
-
 US pushes forward trade enclave over Armenia
US pushes forward trade enclave over Armenia
-
Alpine release reserve driver Doohan ahead of F1 season

-
 Toulouse's Ntamack out of crunch Champions Cup match against Sale
Toulouse's Ntamack out of crunch Champions Cup match against Sale
-
US takes aim at Muslim Brotherhood in Arab world

-
 Gloucester sign Springbok World Cup-winner Kleyn
Gloucester sign Springbok World Cup-winner Kleyn
-
Trump tells Iranians 'help on its way' as crackdown toll soars

-
 Iran threatens death penalty for 'rioters' as concern grows for protester
Iran threatens death penalty for 'rioters' as concern grows for protester
-
US ends protection for Somalis amid escalating migrant crackdown

-
 Oil prices surge following Trump's Iran tariff threat
Oil prices surge following Trump's Iran tariff threat
-
Fashion student, bodybuilder, footballer: the victims of Iran's crackdown

-
 Trump tells Iranians to 'keep protesting', says 'help on its way'
Trump tells Iranians to 'keep protesting', says 'help on its way'
-
Italian Olympians 'insulted' by torch relay snub

-
 Davos braces for Trump's 'America First' onslaught
Davos braces for Trump's 'America First' onslaught
-
How AI 'deepfakes' became Elon Musk's latest scandal

-
 Albania's waste-choked rivers worsen deadly floods
Albania's waste-choked rivers worsen deadly floods
-
Cancelo rejoins Barca on loan from Al-Hilal

-
 India hunts rampaging elephant that killed 20 people
India hunts rampaging elephant that killed 20 people
-
Nuuk, Copenhagen mull Greenland independence in Trump's shadow

-
 WHO says sugary drinks, alcohol getting cheaper, should be taxed more
WHO says sugary drinks, alcohol getting cheaper, should be taxed more
-
Arteta urges Arsenal to learn from League Cup pain ahead of Chelsea semi

-
 Davos elite, devotees of multilateralism, brace for Trump
Davos elite, devotees of multilateralism, brace for Trump
-
Spanish star Julio Iglesias accused of sexual assault by two ex-employees

-
 Trump's Iran tariff threat pushes oil price higher
Trump's Iran tariff threat pushes oil price higher
-
US consumer inflation holds steady as affordability worries linger

-
 Iran to press capital crime charges for 'rioters': prosecutors
Iran to press capital crime charges for 'rioters': prosecutors
-
Denmark, Greenland set for high-stake talks at White House

-
 Iranian goes on trial in France ahead of possible prisoner swap
Iranian goes on trial in France ahead of possible prisoner swap
-
Cold winter and AI boom pushed US emissions increase in 2025

-
 Hong Kong activist investor David Webb dies at 60
Hong Kong activist investor David Webb dies at 60
-
Try to be Mourinho and I'll fail: new Real Madrid coach Arbeloa

-
 Vingegaard targets Giro d'Italia and Tour de France double
Vingegaard targets Giro d'Italia and Tour de France double
-
South Korean prosecutors demand death penalty for ex-leader Yoon

-
 Iwobi hails Nigerian 'unity' with Super Eagles set for Morocco AFCON semi
Iwobi hails Nigerian 'unity' with Super Eagles set for Morocco AFCON semi
-
Le Pen appeal trial opens with French presidential bid at stake

-
 Iran ex-empress urges security forces to join protesters
Iran ex-empress urges security forces to join protesters
-
Sudan 'lost all sources of revenue' in the war: finance minister to AFP

-
 Freezing rain hampers transport in Central Europe
Freezing rain hampers transport in Central Europe
-
Nuuk, Copenhagen cautiously mull Greenland independence

-
 'Proving the boys wrong': Teenage racers picked for elite driver programme
'Proving the boys wrong': Teenage racers picked for elite driver programme
-
Mbappe absent from training as Arbeloa takes charge at Real Madrid

-
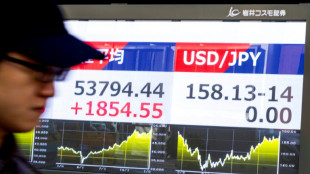 Iran worries push up oil price as world stocks diverge
Iran worries push up oil price as world stocks diverge
-
Volvo Cars pauses battery factory after fruitless partner search

-
 Social media harms teens, watchdog warns, as France weighs ban
Social media harms teens, watchdog warns, as France weighs ban
-
Central bank chiefs voice 'full solidarity' with US Fed, Powell

