
-
 Russell eager to face Scotland team-mates when Bath play Edinburgh
Russell eager to face Scotland team-mates when Bath play Edinburgh
-
Undav scores again as Stuttgart sink Frankfurt to go third

-
 Fuming French farmers camp out in Paris despite government pledges
Fuming French farmers camp out in Paris despite government pledges
-
Man Utd appoint Carrick as manager to end of the season

-
 Russia strikes power plant, kills four in Ukraine barrage
Russia strikes power plant, kills four in Ukraine barrage
-
France's Le Pen says had 'no sense' of any offence as appeal trial opens

-
 JPMorgan Chase reports mixed results as Dimon defends Fed chief
JPMorgan Chase reports mixed results as Dimon defends Fed chief
-
Vingegaard targets first Giro while thirsting for third Tour title

-
 US pushes forward trade enclave over Armenia
US pushes forward trade enclave over Armenia
-
Alpine release reserve driver Doohan ahead of F1 season

-
 Toulouse's Ntamack out of crunch Champions Cup match against Sale
Toulouse's Ntamack out of crunch Champions Cup match against Sale
-
US takes aim at Muslim Brotherhood in Arab world

-
 Gloucester sign Springbok World Cup-winner Kleyn
Gloucester sign Springbok World Cup-winner Kleyn
-
Trump tells Iranians 'help on its way' as crackdown toll soars

-
 Iran threatens death penalty for 'rioters' as concern grows for protester
Iran threatens death penalty for 'rioters' as concern grows for protester
-
US ends protection for Somalis amid escalating migrant crackdown

-
 Oil prices surge following Trump's Iran tariff threat
Oil prices surge following Trump's Iran tariff threat
-
Fashion student, bodybuilder, footballer: the victims of Iran's crackdown

-
 Trump tells Iranians to 'keep protesting', says 'help on its way'
Trump tells Iranians to 'keep protesting', says 'help on its way'
-
Italian Olympians 'insulted' by torch relay snub

-
 Davos braces for Trump's 'America First' onslaught
Davos braces for Trump's 'America First' onslaught
-
How AI 'deepfakes' became Elon Musk's latest scandal

-
 Albania's waste-choked rivers worsen deadly floods
Albania's waste-choked rivers worsen deadly floods
-
Cancelo rejoins Barca on loan from Al-Hilal

-
 India hunts rampaging elephant that killed 20 people
India hunts rampaging elephant that killed 20 people
-
Nuuk, Copenhagen mull Greenland independence in Trump's shadow

-
 WHO says sugary drinks, alcohol getting cheaper, should be taxed more
WHO says sugary drinks, alcohol getting cheaper, should be taxed more
-
Arteta urges Arsenal to learn from League Cup pain ahead of Chelsea semi

-
 Davos elite, devotees of multilateralism, brace for Trump
Davos elite, devotees of multilateralism, brace for Trump
-
Spanish star Julio Iglesias accused of sexual assault by two ex-employees

-
 Trump's Iran tariff threat pushes oil price higher
Trump's Iran tariff threat pushes oil price higher
-
US consumer inflation holds steady as affordability worries linger

-
 Iran to press capital crime charges for 'rioters': prosecutors
Iran to press capital crime charges for 'rioters': prosecutors
-
Denmark, Greenland set for high-stake talks at White House

-
 Iranian goes on trial in France ahead of possible prisoner swap
Iranian goes on trial in France ahead of possible prisoner swap
-
Cold winter and AI boom pushed US emissions increase in 2025

-
 Hong Kong activist investor David Webb dies at 60
Hong Kong activist investor David Webb dies at 60
-
Try to be Mourinho and I'll fail: new Real Madrid coach Arbeloa

-
 Vingegaard targets Giro d'Italia and Tour de France double
Vingegaard targets Giro d'Italia and Tour de France double
-
South Korean prosecutors demand death penalty for ex-leader Yoon

-
 Iwobi hails Nigerian 'unity' with Super Eagles set for Morocco AFCON semi
Iwobi hails Nigerian 'unity' with Super Eagles set for Morocco AFCON semi
-
Le Pen appeal trial opens with French presidential bid at stake

-
 Iran ex-empress urges security forces to join protesters
Iran ex-empress urges security forces to join protesters
-
Sudan 'lost all sources of revenue' in the war: finance minister to AFP

-
 Freezing rain hampers transport in Central Europe
Freezing rain hampers transport in Central Europe
-
Nuuk, Copenhagen cautiously mull Greenland independence

-
 'Proving the boys wrong': Teenage racers picked for elite driver programme
'Proving the boys wrong': Teenage racers picked for elite driver programme
-
Mbappe absent from training as Arbeloa takes charge at Real Madrid

