
-
 Rams survive Panthers scare to advance in NFL playoffs
Rams survive Panthers scare to advance in NFL playoffs
-
Rallies across US after woman shot and killed by immigration agent

-
 Egypt dump out holders Ivory Coast as Nigeria set up AFCON semi with Morocco
Egypt dump out holders Ivory Coast as Nigeria set up AFCON semi with Morocco
-
Rosenior salutes 'outstanding' start to Chelsea reign

-
 Maduro loyalists stage modest rally as Venezuelan govt courts US
Maduro loyalists stage modest rally as Venezuelan govt courts US
-
Byrne late penalty fires Leinster into Champions Cup last 16 after 'ding-dong' battle

-
 Rosenior makes flying start as Chelsea rout Charlton in FA Cup
Rosenior makes flying start as Chelsea rout Charlton in FA Cup
-
Rallies across US against shooting of woman by immigration agent

-
 Salah closer to AFCON glory as Egypt dethrone champions Ivory Coast
Salah closer to AFCON glory as Egypt dethrone champions Ivory Coast
-
O'Neil ends 'crazy three days' with Strasbourg cup canter

-
 Mitchell leads Cavs over T-Wolves
Mitchell leads Cavs over T-Wolves
-
O'Neil ends 'crazy few days' with Strasbourg cup canter

-
 Argentina wildfire burns over 5,500 hectares: governor
Argentina wildfire burns over 5,500 hectares: governor
-
Byrne late penalty fires Leinster into Champions Cup last 16

-
 Roma beat Sassuolo to close in on Serie A leaders Inter
Roma beat Sassuolo to close in on Serie A leaders Inter
-
Villa's FA Cup win at Spurs leaves Frank on the brink

-
 Osimhen focused on Nigeria glory not scoring record
Osimhen focused on Nigeria glory not scoring record
-
Undav calls shots as Stuttgart thump Leverkusen

-
 Venezuelan prisoners smile to hear of Maduro's fall
Venezuelan prisoners smile to hear of Maduro's fall
-
Thousands of Irish, French farmers protest EU-Mercosur trade deal

-
 Kiplimo captures third straight world cross country title
Kiplimo captures third straight world cross country title
-
Osimhen leads Nigeria past Algeria into AFCON semi-finals

-
 US urges fresh talks between Syria govt, Kurds after deadly clashes
US urges fresh talks between Syria govt, Kurds after deadly clashes
-
Weekend of US protests after woman killed by immigration agent
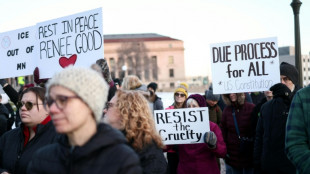
-
 Monaco cling on with 10 men to avoid French Cup shock
Monaco cling on with 10 men to avoid French Cup shock
-
Rooney close to tears as brother masterminds FA Cup history

-
 Semenyo scores on Man City debut in 10-goal rout of Exeter
Semenyo scores on Man City debut in 10-goal rout of Exeter
-
Villarreal sink Alaves to stay in La Liga hunt

-
 Bristol, Glasgow reach Champions Cup last 16
Bristol, Glasgow reach Champions Cup last 16
-
Freiburg beat 10-man Hamburg to climb to eighth in the Bundesliga

-
 Venezuela loyalists to rally one week after Maduro's capture
Venezuela loyalists to rally one week after Maduro's capture
-
Syrian authorities transferring Kurdish fighters from Aleppo to northeast

-
 Football: Five memorable FA Cup upsets
Football: Five memorable FA Cup upsets
-
Odermatt warms up for Winter Games with Adelboden giant slalom win

-
 Benin showcases culture with Vodun Days
Benin showcases culture with Vodun Days
-
Iran crackdown fears grow as protests persist

-
 Odermatt wins Adelboden giant slalom for sixth World Cup success of season
Odermatt wins Adelboden giant slalom for sixth World Cup success of season
-
Holders Crystal Palace stunned by Macclesfield in biggest ever FA Cup shock

-
 Odermatt wins Abelboden giant slalom for sixth World Cup success of season
Odermatt wins Abelboden giant slalom for sixth World Cup success of season
-
Poland reach United Cup final despite Swiatek loss to Gauff

-
 India's Gill calls it 'destiny' after shock T20 World Cup snub
India's Gill calls it 'destiny' after shock T20 World Cup snub
-
'Driven' Vonn storms to 84th World Cup win in Austrian downhill

