
-
 Carrick given Manchester derby baptism of fire, Frank in the firing line
Carrick given Manchester derby baptism of fire, Frank in the firing line
-
Trump announces 'board of peace' formed for Gaza

-
 Sam Darnold: the 'old soul' QB tipped to win Super Bowl
Sam Darnold: the 'old soul' QB tipped to win Super Bowl
-
One year on, it's all about Trump. But for how long?

-
 Australian snowboarder Brockhoff quits ahead of Winter Olympics
Australian snowboarder Brockhoff quits ahead of Winter Olympics
-
Bills battle Broncos as Allen eyes Super Bowl

-
 Magic rally to top Grizzlies in NBA Berlin game
Magic rally to top Grizzlies in NBA Berlin game
-
Venezuela's Machado says she 'presented' Trump with Nobel medal

-
 Key Colombia guerrilla group backs pact to fight US, commander tells AFP
Key Colombia guerrilla group backs pact to fight US, commander tells AFP
-
Chiefs' Mahomes targets NFL 'Week 1' after knee surgery

-
 Venezuelan interim leader vows oil sector reform after Maduro ouster
Venezuelan interim leader vows oil sector reform after Maduro ouster
-
Social media sites block 4.7 million underage accounts in Australia

-
 US court clears Norway's Equinor to resume wind project halted by Trump
US court clears Norway's Equinor to resume wind project halted by Trump
-
Threats to Iran spike 'volatility': UN official

-
 Rabiot and AC Milan give Como French lesson to stay on Inter's heels
Rabiot and AC Milan give Como French lesson to stay on Inter's heels
-
US says reached deal with Taiwan to lower tariffs, boost investments

-
 South Korea's ex-leader Yoon faces first court verdict over martial law chaos
South Korea's ex-leader Yoon faces first court verdict over martial law chaos
-
'Gigantic explosion', fire in Dutch city of Utrecht, four hurt

-
 Twenty-six charged in latest basketball gambling scandal
Twenty-six charged in latest basketball gambling scandal
-
Venezuela's Machado meets Trump for 'positive' talks despite snub
-
 NBA Europe 'must respect tradition', says commissioner Silver
NBA Europe 'must respect tradition', says commissioner Silver
-
Thieves steal Pokemon cards in armed robbery at US store

-
 French Olympic champion Papadakis claims she was under partner's 'control'
French Olympic champion Papadakis claims she was under partner's 'control'
-
Fury over Grok sexualized images despite new restrictions

-
 US says Iran halts executions as Gulf allies pull Trump back from strike
US says Iran halts executions as Gulf allies pull Trump back from strike
-
Frank says Spurs taking 'small steps' in right direction

-
 Syrian activist Sarah Mardini acquitted of migrant trafficking in Greece
Syrian activist Sarah Mardini acquitted of migrant trafficking in Greece
-
Goldman Sachs' profits jump on hot merger market

-
 Platini says Infantino has become 'more of an autocrat'
Platini says Infantino has become 'more of an autocrat'
-
Scottish Borders, Lake District to grace 2027 Tour de France

-
 Venezuela's sidelined Machado arrives at White House for Trump talks
Venezuela's sidelined Machado arrives at White House for Trump talks
-
French mother superior bullied nuns at Paris order: inquiry

-
 Cuba pays tribute to soldiers killed in Maduro capture
Cuba pays tribute to soldiers killed in Maduro capture
-
UK politician joins hard-right Reform just hours after Tories sack him

-
 'Gigantic explosion', fire in Dutch city, four hurt
'Gigantic explosion', fire in Dutch city, four hurt
-
French mother superior bullied nuns at Paris convent - inquiry

-
 Deprived of heating, Kyiv enters survival mode to beat big freeze
Deprived of heating, Kyiv enters survival mode to beat big freeze
-
Oil prices slump after Trump eases concerns over Iran

-
 French mother superior bullied nuns in Montmartre: report
French mother superior bullied nuns in Montmartre: report
-
Rosenior refuses to back Sanchez as Chelsea number one

-
 Harry due to testify to UK court next week in last tabloid case
Harry due to testify to UK court next week in last tabloid case
-
Trump threatens to invoke Insurrection Act over Minnesota protests

-
 Niger faces dilemma over uranium shipment stuck at airport
Niger faces dilemma over uranium shipment stuck at airport
-
UN chief attacks world leaders putting cooperation on 'deathwatch'

-
 Morocco and Senegal prepare for final showdown but Salah's AFCON dream fades
Morocco and Senegal prepare for final showdown but Salah's AFCON dream fades
-
Polls close in Uganda after delays, internet blackout

-
 Forced confession fears as Iran chief justice interrogates protesters
Forced confession fears as Iran chief justice interrogates protesters
-
Al-Attiyah closes on sixth Dakar Rally as Ekstrom wins 11th stage

-
 Luis Enrique has no doubts about PSG's title credentials
Luis Enrique has no doubts about PSG's title credentials
-
England off-spinner Bashir signs for Derbyshire after Ashes exile


