
-
 Sabalenka fires Australian Open warning with Brisbane domination
Sabalenka fires Australian Open warning with Brisbane domination
-
In Gaza hospital, patients cling to MSF as Israel orders it out

-
 New protests hit Iran as alarm grows over crackdown 'massacre'
New protests hit Iran as alarm grows over crackdown 'massacre'
-
Svitolina powers to Auckland title in Australian Open warm-up

-
 Keys draws on happy Adelaide memories before Australian Open defence
Keys draws on happy Adelaide memories before Australian Open defence
-
Scores of homes razed, one dead in Australian bushfires

-
 Ugandan opposition turns national flag into protest symbol
Ugandan opposition turns national flag into protest symbol
-
Bears banish Packers, Rams survive Panthers playoff scare

-
 'Quad God' Malinin warms up for Olympics with US skating crown
'Quad God' Malinin warms up for Olympics with US skating crown
-
India eyes new markets with US trade deal limbo

-
 Syria's Kurdish fighters agree to leave Aleppo after deadly clashes
Syria's Kurdish fighters agree to leave Aleppo after deadly clashes
-
New York's Chrysler Building, an art deco jewel, seeks new owner

-
 AI toys look for bright side after troubled start
AI toys look for bright side after troubled start
-
AI pendants back in vogue at tech show after early setback

-
 Grateful Dead co-founder and guitarist Bob Weir dies aged 78
Grateful Dead co-founder and guitarist Bob Weir dies aged 78
-
Myanmar votes in second phase of junta-run election

-
 'One Battle After Another' heads into Golden Globes as favorite
'One Battle After Another' heads into Golden Globes as favorite
-
Rams survive Panthers scare to advance in NFL playoffs

-
 Rallies across US after woman shot and killed by immigration agent
Rallies across US after woman shot and killed by immigration agent
-
Egypt dump out holders Ivory Coast as Nigeria set up AFCON semi with Morocco

-
 Rosenior salutes 'outstanding' start to Chelsea reign
Rosenior salutes 'outstanding' start to Chelsea reign
-
Maduro loyalists stage modest rally as Venezuelan govt courts US

-
 Byrne late penalty fires Leinster into Champions Cup last 16 after 'ding-dong' battle
Byrne late penalty fires Leinster into Champions Cup last 16 after 'ding-dong' battle
-
Rosenior makes flying start as Chelsea rout Charlton in FA Cup

-
 Rallies across US against shooting of woman by immigration agent
Rallies across US against shooting of woman by immigration agent
-
Salah closer to AFCON glory as Egypt dethrone champions Ivory Coast

-
 O'Neil ends 'crazy three days' with Strasbourg cup canter
O'Neil ends 'crazy three days' with Strasbourg cup canter
-
Mitchell leads Cavs over T-Wolves

-
 O'Neil ends 'crazy few days' with Strasbourg cup canter
O'Neil ends 'crazy few days' with Strasbourg cup canter
-
Argentina wildfire burns over 5,500 hectares: governor

-
 Byrne late penalty fires Leinster into Champions Cup last 16
Byrne late penalty fires Leinster into Champions Cup last 16
-
Roma beat Sassuolo to close in on Serie A leaders Inter

-
 Villa's FA Cup win at Spurs leaves Frank on the brink
Villa's FA Cup win at Spurs leaves Frank on the brink
-
Osimhen focused on Nigeria glory not scoring record

-
 Undav calls shots as Stuttgart thump Leverkusen
Undav calls shots as Stuttgart thump Leverkusen
-
Venezuelan prisoners smile to hear of Maduro's fall

-
 Thousands of Irish, French farmers protest EU-Mercosur trade deal
Thousands of Irish, French farmers protest EU-Mercosur trade deal
-
Kiplimo captures third straight world cross country title

-
 Osimhen leads Nigeria past Algeria into AFCON semi-finals
Osimhen leads Nigeria past Algeria into AFCON semi-finals
-
US urges fresh talks between Syria govt, Kurds after deadly clashes

-
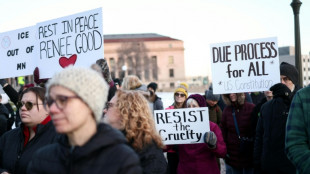 Weekend of US protests after woman killed by immigration agent
Weekend of US protests after woman killed by immigration agent
-
Monaco cling on with 10 men to avoid French Cup shock

-
 Rooney close to tears as brother masterminds FA Cup history
Rooney close to tears as brother masterminds FA Cup history
-
Semenyo scores on Man City debut in 10-goal rout of Exeter

-
 Villarreal sink Alaves to stay in La Liga hunt
Villarreal sink Alaves to stay in La Liga hunt
-
Bristol, Glasgow reach Champions Cup last 16

