
-
 Iran to press capital crime charges for 'rioters': prosecutors
Iran to press capital crime charges for 'rioters': prosecutors
-
Denmark, Greenland set for high-stake talks at White House

-
 Iranian goes on trial in France ahead of possible prisoner swap
Iranian goes on trial in France ahead of possible prisoner swap
-
Cold winter and AI boom pushed US emissions increase in 2025

-
 Hong Kong activist investor David Webb dies at 60
Hong Kong activist investor David Webb dies at 60
-
Try to be Mourinho and I'll fail: new Real Madrid coach Arbeloa

-
 Vingegaard targets Giro d'Italia and Tour de France double
Vingegaard targets Giro d'Italia and Tour de France double
-
South Korean prosecutors demand death penalty for ex-leader Yoon

-
 Iwobi hails Nigerian 'unity' with Super Eagles set for Morocco AFCON semi
Iwobi hails Nigerian 'unity' with Super Eagles set for Morocco AFCON semi
-
Le Pen appeal trial opens with French presidential bid at stake

-
 Iran ex-empress urges security forces to join protesters
Iran ex-empress urges security forces to join protesters
-
Sudan 'lost all sources of revenue' in the war: finance minister to AFP

-
 Freezing rain hampers transport in Central Europe
Freezing rain hampers transport in Central Europe
-
Nuuk, Copenhagen cautiously mull Greenland independence

-
 'Proving the boys wrong': Teenage racers picked for elite driver programme
'Proving the boys wrong': Teenage racers picked for elite driver programme
-
Mbappe absent from training as Arbeloa takes charge at Real Madrid

-
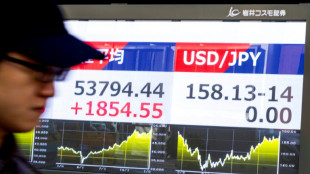 Iran worries push up oil price as world stocks diverge
Iran worries push up oil price as world stocks diverge
-
Volvo Cars pauses battery factory after fruitless partner search

-
 Social media harms teens, watchdog warns, as France weighs ban
Social media harms teens, watchdog warns, as France weighs ban
-
Central bank chiefs voice 'full solidarity' with US Fed, Powell

-
 Greece airspace shutdown exposes badly outdated systems
Greece airspace shutdown exposes badly outdated systems
-
France climate goals off track as emissions cuts slow again

-
 Boeing sells 50 737 MAX jets to leasing group ACG
Boeing sells 50 737 MAX jets to leasing group ACG
-
Freezing rain paralyses transport in Central Europe

-
 Man Utd reach deal to appoint Carrick as interim boss: reports
Man Utd reach deal to appoint Carrick as interim boss: reports
-
Trump hits Iran trade partners with tariffs as protest toll soars

-
 Is China a threat to Greenland as Trump argues?
Is China a threat to Greenland as Trump argues?
-
Takaichi says urged S. Korea's Lee to help 'ensure regional stability'

-
 South Korean prosecutors set to demand heavy sentence for Yoon
South Korean prosecutors set to demand heavy sentence for Yoon
-
Honduras electoral authorities reject vote recount

-
 Tractors in Paris to protest EU's trade deal with S. America
Tractors in Paris to protest EU's trade deal with S. America
-
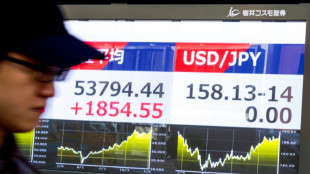
Asian markets rise, Iran worries push up oil
-
 Williams loses golden oldie clash in final Australian Open warm-up
Williams loses golden oldie clash in final Australian Open warm-up
-
Kyrgios stands by decision to skip Australian Open singles

-
 Disaster losses drop in 2025, picture still 'alarming': Munich Re
Disaster losses drop in 2025, picture still 'alarming': Munich Re
-
Williams, 45, loses in first round of final Australian Open warm-up

-
 Doncic scores 42 points but Lakers humbled by Kings
Doncic scores 42 points but Lakers humbled by Kings
-
'Serious threat': Indonesia legal reform sparks rights challenges

-
 Rodgers misery as Texans rout Steelers to advance in NFL playoffs
Rodgers misery as Texans rout Steelers to advance in NFL playoffs
-
Morocco's Bono 'one of best goalkeepers in the world'

-
 Salah and Mane meet again with AFCON final place on the line
Salah and Mane meet again with AFCON final place on the line
-
French museum fare hikes for non-European tourists spark outcry

-
 In 'big trouble'? The factors determining Iran's future
In 'big trouble'? The factors determining Iran's future
-
Osimhen finds AFCON scoring touch to give Nigeria cutting edge

