-
 Reyna, Balogun on target for USA in 2-1 win over Paraguay
Reyna, Balogun on target for USA in 2-1 win over Paraguay
-
Japa's Miura and Kihara capture Skate America pairs gold

-
 Who can qualify for 2026 World Cup in final round of European qualifiers
Who can qualify for 2026 World Cup in final round of European qualifiers
-
UK to cut protections for refugees under asylum 'overhaul'

-
 England's Tuchel plays down records before final World Cup qualifier
England's Tuchel plays down records before final World Cup qualifier
-
Depoortere double helps France hold off spirited Fiji

-
 Scotland face World Cup shootout against Denmark after Greece defeat
Scotland face World Cup shootout against Denmark after Greece defeat
-
Hansen hat-trick inspires Irish to record win over Australia

-
 Alcaraz secures ATP Finals showdown with 'favourite' Sinner
Alcaraz secures ATP Finals showdown with 'favourite' Sinner
-
UK to cut protections for refugees under asylum 'overhaul': govt

-
 Spain, Switzerland on World Cup brink as Belgium also made to wait
Spain, Switzerland on World Cup brink as Belgium also made to wait
-
Sweden's Grant leads by one at LPGA Annika tournament

-
 Scotland cling to hopes of automatic World Cup qualification despite Greece defeat
Scotland cling to hopes of automatic World Cup qualification despite Greece defeat
-
Alcaraz secures ATP Finals showdown with great rival Sinner

-
 England captain Itoje savours 'special' New Zealand win
England captain Itoje savours 'special' New Zealand win
-
Wales's Evans denies Japan historic win with last-gasp penalty

-
 Zelensky renews calls for more air defence after deadly strike on Kyiv
Zelensky renews calls for more air defence after deadly strike on Kyiv
-
NBA's struggling Pelicans sack coach Willie Green

-
 Petain tribute comments raise 'revisionist' storm in France
Petain tribute comments raise 'revisionist' storm in France
-
Spain on World Cup brink as Belgium also made to wait

-
 Spain virtually seal World Cup qualification in Georgia romp
Spain virtually seal World Cup qualification in Georgia romp
-
M23, DR Congo sign new peace roadmap in Doha

-
 Estevao, Casemiro on target for Brazil in Senegal win
Estevao, Casemiro on target for Brazil in Senegal win
-
Ford steers England to rare win over New Zealand

-
 Massive march in Brazil marks first big UN climate protest in years
Massive march in Brazil marks first big UN climate protest in years
-
Spain rescues hundreds of exotic animals from unlicensed shelter

-
 Huge fire sparked by explosions near Argentine capital 'contained'
Huge fire sparked by explosions near Argentine capital 'contained'
-
South Africa defy early red card to beat battling Italy

-
 Sinner beats De Minaur to reach ATP Finals title match
Sinner beats De Minaur to reach ATP Finals title match
-
Zelensky vows overhaul of Ukraine's scandal-hit energy firms

-
 South Africa defy early red card to beat Italy
South Africa defy early red card to beat Italy
-
Alex Marquez claims Valencia MotoGP sprint victory

-
 McIlroy shares lead with Race to Dubai title in sight
McIlroy shares lead with Race to Dubai title in sight
-
Climate protesters rally in Brazil at COP30 halfway mark

-
 Spike Lee gifts pope Knicks jersey as pontiff meets film stars
Spike Lee gifts pope Knicks jersey as pontiff meets film stars
-
BBC caught in crossfire of polarised political and media landscape

-
 'Happy' Shiffrin dominates in Levi slalom for 102nd World Cup win
'Happy' Shiffrin dominates in Levi slalom for 102nd World Cup win
-
Palestinian national team on 'mission' for peace in Spain visit

-
 Brazilian 'Superman' cheers child cancer patients in Ghana
Brazilian 'Superman' cheers child cancer patients in Ghana
-
India close in on win over South Africa after Jadeja heroics

-
 Huge explosions rock industrial area near Argentina's capital
Huge explosions rock industrial area near Argentina's capital
-
Bezzecchi takes pole for Valencia sprint and MotoGP

-
 Dominant Shiffrin leads after first slalom run in Levi
Dominant Shiffrin leads after first slalom run in Levi
-
Nine killed in accidental explosion at Indian Kashmir police station

-
 Climate protesters to rally at COP30's halfway mark
Climate protesters to rally at COP30's halfway mark
-
Fighting South Africa lose Rickelton after India 189 all out

-
 Harmer leads South Africa fightback as India 189 all out
Harmer leads South Africa fightback as India 189 all out
-
Prison looms for Brazil's Bolsonaro after court rejects his appeal

-
 EU bows to pressure on loosening AI, privacy rules
EU bows to pressure on loosening AI, privacy rules
-
India close in on lead despite South African strikes


