
-
 Trump tells Iranians to 'keep protesting', says 'help on its way'
Trump tells Iranians to 'keep protesting', says 'help on its way'
-
Italian Olympians 'insulted' by torch relay snub

-
 Davos braces for Trump's 'America First' onslaught
Davos braces for Trump's 'America First' onslaught
-
How AI 'deepfakes' became Elon Musk's latest scandal

-
 Albania's waste-choked rivers worsen deadly floods
Albania's waste-choked rivers worsen deadly floods
-
Cancelo rejoins Barca on loan from Al-Hilal

-
 India hunts rampaging elephant that killed 20 people
India hunts rampaging elephant that killed 20 people
-
Nuuk, Copenhagen mull Greenland independence in Trump's shadow

-
 WHO says sugary drinks, alcohol getting cheaper, should be taxed more
WHO says sugary drinks, alcohol getting cheaper, should be taxed more
-
Arteta urges Arsenal to learn from League Cup pain ahead of Chelsea semi

-
 Davos elite, devotees of multilateralism, brace for Trump
Davos elite, devotees of multilateralism, brace for Trump
-
Spanish star Julio Iglesias accused of sexual assault by two ex-employees

-
 Trump's Iran tariff threat pushes oil price higher
Trump's Iran tariff threat pushes oil price higher
-
US consumer inflation holds steady as affordability worries linger

-
 Iran to press capital crime charges for 'rioters': prosecutors
Iran to press capital crime charges for 'rioters': prosecutors
-
Denmark, Greenland set for high-stake talks at White House

-
 Iranian goes on trial in France ahead of possible prisoner swap
Iranian goes on trial in France ahead of possible prisoner swap
-
Cold winter and AI boom pushed US emissions increase in 2025

-
 Hong Kong activist investor David Webb dies at 60
Hong Kong activist investor David Webb dies at 60
-
Try to be Mourinho and I'll fail: new Real Madrid coach Arbeloa

-
 Vingegaard targets Giro d'Italia and Tour de France double
Vingegaard targets Giro d'Italia and Tour de France double
-
South Korean prosecutors demand death penalty for ex-leader Yoon

-
 Iwobi hails Nigerian 'unity' with Super Eagles set for Morocco AFCON semi
Iwobi hails Nigerian 'unity' with Super Eagles set for Morocco AFCON semi
-
Le Pen appeal trial opens with French presidential bid at stake

-
 Iran ex-empress urges security forces to join protesters
Iran ex-empress urges security forces to join protesters
-
Sudan 'lost all sources of revenue' in the war: finance minister to AFP

-
 Freezing rain hampers transport in Central Europe
Freezing rain hampers transport in Central Europe
-
Nuuk, Copenhagen cautiously mull Greenland independence

-
 'Proving the boys wrong': Teenage racers picked for elite driver programme
'Proving the boys wrong': Teenage racers picked for elite driver programme
-
Mbappe absent from training as Arbeloa takes charge at Real Madrid

-
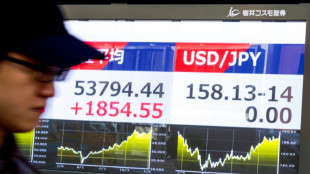
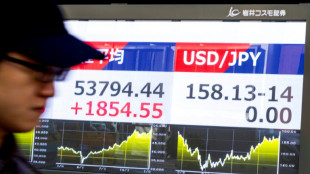 Iran worries push up oil price as world stocks diverge
Iran worries push up oil price as world stocks diverge
-
Volvo Cars pauses battery factory after fruitless partner search

-
 Social media harms teens, watchdog warns, as France weighs ban
Social media harms teens, watchdog warns, as France weighs ban
-
Central bank chiefs voice 'full solidarity' with US Fed, Powell

-
 Greece airspace shutdown exposes badly outdated systems
Greece airspace shutdown exposes badly outdated systems
-
France climate goals off track as emissions cuts slow again

-
 Boeing sells 50 737 MAX jets to leasing group ACG
Boeing sells 50 737 MAX jets to leasing group ACG
-
Freezing rain paralyses transport in Central Europe

-
 Man Utd reach deal to appoint Carrick as interim boss: reports
Man Utd reach deal to appoint Carrick as interim boss: reports
-
Trump hits Iran trade partners with tariffs as protest toll soars

-
 Is China a threat to Greenland as Trump argues?
Is China a threat to Greenland as Trump argues?
-
Takaichi says urged S. Korea's Lee to help 'ensure regional stability'

-
 South Korean prosecutors set to demand heavy sentence for Yoon
South Korean prosecutors set to demand heavy sentence for Yoon
-
Honduras electoral authorities reject vote recount