-
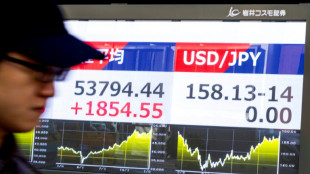 Iran worries push up oil price as world stocks diverge
Iran worries push up oil price as world stocks diverge
-
Volvo Cars pauses battery factory after fruitless partner search

| RBGPF | 1.13% | 82.5 | $ | |
| RYCEF | -0.06% | 17.28 | $ | |
| BP | 2.81% | 35.405 | $ | |
| CMSC | 0.34% | 23.39 | $ | |
| NGG | -2.19% | 78.05 | $ | |
| BTI | 1.63% | 56.605 | $ | |
| AZN | 0.76% | 94.348 | $ | |
| SCS | 0.12% | 16.14 | $ | |
| GSK | -0.74% | 50.02 | $ | |
| RELX | -1.33% | 42.21 | $ | |
| RIO | 1.06% | 83.77 | $ | |
| VOD | -2.85% | 13.175 | $ | |
| JRI | -0.07% | 13.8 | $ | |
| BCC | 0.84% | 83.66 | $ | |
| CMSD | -0.05% | 23.852 | $ | |
| BCE | -0.68% | 23.68 | $ |

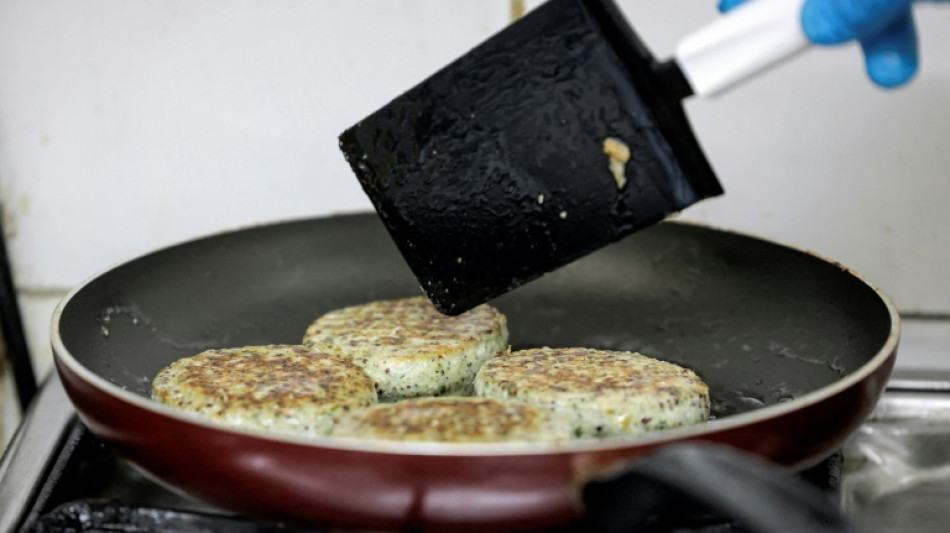
Scientists find simple, safe method to destroy 'forever chemicals'
"Forever chemicals" used in daily items like nonstick pans have long been linked to serious health issues –- a result of their toxicity and extreme resistance to being broken down as waste products.
Chemists in the United States and China on Thursday said they had finally found a breakthrough method to degrade these polluting compounds, referred to as PFAS, using relatively low temperatures and common reagents.
Their results were published in the journal Science, potentially offering a solution to a longstanding source of harm to the environment, livestock and humans.
"It really is why I do science -- so that I can have a positive impact on the world," senior author William Dichtel of Northwestern University told reporters during a news conference.
PFAS, or per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances, were first developed in the 1940s and are now found in a variety of products, including nonstick pans, water-resistant textiles, and fire suppression foams.
Over time, the pollutants have accumulated in the environment, entering the air, soil, groundwater and lakes and rivers as a result of industrial processes and from leaching through landfills.
A study published last week by Stockholm University scientists found rainwater everywhere on the planet is unsafe to drink because of PFAS contamination.
Chronic exposure to even low levels has been linked to liver damage, high cholesterol, reduced immune responses, low birth weights, and several kinds of cancer.
Although PFAS chemicals can be filtered out of water, there are few good solutions for how to dispose of them once they have been removed.
- 10 down, thousands to go -
Current methods to destroy PFAS require harsh treatments, such as incineration at extremely high temperatures or irradiating them ultrasonic waves.
PFAS' indestructability comes from their carbon-flouride bonds, one of the strongest types of bonds in organic chemistry.
Fluorine is the most electronegative element and wants to gain electrons, while carbon is keen to share them.
PFAS molecules contain long chains of these bonds, but the research team was able to identify a glaring weakness common to a certain class of PFAS.
At one end of the molecule, there is a group of charged oxygen atoms which can be targeted using a common solvent and reagent at mild temperatures of 80-120 degrees Celsius, decapitating the head group and leaving behind a reactive tail.
"Once that happens, that provides access to previously unrecognized pathways that cause the entire molecule to fall apart in a cascade of complex reactions," said Dichtel, ultimately making benign end products.
A second part of the study involved using powerful computational methods to map out the quantum mechanics behind the chemical reactions the team performed to destroy the molecules.
The new knowledge could eventually guide further improvements to the method.
The current study focused on 10 PFAS chemicals including a major pollutant called GenX, which for example has contaminated the Cape Fear River in North Carolina.
But it represents just the tip of the iceberg, since the US Environmental Protection Agency has identified more than 12,000 PFAS chemicals.
"There are other classes that don't have the same Achilles’ heel, but each one will have its own weakness," said Dichtel in a statement.
"If we can identify it, then we know how to activate it to destroy it."
P.AbuBaker--SF-PST