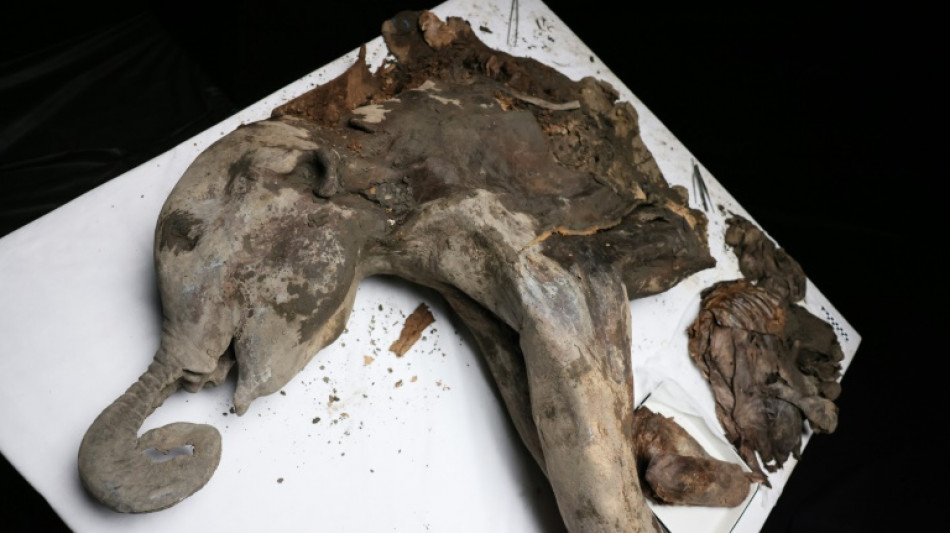
Yana, a 130,000-year-old baby mammoth, goes under the scalpel
Making incisions and carefully taking samples, the scientists at a laboratory in Russia's far east looked like pathologists carrying out a post-mortem.
But the body they were dissecting is a baby mammoth who died around 130,000 years ago.
Discovered last year, the calf -- nicknamed Yana, for the river basin where she was found -- is in a remarkable state of preservation, giving scientists a glimpse into the past and, potentially, the future as climate change thaws the permafrost in which she was found.
Yana's skin has kept its greyish-brown colour and clumps of reddish hairs. Her wrinkled trunk is curved and points to her mouth. The orbits of her eyes are perfectly recognisable and her sturdy legs resemble those of a modern-day elephant.
This necropsy -- an autopsy on an animal -- "is an opportunity to look into the past of our planet", said Artemy Goncharov, head of the Laboratory of Functional Genomics and Proteomics of Microorganisms at the Institute of Experimental Medicine in Saint Petersburg.
Scientists hope to find unique ancient bacteria and carry out genetic analysis of the plants and spores Yana ate to learn more about the place and time she lived.
The calf largely avoided the ravages of time because she lay for thousands of years encased in permafrost in the Sakha region in Siberia.
Measuring 1.2 metres (nearly four feet) at the shoulder and two metres long, and weighing 180 kilogrammes (nearly 400 pounds), Yana could be the best-preserved mammoth specimen ever found, retaining internal organs and soft tissues, the Russian scientists said.
- Stomach, intestines -
Dissecting her body is a treasure trove for the half-dozen scientists that were carrying out the necropsy in late March at the Mammoth Museum at North-Eastern Federal University in the regional capital, Yakutsk.
Wearing white sterile bodysuits, goggles and facemasks, the zoologists and biologists spent several hours working on the front quarters of the mammoth, a species that died out almost 4,000 years ago.
"We can see that many organs and tissues are very well preserved," Goncharov said.
"The digestive tract is partly preserved, the stomach is preserved. There are still fragments of the intestines, in particular the colon," enabling scientists to take samples, he said.
They are "searching for ancient microorganisms" preserved inside the mammoth, so they can study their "evolutionary relationship with modern microorganisms," he said.
While one scientist cut Yana's skin with scissors, another made an incision in the inner wall with a scalpel. They then placed tissue samples in test tubes and bags for analysis.
Another table held the mammoth's hindquarters, which remained embedded in a cliff when the front quarters fell below.
The scent emanating from the mammoth was reminiscent of a mixture of fermented earth and flesh, macerated in the Siberian subsoil.
"We are trying to reach the genitals," said Artyom Nedoluzhko, director of the Paleogenomics Laboratory of the European University at Saint Petersburg.
"Using special tools, we want to go into her vagina in order to gather material to understand what microbiota lived in her when she was alive."
- 'Milk tusks' -
Yana was first estimated to have died around 50,000 years ago, but is now dated at "more than 130,000 years" following analysis of the permafrost layer where she lay, said Maxim Cheprasov, director of the Mammoth Museum.
As for her age at death, "it's already clear that she is over a year old because her milk tusks have already appeared," he added.
Both elephants and mammoths have early milk tusks that later fall out.
Scientists are yet to determine why Yana died so young.
At the time when this herbivore mammal was chewing grass, "here on the territory of Yakutia there were not yet any humans", Cheprasov said, since they appeared in modern-day Siberia between 28,000 and 32,000 years ago.
The secret to Yana's exceptional preservation lies in the permafrost: the soil in this region of Siberia that is frozen year-round and acts like a gigantic freezer, preserving the carcasses of prehistoric animals.
The discovery of Yana's exposed body came about because of thawing permafrost, which scientists believe is due to global warming.
The study of the microbiology of such ancient remains also explores the "biological risks" of global warming, Goncharov said.
Some scientists are researching whether the melting permafrost could release potentially harmful pathogens, he explained.
"There are some hypotheses or conjectures that in the permafrost there could be preserved pathogenic microorganisms, which when it thaws can get into the water, plants and the bodies of animals -- and humans," he said.
U.AlSharif--SF-PST