-
 Tractors in Paris to protest EU's trade deal with S. America
Tractors in Paris to protest EU's trade deal with S. America
-
Asian markets rise, Iran worries push up oil
-
 Williams loses golden oldie clash in final Australian Open warm-up
Williams loses golden oldie clash in final Australian Open warm-up
-
Kyrgios stands by decision to skip Australian Open singles

-
 Disaster losses drop in 2025, picture still 'alarming': Munich Re
Disaster losses drop in 2025, picture still 'alarming': Munich Re
-
Williams, 45, loses in first round of final Australian Open warm-up

| SCS | 0.12% | 16.14 | $ | |
| CMSC | -0.21% | 23.26 | $ | |
| BCC | -0.21% | 82.79 | $ | |
| RIO | 1.07% | 83.775 | $ | |
| NGG | -2.7% | 77.66 | $ | |
| GSK | -0.9% | 49.94 | $ | |
| RBGPF | 1.13% | 82.5 | $ | |
| CMSD | -0.44% | 23.761 | $ | |
| BCE | -0.32% | 23.765 | $ | |
| JRI | -0.15% | 13.79 | $ | |
| RYCEF | -0.06% | 17.28 | $ | |
| VOD | -2.61% | 13.205 | $ | |
| BP | 1.95% | 35.095 | $ | |
| AZN | 0.39% | 94 | $ | |
| BTI | 1.51% | 56.535 | $ | |
| RELX | -1.6% | 42.095 | $ |

Pair of new studies point to natural Covid origin
An animal market in China's Wuhan really was the epicenter of the Covid pandemic, according to a pair of new studies in the journal Science published Tuesday that claimed to have tipped the balance in the debate about the virus' origins.
Answering the question of whether the disease spilled over naturally from animals to humans, or was the result of a lab accident, is viewed as vital to averting the next pandemic and saving millions of lives.
The first paper analyzed the geographic pattern of Covid cases in the outbreak's first month, December 2019, showing the first cases were tightly clustered around the Huanan Market.
The second examined genomic data from the earliest cases to study the virus' early evolution, concluding it was unlikely the coronavirus circulated widely in humans prior to November 2019.
Both were previously posted as "preprints" but have now been vetted by scientific peer review and appear in a prestigious journal.
Michael Worobey of the University of Arizona, who co-authored both papers, had previously called on the scientific community in a letter to be more open to the idea that the virus was the result of a lab leak.
But the findings moved him "to the point where now I also think it's just not plausible that this virus was introduced any other way than through the wildlife trade at the Wuhan market," he told reporters on a call about the findings.
Though previous investigation had centered on the live animal market, researchers wanted more evidence to determine it was really the progenitor of the outbreak, as opposed to an amplifier.
This required neighborhood-level study within Wuhan to be more certain the virus was "zoonotic" -- that it jumped from animals to people.
The first study's team used mapping tools to determine the location of the first 174 cases identified by the World Health Organization, finding 155 of them were in Wuhan.
Further, these cases clustered tightly around the market -- and some early patients with no recent history of visiting the market lived very close to it.
Mammals now known to be infectable with the virus -- including red foxes, hog badgers and raccoon dogs, were all sold live in the market, the team showed.
- Two introductions to humans -
They also tied positive samples from patients in early 2020 to the western portion of the market, which sold live or freshly butchered animals in late 2019.
The tightly confined early cases contrasted with how it radiated throughout the rest of the city by January and February, which the researchers confirmed by drilling into social media check-in data from the Weibo app.
"This tells us the virus was not circulating cryptically," Worobey said in a statement. "It really originated at that market and spread out from there."
The second study focused on resolving an apparent discrepancy in the virus' early evolution.
Two lineages, A and B, marked the early pandemic.
But while A was closer to the virus found in bats, suggesting the coronavirus in humans came from this source and that A gave rise to B, it was B that was found to be far more present around the market.
The researchers used a technique called "molecular clock analysis," which relies on the rate at which genetic mutations occur over time to reconstruct a timeline of evolution -- and found it unlikely that A gave rise to B.
"Otherwise, lineage A would have had to have been evolving in slow motion compared to the lineage B virus, which just doesn't make biological sense," said Worobey.
Instead, the probable scenario was both jumped from animals at the market to humans on separate occasions, in November and December 2019. The researchers concluded it was unlikely that there was human circulation prior to November 2019.
Under this scenario, there were probably other animal-to-human transmissions at the market that failed to manifest as Covid cases.
"Have we disproven the lab leak theory? No, we have not. Will we ever be able to know? No," said co-author Kristian Anderson of The Scripps Research Institute.
"But I think what's really important here is that there are possible scenarios and they're plausible scenarios and it's really important to understand that possible does not mean equally likely."
C.AbuSway--SF-PST



