-
 On rare earth supply, Trump for once seeks allies
On rare earth supply, Trump for once seeks allies
-
Ukrainian chasing sumo greatness after meteoric rise

-
 Draper to make long-awaited return in Davis Cup qualifier
Draper to make long-awaited return in Davis Cup qualifier
-
Can Ilia Malinin fulfil his promise at the Winter Olympics?

-
 CK Hutchison begins arbitration against Panama over annulled canal contract
CK Hutchison begins arbitration against Panama over annulled canal contract
-
UNESCO recognition inspires hope in Afghan artist's city

-
 Ukraine, Russia, US negotiators gather in Abu Dhabi for war talks
Ukraine, Russia, US negotiators gather in Abu Dhabi for war talks
-
WTO must 'reform or die': talks facilitator

-
 Doctors hope UK archive can solve under-50s bowel cancer mystery
Doctors hope UK archive can solve under-50s bowel cancer mystery
-
Stocks swing following latest AI-fuelled sell-off on Wall St

-
 Demanding Dupont set to fire France in Ireland opener
Demanding Dupont set to fire France in Ireland opener
-
Britain's ex-prince Andrew leaves Windsor home: BBC

-
 Coach plots first South Africa World Cup win after Test triumph
Coach plots first South Africa World Cup win after Test triumph
-
Spin-heavy Pakistan hit form, but India boycott risks early T20 exit

-
 Japan eyes Premier League parity by aligning calendar with Europe
Japan eyes Premier League parity by aligning calendar with Europe
-
Whack-a-mole: US academic fights to purge his AI deepfakes

-
 Love in a time of war for journalist and activist in new documentary
Love in a time of war for journalist and activist in new documentary
-
'Unprecedented mass killing': NGOs battle to quantify Iran crackdown scale

-
 Seahawks kid Cooper Kupp seeks new Super Bowl memories
Seahawks kid Cooper Kupp seeks new Super Bowl memories
-
Thousands of Venezuelans march to demand Maduro's release

-
 AI, manipulated images falsely link some US politicians with Epstein
AI, manipulated images falsely link some US politicians with Epstein
-
Move on, says Trump as Epstein files trigger probe into British politician

-
 Arteta backs Arsenal to build on 'magical' place in League Cup final
Arteta backs Arsenal to build on 'magical' place in League Cup final
-
Evil Empire to underdogs: Patriots eye 7th Super Bowl

-
 UBS grilled on Capitol Hill over Nazi-era probe
UBS grilled on Capitol Hill over Nazi-era probe
-
Guardiola 'hurt' by suffering caused in global conflicts

-
 Marseille do their work early to beat Rennes in French Cup
Marseille do their work early to beat Rennes in French Cup
-
Colombia's Petro, Trump hail talks after bitter rift

-
 Trump signs spending bill ending US government shutdown
Trump signs spending bill ending US government shutdown
-
Arsenal sink Chelsea to reach League Cup final

-
 Leverkusen sink St Pauli to book spot in German Cup semis
Leverkusen sink St Pauli to book spot in German Cup semis
-
'We just need something positive' - Monks' peace walk across US draws large crowds

-
 Milan close gap on Inter with 3-0 win over Bologna
Milan close gap on Inter with 3-0 win over Bologna
-
No US immigration agents at Super Bowl: security chief

-
 NASA Moon mission launch delayed to March after test
NASA Moon mission launch delayed to March after test
-
'You are great': Trump makes up with Colombia's Petro in fireworks-free meeting

-
 Spain to seek social media ban for under-16s
Spain to seek social media ban for under-16s
-
X hits back after France summons Musk, raids offices in deepfake probe

-
 LIV Golf events to receive world ranking points: official
LIV Golf events to receive world ranking points: official
-
Russia resumes large-scale Ukraine strikes in glacial weather

-
 US House passes spending bill ending government shutdown
US House passes spending bill ending government shutdown
-
US jet downs Iran drone but talks still on course

-
 UK police launching criminal probe into ex-envoy Mandelson
UK police launching criminal probe into ex-envoy Mandelson
-
US-Iran talks 'still scheduled' after drone shot down: White House

-
 Chomsky sympathized with Epstein over 'horrible' press treatment
Chomsky sympathized with Epstein over 'horrible' press treatment
-
French prosecutors stick to demand for five-year ban for Le Pen

-
 Russia's economic growth slowed to 1% in 2025: Putin
Russia's economic growth slowed to 1% in 2025: Putin
-
Bethell spins England to 3-0 sweep over Sri Lanka in World Cup warm-up

