chelsea rout Charlton in FA Cup

-
 Rallies across US against shooting of woman by immigration agent
Rallies across US against shooting of woman by immigration agent
-
Salah closer to AFCON glory as Egypt dethrone champions Ivory Coast

-
 O'Neil ends 'crazy three days' with Strasbourg cup canter
O'Neil ends 'crazy three days' with Strasbourg cup canter
-
Mitchell leads Cavs over T-Wolves

-
 O'Neil ends 'crazy few days' with Strasbourg cup canter
O'Neil ends 'crazy few days' with Strasbourg cup canter
-
Argentina wildfire burns over 5,500 hectares: governor

-
 Byrne late penalty fires Leinster into Champions Cup last 16
Byrne late penalty fires Leinster into Champions Cup last 16
-
Roma beat Sassuolo to close in on Serie A leaders Inter

-
 Villa's FA Cup win at Spurs leaves Frank on the brink
Villa's FA Cup win at Spurs leaves Frank on the brink
-
Osimhen focused on Nigeria glory not scoring record

-
 Undav calls shots as Stuttgart thump Leverkusen
Undav calls shots as Stuttgart thump Leverkusen
-
Venezuelan prisoners smile to hear of Maduro's fall

-
 Thousands of Irish, French farmers protest EU-Mercosur trade deal
Thousands of Irish, French farmers protest EU-Mercosur trade deal
-
Kiplimo captures third straight world cross country title

-
 Osimhen leads Nigeria past Algeria into AFCON semi-finals
Osimhen leads Nigeria past Algeria into AFCON semi-finals
-
US urges fresh talks between Syria govt, Kurds after deadly clashes

-
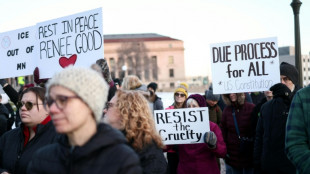 Weekend of US protests after woman killed by immigration agent
Weekend of US protests after woman killed by immigration agent
-
Monaco cling on with 10 men to avoid French Cup shock

-
 Rooney close to tears as brother masterminds FA Cup history
Rooney close to tears as brother masterminds FA Cup history
-
Semenyo scores on Man City debut in 10-goal rout of Exeter

-
 Villarreal sink Alaves to stay in La Liga hunt
Villarreal sink Alaves to stay in La Liga hunt
-
Bristol, Glasgow reach Champions Cup last 16

-
 Freiburg beat 10-man Hamburg to climb to eighth in the Bundesliga
Freiburg beat 10-man Hamburg to climb to eighth in the Bundesliga
-
Venezuela loyalists to rally one week after Maduro's capture

-
 Syrian authorities transferring Kurdish fighters from Aleppo to northeast
Syrian authorities transferring Kurdish fighters from Aleppo to northeast
-
Football: Five memorable FA Cup upsets

-
 Odermatt warms up for Winter Games with Adelboden giant slalom win
Odermatt warms up for Winter Games with Adelboden giant slalom win
-
Benin showcases culture with Vodun Days

-
 Iran crackdown fears grow as protests persist
Iran crackdown fears grow as protests persist
-
Odermatt wins Adelboden giant slalom for sixth World Cup success of season

-
 Holders Crystal Palace stunned by Macclesfield in biggest ever FA Cup shock
Holders Crystal Palace stunned by Macclesfield in biggest ever FA Cup shock
-
Odermatt wins Abelboden giant slalom for sixth World Cup success of season

-
 Poland reach United Cup final despite Swiatek loss to Gauff
Poland reach United Cup final despite Swiatek loss to Gauff
-
India's Gill calls it 'destiny' after shock T20 World Cup snub

-
 'Driven' Vonn storms to 84th World Cup win in Austrian downhill
'Driven' Vonn storms to 84th World Cup win in Austrian downhill
-
Syrian army says stopping Aleppo operations, but Kurds deny fighting over

-
 Thousands of Irish farmers protest EU-Mercosur trade deal
Thousands of Irish farmers protest EU-Mercosur trade deal
-
Vonn storms to 84th World Cup win in Austrian downhill