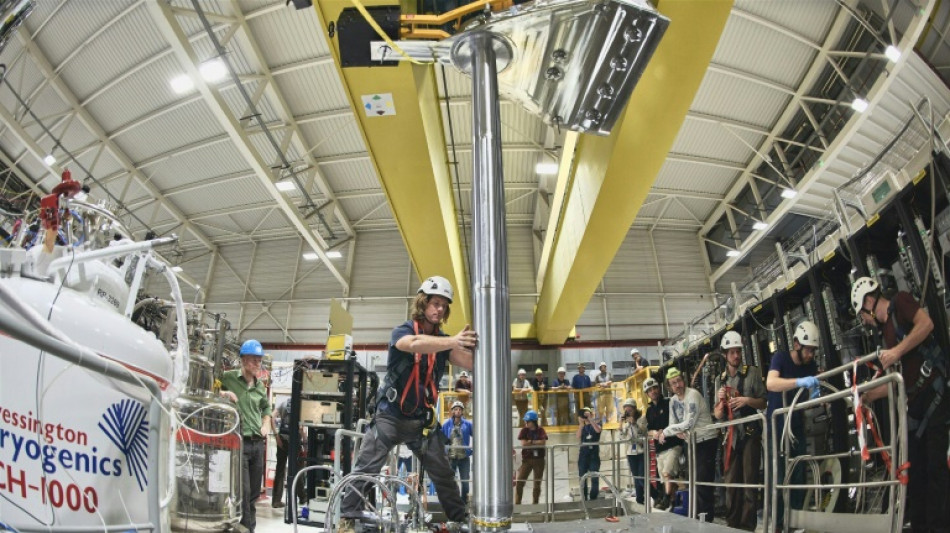
Mysterious antimatter observed falling down for first time
For the first time, scientists have observed antimatter particles -- the mysterious twins of the visible matter all around us -- falling downwards due to the effect of gravity, Europe's physics lab CERN announced on Wednesday.
The experiment was hailed as "huge milestone", though most physicists anticipated the result, and it had been predicted by Einstein's 1915 theory of relativity.
It definitively rules out that gravity repels antimatter upwards -- a finding that would have upended our fundamental understanding of the universe.
Around 13.8 billion years ago, the Big Bang is believed to have produced an equal amount of matter -- what everything you can see is made out of -- and antimatter, its equal yet opposite counterpart.
However there is virtually no antimatter in the universe, which prompted one of the greatest mysteries of physics: what happened to all the antimatter?
"Half the universe is missing," said Jeffrey Hangst, a member of CERN's ALPHA collaboration in Geneva which conducted the new experiment.
"In principle, we could build a universe -- everything that we know about -- with only antimatter, and it would work in exactly the same way," he told AFP.
Physicists believe that matter and antimatter did meet and almost entirely destroyed each other after the Big Bang.
Yet matter now makes up nearly five percent of the universe -- the rest is even less understood dark matter and dark energy -- while antimatter vanished.
- Newton's apple flying up? -
One of the key outstanding questions about antimatter was whether gravity caused it to fall in the same way as normal matter.
While most physicists believed that it did, a few had speculated otherwise.
A falling apple famously inspired Isaac Newton's work on gravity -- but if that apple was made of antimatter, would it have shot up into the sky?
And if gravity did in fact repel antimatter, it could have meant that impossibilities such as a perpetual motion machine were possible.
"So why not drop some and see what happens?" Hangst said.
He compared the experiment to Galileo's famous -- though likely apocryphal -- 16th-century demonstration that two balls of different mass dropped from the Leaning Tower of Pisa would fall at the same rate.
But this experiment -- the result of 30 years of work on antimatter at CERN -- was "a little bit more involved" than Galileo's, Hangst said.
One problem was that antimatter barely exists outside of rare, short-lived particles in outer space.
However in 1996, CERN scientists produced the first atoms of antimatter -- antihydrogen.
Another challenge was that, because matter and antimatter have an opposite electrical charge, the moment they meet they destroy each other in a violent flash of energy scientists call annihilation.
- A magnetic trap -
To study gravity's effect on antimatter, the ALPHA team constructed a 25-centimetre-long (10-inch) bottle placed on its end, with magnets at the top and bottom.
Late last year, the scientists placed around 100 very cold antihydrogen atoms into this "magnetic trap" called ALPHA-g.
As they turned down the strength of both magnets, the antihydrogen particles -- which were bouncing around at 100 metres a second -- were able to escape out either end of the bottle.
The scientists then simply counted how much antimatter was annihilated at each end of the bottle.
Around 80 percent of the antihydrogen went out of the bottom, which is a similar rate to how regular bouncing hydrogen atoms would behave if they were in the bottle.
This result, published in the journal Nature, shows that gravity causes antimatter to fall downwards, as predicted by Einstein's 1915 theory of relativity.
In more than a dozen experiments, the CERN scientists varied the strength of the magnets, observing gravity's effect on antimatter at different rates.
While the experiment rules out that gravity makes antihydrogen go upwards, Hangst emphasised it did not prove that antimatter behaves in exactly the same way as normal matter.
"That's our next task," he said.
Marco Gersabeck, a physicist who works at CERN but was not involved in the ALPHA research, said it was "a huge milestone".
But it marks "only the start of an era" of more precise measurements of gravity's effect on antimatter, he told AFP.
Other attempts to better understand antimatter include using CERN's Large Hadron Collider to investigate strange particles called beauty quarks.
And there is an experiment onboard the International Space Station trying to catch antimatter in cosmic rays.
But for now, exactly why the universe is awash with matter but devoid of antimatter "remains a mystery," said physicist Harry Cliff.
Since both should have annihilated each other completely in the early universe, "the fact that we exist suggests there is something we don't understand" going on, he added.
L.AbuAli--SF-PST




