
-
 Rallies across US after woman shot and killed by immigration agent
Rallies across US after woman shot and killed by immigration agent
-
Egypt dump out holders Ivory Coast as Nigeria set up AFCON semi with Morocco

-
 Rosenior salutes 'outstanding' start to Chelsea reign
Rosenior salutes 'outstanding' start to Chelsea reign
-
Maduro loyalists stage modest rally as Venezuelan govt courts US

-
 Byrne late penalty fires Leinster into Champions Cup last 16 after 'ding-dong' battle
Byrne late penalty fires Leinster into Champions Cup last 16 after 'ding-dong' battle
-
Rosenior makes flying start as Chelsea rout Charlton in FA Cup

-
 Rallies across US against shooting of woman by immigration agent
Rallies across US against shooting of woman by immigration agent
-
Salah closer to AFCON glory as Egypt dethrone champions Ivory Coast

-
 O'Neil ends 'crazy three days' with Strasbourg cup canter
O'Neil ends 'crazy three days' with Strasbourg cup canter
-
Mitchell leads Cavs over T-Wolves

-
 O'Neil ends 'crazy few days' with Strasbourg cup canter
O'Neil ends 'crazy few days' with Strasbourg cup canter
-
Argentina wildfire burns over 5,500 hectares: governor

-
 Byrne late penalty fires Leinster into Champions Cup last 16
Byrne late penalty fires Leinster into Champions Cup last 16
-
Roma beat Sassuolo to close in on Serie A leaders Inter

-
 Villa's FA Cup win at Spurs leaves Frank on the brink
Villa's FA Cup win at Spurs leaves Frank on the brink
-
Osimhen focused on Nigeria glory not scoring record

-
 Undav calls shots as Stuttgart thump Leverkusen
Undav calls shots as Stuttgart thump Leverkusen
-
Venezuelan prisoners smile to hear of Maduro's fall

-
 Thousands of Irish, French farmers protest EU-Mercosur trade deal
Thousands of Irish, French farmers protest EU-Mercosur trade deal
-
Kiplimo captures third straight world cross country title

-
 Osimhen leads Nigeria past Algeria into AFCON semi-finals
Osimhen leads Nigeria past Algeria into AFCON semi-finals
-
US urges fresh talks between Syria govt, Kurds after deadly clashes

-
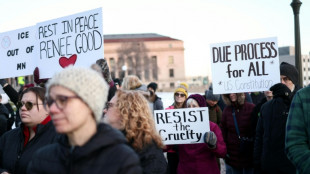 Weekend of US protests after woman killed by immigration agent
Weekend of US protests after woman killed by immigration agent
-
Monaco cling on with 10 men to avoid French Cup shock

-
 Rooney close to tears as brother masterminds FA Cup history
Rooney close to tears as brother masterminds FA Cup history
-
Semenyo scores on Man City debut in 10-goal rout of Exeter

-
 Villarreal sink Alaves to stay in La Liga hunt
Villarreal sink Alaves to stay in La Liga hunt
-
Bristol, Glasgow reach Champions Cup last 16

-
 Freiburg beat 10-man Hamburg to climb to eighth in the Bundesliga
Freiburg beat 10-man Hamburg to climb to eighth in the Bundesliga
-
Venezuela loyalists to rally one week after Maduro's capture

-
 Syrian authorities transferring Kurdish fighters from Aleppo to northeast
Syrian authorities transferring Kurdish fighters from Aleppo to northeast
-
Football: Five memorable FA Cup upsets

-
 Odermatt warms up for Winter Games with Adelboden giant slalom win
Odermatt warms up for Winter Games with Adelboden giant slalom win
-
Benin showcases culture with Vodun Days

-
 Iran crackdown fears grow as protests persist
Iran crackdown fears grow as protests persist
-
Odermatt wins Adelboden giant slalom for sixth World Cup success of season

-
 Holders Crystal Palace stunned by Macclesfield in biggest ever FA Cup shock
Holders Crystal Palace stunned by Macclesfield in biggest ever FA Cup shock
-
Odermatt wins Abelboden giant slalom for sixth World Cup success of season

-
 Poland reach United Cup final despite Swiatek loss to Gauff
Poland reach United Cup final despite Swiatek loss to Gauff
-
India's Gill calls it 'destiny' after shock T20 World Cup snub