-
 Anger over fatal Minneapolis shooting fuels US protests
Anger over fatal Minneapolis shooting fuels US protests
-
New rallies erupt in Iran as crackdown fears grow
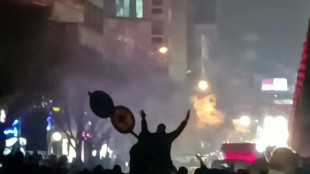
-
 Real Madrid not 'kamikaze' with Mbappe health: Alonso
Real Madrid not 'kamikaze' with Mbappe health: Alonso
-
South Africa defends naval drills with Iran, Russia as 'essential'

-
 Alcaraz beats Sinner in sold-out South Korea exhibition match
Alcaraz beats Sinner in sold-out South Korea exhibition match
-
'Racing against time': Death toll rises after Philippines trash site collapse


Slow but savage: Why hurricanes like Melissa are becoming more common
Fueled by abnormally warm Caribbean waters, Hurricane Melissa exploded into a Category 5 cyclone while moving at little more than a strolling pace -- a dangerous mix that could amplify its impacts through relentless rain, storm surge and wind.
Scientists say both rapid intensification and stalling storms are on the rise in a warming climate. Here's what to know.
- Supercharged by climate change -
Melissa jumped from a tropical storm with 70 mph (110 kph) winds on Saturday morning to a 140 mph Category 4 within 24 hours. It's since strengthened further into a Category 5, the highest level on the Saffir-Simpson, where even well-built structures face catastrophic damage.
It was the fourth of five Atlantic hurricanes this season to intensify in such dramatic fashion.
"We haven't had that many hurricanes in the Atlantic this season, but an unusual proportion of them went through a phase of intensifying quite rapidly," meteorologist and climate scientist Kerry Emanuel of MIT told AFP.
While it's hard to read the fingerprints of human-caused climate change into individual events, scientists are more confident when it comes to trends. "This may very well be collectively a signature of climate change," he said.
Warmer sea surface temperatures injects more energy into storms, giving them extra fuel. But the relationship is nuanced: it's actually the temperature difference between the water and the atmosphere that sets a hurricane's potential strength, a concept Emanuel pioneered.
"There's this atmospheric warming that tends to reduce the intensity, and there's sea surface temperature warming, which tends to increase the intensity," atmospheric scientist Daniel Gilford of nonprofit Climate Central told AFP. "Generally speaking...we find that the sea surface temperature wins out."
Melissa passed over waters made 1.4C (2.5F) warmer due to climate change, Climate Central's rapid analysis said -- temperatures that were at least 500 times more likely due to human-caused warming.
- 'A terrifying situation' -
Warmer oceans also mean wetter storms. "We expect something like between 25-50 percent extra rainfall in a storm like Melissa because of human-caused climate change," said Gilford.
Compounding matters further is the storm's slow crawl -- currently three miles per hour. Melissa is projected to dump 20-25 inches of rainfall to parts of Jamaica.
"It's this repetitive or continuous threat and existence in a dangerous situation," Jill Trepanier, a hurricane climatology expert at Louisiana State University, told AFP.
"It could be a prolonged surge. It could be high level rainfall over a longer period of time, and your watershed can't handle it. It could be extreme wind speed over an extended period of time, and most infrastructure can't handle that. It could be a combination of all three."
Trepanier authored a research paper last year on the subject of so-called stalling storms, finding that such events in the Caribbean typically happen in October, near coastlines.
Normally stalling storms tend to be dying out, as they pull up cold water from the depths of the ocean and are exposed to wavy, up-and-down winds in the atmosphere tearing them apart.
What makes Melissa unusual is that it stalled and intensified in the same spot -- a sign that the water was so warm, and the warmth ran so deep, it avoided the usual self-destructing effect.
"It's a bit of a terrifying situation," said Trepanier.
Former NOAA climatologist James Kossin, who has published several papers on the subject, said data clearly show that stalling storms are on the rise.
A possible driver is "Arctic amplification" -- global warming reduces the temperature difference from the planet's low to high latitudes, weakening the winds that normally steer storms "like a cork in stream." But more research is needed to confirm a causal link, he said.
Trepanier added that understanding the human and ecological dimensions is just as important as the physics because humans respond differently to risk.
With Jamaica's mountainous terrain, torrential rainfall could trigger landslides, while heavy damage to hotel infrastructure could batter the tourism-dependent economy for years, she warned.
G.AbuOdeh--SF-PST