-
 Greece airspace shutdown exposes badly outdated systems
Greece airspace shutdown exposes badly outdated systems
-
France climate goals off track as emissions cuts slow again

-
 Boeing sells 50 737 MAX jets to leasing group ACG
Boeing sells 50 737 MAX jets to leasing group ACG
-
Freezing rain paralyses transport in Central Europe

-
 Man Utd reach deal to appoint Carrick as interim boss: reports
Man Utd reach deal to appoint Carrick as interim boss: reports
-
Trump hits Iran trade partners with tariffs as protest toll soars

| SCS | 0.12% | 16.14 | $ | |
| RBGPF | 1.13% | 82.5 | $ | |
| CMSC | 0.34% | 23.39 | $ | |
| GSK | -1.18% | 49.8 | $ | |
| RELX | -1.66% | 42.07 | $ | |
| RIO | 1.21% | 83.895 | $ | |
| CMSD | 0.06% | 23.879 | $ | |
| NGG | -2.52% | 77.8 | $ | |
| BCC | 0.76% | 83.595 | $ | |
| RYCEF | -0.06% | 17.28 | $ | |
| BCE | -0.44% | 23.735 | $ | |
| JRI | -0.07% | 13.8 | $ | |
| AZN | -0.1% | 93.54 | $ | |
| VOD | -2.65% | 13.2 | $ | |
| BP | 2.81% | 35.405 | $ | |
| BTI | 1.54% | 56.55 | $ |

What we know of the symptoms and spread of monkeypox
With monkeypox surging across the world, experts are gathering more evidence on how people catch it and its typical symptoms.
Several months into the epidemic, it is clear the wave of infections is linked above all to sexual intercourse between men.
Nearly 28,000 cases have been confirmed worldwide in the last three months and the first deaths are starting to be recorded.
Here is a summary of what we know:
- Who is catching it? -
Monkeypox has been around in a dozen African countries for decades, but in contrast to previous outbreaks on the continent, the virus is now predominantly spread through sexual activity.
Some 99 percent of US cases have so far been among men who have sex with men (MSM).
In Africa, the virus notably affects children.
In the last three weeks studies printed in leading medical publications -- British Medical Journal (BMJ), The Lancet and New England Journal of Medicine (NEJM) -- painted a clinical picture of the current spike in infections, even if it is still early days and the results are based on only a few hundred cases.
In each study, the MSM community accounts for nearly all cases.
- How is it transmitted? -
The male sex link was no surprise as it appeared from the first recorded observations and has been targeted by health authorities.
This leads to the sensitive question of whether the virus is transmitted through sexual activity.
The latest clinical reports leave little doubt.
"Our study strengthens the evidence for skin-to-skin contact during sex as the dominant mechanism of transmission of monkeypox, with important implications for disease control," said The Lancet with data from several Spanish hospitals.
The viral charge had been found to be much higher in patients' skin lesions than in their breathing equipment.
This observation seems to undermine the idea pushed by some researchers that airborne transmission was also playing a major role in the spread of cases.
At the same time monkeypox is not thought to be caught via sperm, and although that has not been totally ruled out, current research is far from proving it.
- Symptoms? -
All three studies agreed on the main symptoms.
"The characteristics of the cohort we describe differ from those of populations affected in previous outbreaks in endemic regions," the BMJ noted in the study of UK cases.
The two key elements are fever, often with muscular aches, and skin lesions which scab over.
But the details vary, probably because of the type of transmission, with recent cases heavily linked to sexual activity.
For all three studies, the lesions often break out in the anus, penis and mouth. One complication that has previously been rarely observed has been inflammation of the rectum or a swelling on the penis.
The Lancet found complications occurred in 40 percent of cases and the NEJM in some 20 percent.
But there was also some good news about the gravity of the illness.
"Clinical outcomes in this case series were reassuring. Most cases were mild and self-limited, and there were no deaths," the NEJM said.
"Although 13 percent of the persons were admitted to a hospital, no serious complications were reported in the majority of those admitted."
- Questions remain -
The Lancet report raised the issue of the efficacy of vaccines, given that 18 percent of cases were in people who had already received a jab meant to protect against monkeypox.
But some patients had had the vaccination for many years, even decades before catching the virus.
It is also unclear how other illnesses increase the risk of catching monkeypox. About 40 percent of patients in the Lancet study carried HIV, but it was impossible to work out if there was a direct link between the two.
F.Qawasmeh--SF-PST