-
 Nagelsmann backs Ter Stegen for World Cup despite 'cruel' injury
Nagelsmann backs Ter Stegen for World Cup despite 'cruel' injury
-
Homage or propaganda? Carnival parade stars Brazil's Lula


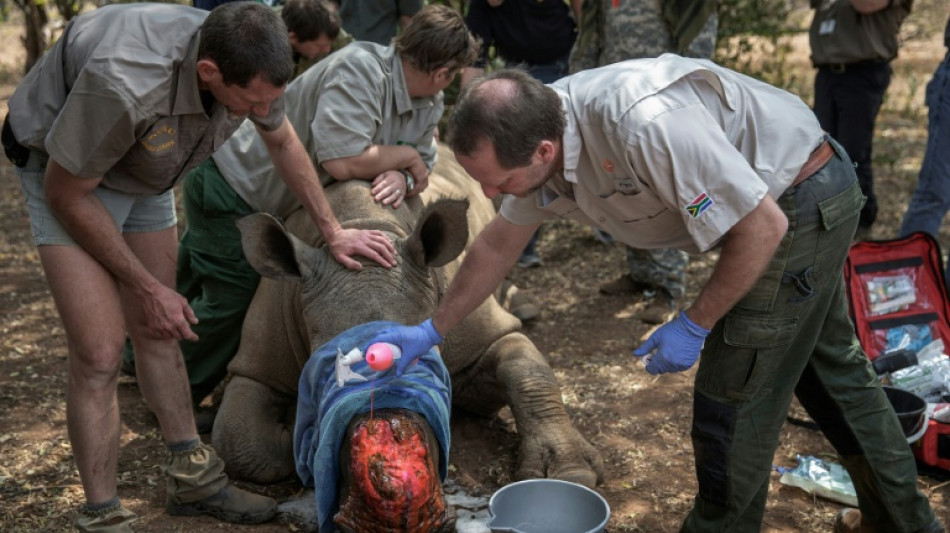
Dehorning of S.African rhinos slashed poaching: study
The dehorning of rhinos resulted in a nearly 80-percent reduction in the poaching of the animals during a seven-year study in a major South African conservation area, researchers said Thursday.
Sawing off the sought-after horns was also a fraction of the cost of other counter-poaching measures such as deploying rangers or tracking dogs, according to the study published in the journal Science.
The study was carried out between 2017 and 2023 in 11 reserves around South Africa's famed Kruger National Park that protect the world's largest rhino population.
During this period, some 1,985 rhinos were poached in the reserves in the Greater Kruger area despite $74 million spent mostly on reactive law enforcement measures that netted around 700 poachers, it said.
By contrast, dehorning 2,284 rhinos cut poaching by 78 percent at just 1.2 percent of that budget, said the study published by the American Association for the Advancement of Science.
"Some poaching of dehorned rhinos continued because poachers targeted horn stumps and regrowth, signalling the need for regular dehorning alongside judicious use of law enforcement," the study said.
South Africa is home to most of the world's rhinos, including the critically endangered black rhino, and is a hotspot for poaching driven by demand in Asia where the horns are used in traditional medicine.
Rhino horn is highly sought after on the black market, where the price by weight rivals that of gold and cocaine.
Alongside ivory, the horns are coveted as status symbols or used in traditional medicine for their supposed aphrodisiac properties.
"Ongoing socioeconomic inequality incentivises a large pool of vulnerable and motivated people to join, or poach for, criminal syndicates even when the risks are high," the researchers said.
Corruption also played a role with gangs receiving insider tips to evade detection and arrest, they said.
- Impacts unclear -
"Although detecting and arresting poachers is essential, strategies that focus on reducing opportunities for and rewards from poaching may be more effective," the study said.
It added, however, that "the effects of dehorning on rhino biology are still unclear, with present research suggesting that dehorning may alter rhino space use but not survival and reproduction."
The co-authors of the study are from South Africa's Nelson Mandela University and the University of Cape Town, and various conservation groups including the Wildlife Conservation Network and United Kingdom's Save the Rhino International.
South Africa had more than 16,000 rhinos at the end of 2023, mostly white rhinos, according to government data.
But at least 34 rhinos were killed each month, the environment minister said in May.
In 2024 South African scientists injected radioactive material into live rhino horns to make them easier to detect at border posts in a pioneering project aimed at curbing poaching.
The radioactive material would not impact the animal's health or the environment in any way but make it poisonous for human consumption, according to the University of the Witwatersrand's radiation and health physics unit which spearheaded the initiative.
Black rhinos are listed by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) as critically endangered.
F.Qawasmeh--SF-PST