-
 Trump announces tariffs on Iran trade partners as protest toll rises
Trump announces tariffs on Iran trade partners as protest toll rises
-
Sabalenka favourite at Australian Open but faces Swiatek, US threats

-
 Gay Australian footballer Cavallo alleges former club was homophobic
Gay Australian footballer Cavallo alleges former club was homophobic
-
Global Sports Brand U.S. Polo Assn. Announced as Official Jersey and Apparel Sponsor for the Legendary Snow Polo World Cup St. Moritz

-
 Trump has options on Iran, but first must define goal
Trump has options on Iran, but first must define goal
-
Paris FC's Ikone stuns PSG to knock out former club from French Cup

| SCS | 0.12% | 16.14 | $ | |
| CMSD | -0.32% | 23.79 | $ | |
| BCC | -0.19% | 82.72 | $ | |
| BCE | -0.27% | 23.77 | $ | |
| RIO | 1.03% | 83.72 | $ | |
| RELX | -0.51% | 42.55 | $ | |
| RYCEF | -0.93% | 17.29 | $ | |
| NGG | -2.37% | 77.91 | $ | |
| JRI | 0.1% | 13.814 | $ | |
| VOD | -2.08% | 13.274 | $ | |
| RBGPF | 1.13% | 82.5 | $ | |
| CMSC | 0.17% | 23.31 | $ | |
| AZN | -0.39% | 93.265 | $ | |
| GSK | -1.63% | 49.57 | $ | |
| BTI | 0.2% | 55.79 | $ | |
| BP | 1.43% | 34.895 | $ |

Climate change's fingerprints on ever hotter heatwaves
Hotter, longer, more frequent. Heatwaves such as the one currently roasting much of Europe, or the record-shattering hot spell endured by India and Pakistan in March, are an unmistakable sign of climate change, experts said Monday.
- Humans to blame -
"Every heatwave that we are experiencing today has been made hotter and more frequent because of human induced climate change," said Friederike Otto, senior lecturer at Imperial College London's Grantham Institute for Climate Change.
"It's pure physics, we know how greenhouse gas molecules behave, we know there are more in the atmosphere, the atmosphere is getting warmer and that means we are expecting to see more frequent heatwaves and hotter heatwaves."
In recent years, advances in the discipline known as attribution science have allowed climatologists to calculate how much global heating contributes to individual extreme weather events.
The India-Pakistan heatwave, for example, was calculated to have been 30 times more likely with the more than 1.1 degrees Celsius of warming that human activity has caused since the mid-nineteenth century.
The heatwave that shattered records in North America in June 2021, leaving hundreds dead as temperatures soared to 50C in places, would have been virtually impossible without global heating.
And the last major European heatwave, in 2019, was made 3C hotter by climate change.
"The increase in the frequency, duration, and intensity of these events over recent decades is clearly linked to the observed warming of the planet and can be attributed to human activity," the World Meteorological Organisation said in a Monday statement.
- Worse to come -
However unbearable temperatures get this week, scientists are unanimous: there is worse to come.
At 1.5C of warming -- the most ambitious Paris climate agreement goal -- UN climate scientists calculate that heatwaves will be more than four times more likely than the pre-industrial baseline.
At 2C or warming, that figure reaches 5.6 times more likely, and at 4C heatwaves will be nearly 10 times more likely to occur.
Despite three decades of UN-led negotiations, countries' climate plans currently put Earth on course to warm a "catastrophic" 2.7C, according to the UN.
Matthieu Sorel, a climatologist at Meteo-France, said that climate change was already influencing the frequency and severity of heatwaves.
"We're on the way to hotter and hotter summers, where 35C becomes the norm and 40C will be reached regularly," he said.
- Danger of death -
The heatwaves of the future depend largely on how rapidly the global economy can decarbonise.
The UN's climate science panel has calculated that 14 percent of humanity will be hit with dangerous heat every five years on average with 1.5C of warming, compared with 37 percent at 2C.
"In all of places in the world where we have data there is an increase in mortality risk when we are exposed to high temperatures," said Eunice Lo, a climate scientist at the University of Bristol's Cabot Institute for the Environment.
It's not only the most vulnerable people who are at risk of health impacts frim heat, it's even the fit and healthy people who will be at risk."
There is a real risk in future of so-called "wet bulb" temperatures -- where heat combines with humidity to create conditions where the human body cannot cool itself via perspiration -- breaching lethal levels in many parts of the world.
As well as the imminent threat to human health, heatwaves compound drought and make larger areas vulnerable to wild fires, such as those now raging across parts of France, Portugal, Spain, Greece and Morocco.
They also menace the food supply.
India, the world's second-largest wheat producer, chose to ban grain exports after the heatwave impacted harvests, worsening a shortage in some countries prompted by Russia's invasion of key exporter Ukraine.
K.AbuTaha--SF-PST