-
 Syrian army says stopping Aleppo operations, but Kurds deny fighting over
Syrian army says stopping Aleppo operations, but Kurds deny fighting over
-
Thousands of Irish farmers protest EU-Mercosur trade deal

-
 Vonn storms to 84th World Cup win in Austrian downhill
Vonn storms to 84th World Cup win in Austrian downhill
-
Anger over fatal Minneapolis shooting fuels US protests

-
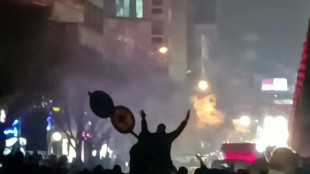 New rallies erupt in Iran as crackdown fears grow
New rallies erupt in Iran as crackdown fears grow
-
Real Madrid not 'kamikaze' with Mbappe health: Alonso

-
 South Africa defends naval drills with Iran, Russia as 'essential'
South Africa defends naval drills with Iran, Russia as 'essential'
-
Alcaraz beats Sinner in sold-out South Korea exhibition match


How much progress has been made against Alzheimer's disease?
After decades of unsuccessful research, two new drugs and a pioneering blood test have recently given Alzheimer's patients hope of fighting back against the debilitating disease -- but questions remain about their effectiveness.
Any path toward a cure also remains elusive for Alzheimer's, which accounts for around 70 percent of dementia cases worldwide and is a leading cause of death among the elderly.
Ahead of Alzheimer's Day on Sunday, here is what to know about recent advances to prevent, diagnose and treat the disease.
- How effective are the new drugs? -
Billions of dollars have been spent trying to find a treatment for Alzheimer's disease over the decades, but those efforts have stubbornly fallen short -- at least until recently.
Eli Lilly's donanemab and Biogen and Eisai's lecanemab are the first treatments proven to significantly slow the progression of Alzheimer's.
But the expensive treatments are only modestly effective, and work only for patients at an early stage of the disease. There can also be serious side effects including potentially deadly brain haemorrhages.
That has sparked a debate about whether the benefits of the drugs outweigh the risks, leading to national health regulators taking different stances.
Lecanemab, which is sold under the brand name Leqembi, has been approved in many countries including the United States.
But French health authorities advised the state-run insurance system not to reimburse payment for the drug.
It followed in the footsteps of the UK's state-run health service, whose spending watchdog said this year that both new Alzheimer's drugs did not show enough benefits given their price.
- What about early diagnosis? -
Another debate roiling Alzheimer's research -- and which has also seen a growing divide between Europe and the United States -- revolves around how to diagnose the disease.
The standard method of diagnosing Alzheimer's has required an invasive and expensive lumbar puncture, which can rule out some more at-risk patients.
But a simple blood test that detects "biological markers" of the disease has recently been developed.
US authorities have authorised the test since May, but Europe has not yet approved any Alzheimer's blood test, one of which is the subject of a recently launched national clinical trial in Britain.
The question is whether the blood test will ever be enough by itself to confidently diagnose the disease.
Last year the US nonprofit Alzheimer's Association changed its criteria to say that biomarkers alone were sufficient.
But in Europe, most specialists think a thorough clinical exam will still be needed to confirm a person's cognitive and functional decline.
Many patients "with abnormal biomarkers never develop dementia", Dutch neurologist Edo Richard told AFP.
Richard is also sceptical of the two new Alzheimer's drugs.
The two issues are linked, because proponents of the drugs believe that being able to diagnose the disease before noticeable symptoms appear could amplify the impact of the treatments.
- Can Alzheimer's be prevented? -
One area of consensus is what makes people more at risk of getting Alzheimer's disease and dementia more broadly.
Nearly half of all cases are linked to factors such as obesity, smoking, drinking alcohol, physical inactivity and hearing loss, according to an expert review in The Lancet last year.
There is an increasing amount of research seeking to determine whether programmes encouraging people to exercise and eat better are effective at fighting Alzheimer's.
But so far the randomised controlled trials "targeting these risk factors have shown limited to no effects on cognitive decline or dementia", Richard said.
A recent JAMA study found that the cognitive decline of Alzheimer's patients slowed slightly after undergoing two years of intensive support to be healthier.
For people suffering from Alzheimer's and their families, this kind of progress may not look like much, French epidemiologist Cecilia Samieri acknowledged at a conference this month.
But compared to where things were just a few years ago, "it's already huge", Samieri said.
She said she believed that only trials lasting 10 to 15 years could really show how effective such interventions could be against long-developing diseases such as Alzheimer's.
F.AbuShamala--SF-PST