-
 Freiburg beat 10-man Hamburg to climb to eighth in the Bundesliga
Freiburg beat 10-man Hamburg to climb to eighth in the Bundesliga
-
Venezuela loyalists to rally one week after Maduro's capture

-
 Syrian authorities transferring Kurdish fighters from Aleppo to northeast
Syrian authorities transferring Kurdish fighters from Aleppo to northeast
-
Football: Five memorable FA Cup upsets


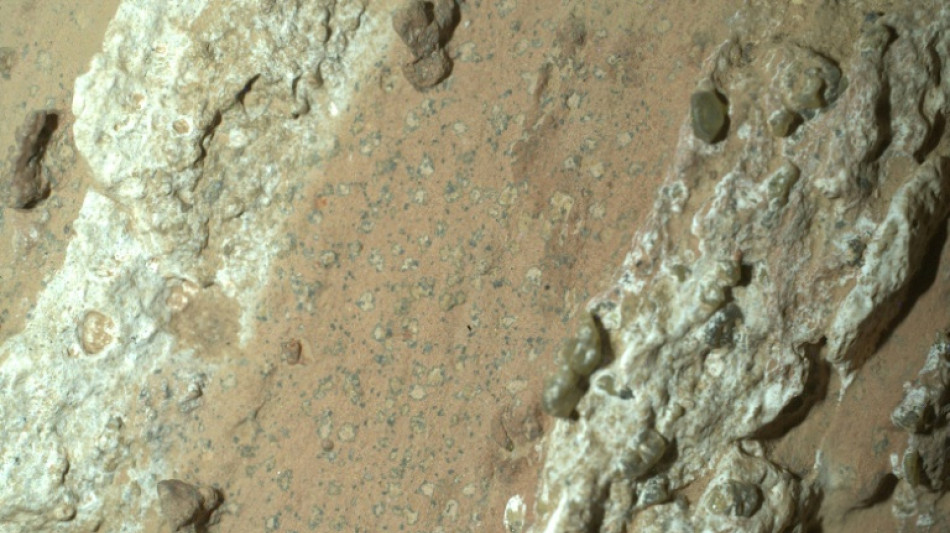
Martian rocks offer clues that might indicate ancient life
Colorful, speckled rocks found on the surface of Mars have offered among the most encouraging evidence yet of ancient life on our neighboring planet, scientists at NASA announced Wednesday.
The Perseverance Mars rover collected the "Sapphire Canyon" rock samples in July 2024 from what's thought to be an ancient lakebed, and its poppyseed and leopard-esque spots pointed to potential chemical reactions that piqued the interest of researchers.
If the features resulted from microbial activity that created minerals in the way they do on Earth -- well, that might point to life on Mars.
It's far too soon for scientists to say that definitively, but the findings, which were detailed in research published in the journal Nature, are alluring, scientists said.
"It's kind of the equivalent of seeing like leftover fossils, you know, leftovers from a meal, and maybe that meal has been excreted by a microbe. And that's what we're seeing in this sample," Nicky Fox, administrator of NASA's Science Mission Directorate, told journalists.
When those kinds of mineral and textured features form in sediment on Earth, it's frequently the product of reactions from mud and organic matter, explained the study's lead author Joel Hurowitz -- a potential "biosignature," or sign of life.
Specifically, Perserverance's instruments identified the minerals vivianite and greigite. On Earth, vivianite is often found in sediments, peat bogs, and around decaying organic matter. Some forms of microbial life on Earth can produce greigite.
"But there are non-biological ways to make these features that we cannot completely rule out on the basis of the data that we collected," Hurowitz said.
Still, the findings are "exciting," he told journalists, explaining that researchers would need to analyze the sample in person to better understand if microbial activity had created the "fantastic textures" and colors including blue and green.
- Return to Earth -
That's no small feat, particularly in light of President Donald Trump administration's plans to cancel the Mars Sample Return program -- a robotic mission planned for the 2030s to bring Perseverance's samples back to Earth.
Asked by journalists if that was still the plan, acting director of NASA Sean Duffy was non-committal, hinting the samples might be brought back by a future crewed mission instead.
"We care about resources, we care about the timeframe, we believe there's a better way to do this, a faster way to get these samples back. And so that is the analysis that we've gone through. Can we do it faster? Can we do it cheaper? And we think we can," he said.
"We're going to actually figure out a different way to bring it back again, and we think we can do it faster and more cost effectively."
There are several rovers ambling across Mars -- Perseverance has been there since 2021 -- seeking signs of life that could have existed millions to billions of years ago, when the planet was thought to have been more habitable.
Evidence that ancient rivers and lakes carved into the planet's surface would indicate that water once flowed there.
And the latest discovery, said Fox, brought researchers "one step closer" to answering the burning question: "Are we truly alone in the universe?"
J.AbuHassan--SF-PST