-
 'Driven' Vonn storms to 84th World Cup win in Austrian downhill
'Driven' Vonn storms to 84th World Cup win in Austrian downhill
-
Syrian army says stopping Aleppo operations, but Kurds deny fighting over

-
 Thousands of Irish farmers protest EU-Mercosur trade deal
Thousands of Irish farmers protest EU-Mercosur trade deal
-
Vonn storms to 84th World Cup win in Austrian downhill

-
 Anger over fatal Minneapolis shooting fuels US protests
Anger over fatal Minneapolis shooting fuels US protests
-
New rallies erupt in Iran as crackdown fears grow
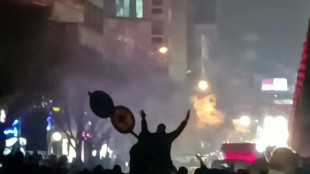
-
 Real Madrid not 'kamikaze' with Mbappe health: Alonso
Real Madrid not 'kamikaze' with Mbappe health: Alonso
-
South Africa defends naval drills with Iran, Russia as 'essential'

-
 Alcaraz beats Sinner in sold-out South Korea exhibition match
Alcaraz beats Sinner in sold-out South Korea exhibition match
-
'Racing against time': Death toll rises after Philippines trash site collapse


Planetary health check warns risk of 'destabilising' Earth systems
Humans are gambling the very stability of Earth's life support systems, scientists said Wednesday, warning that ocean acidity was yet another key planetary threshold to be breached.
A team of global scientists assessed that seven of nine so-called "planetary boundaries" -- processes that regulate Earth's stability, resilience and ability to sustain life -- had now been crossed.
Climate change, biodiversity loss, deforestation, freshwater depletion, overuse of agricultural fertilisers, and the release of artificial chemicals and plastics into the environment were all already deep in the red.
In their new report, the scientists said all seven were "showing trends of increasing pressure -- suggesting further deterioration and destabilisation of planetary health in the near future".
Destructive and polluting activities, particularly the burning of fossil fuels, are driving these further into risky territory and increasingly interacting with each other.
"We are putting the stability of the entire life support system on Earth at risk," said Johan Rockstrom, Director of the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK) in a press conference to launch the research.
The concept of planetary boundaries was first coined in 2009 when only global warming, extinction rates, and nitrogen levels had transgressed their limits.
"We are moving even further away from the safe operating space, risking destabilising our Earth and with an increasing risk growing year by year," said Levke Caesar, co-lead of Planetary Boundaries Science at PIK.
Many of the causes of deterioration are interlinked, showing both the wide-ranging impact of human activities, but also avenues for action.
The use of fossil fuels is a key example, driving climate change, as well as fuelling plastic pollution and the rise in ocean acidification.
- Safety net 'unravelling' -
The world's seas are estimated to have absorbed roughly 30 percent of the excess carbon dioxide released into the atmosphere from the burning of oil, gas and coal.
This alters the pH of the ocean, affecting the ability of organisms like corals, shellfish and some forms of plankton to form shells and skeletons.
Increased ocean acidification since last year's report was partly due to better data and revised calculations.
Scientists said there was already evidence of shell damage, particularly for marine animals in polar and coastal regions.
"What we see in the data is no longer abstract. It is showing up in the world around us right now," said Caesar.
One positive in this year's report is an improvement in global air quality as aerosol emissions fall across the world, despite the continued scourge of severe particulate pollution in some regions.
The final boundary -- ozone depletion -- remains comfortably within safe bounds, which scientists said shows the success of global cooperation to restrict ozone-depleting pollutants.
Researchers have quantified safe boundaries for these interlocking facets of the Earth system, which feed off and amplify each other.
For climate change, for example, the threshold is linked to the concentration of heat-trapping carbon dioxide (CO2) in the atmosphere.
This hovered close to 280 parts per million (ppm) for at least 10,000 years prior to the industrial revolution and researchers suggest the boundary is 350 ppm. Concentrations in 2025 are 423 ppm.
The assessment of the world's biodiversity and ecosystems is even more perilous.
"Nature's safety net is unravelling: Extinctions and loss of natural productivity are far above safe levels, and there is no sign of improvement," the report said.
P.Tamimi--SF-PST



