
-
 'Gigantic explosion', fire in Dutch city of Utrecht, four hurt
'Gigantic explosion', fire in Dutch city of Utrecht, four hurt
-
Twenty-six charged in latest basketball gambling scandal

-
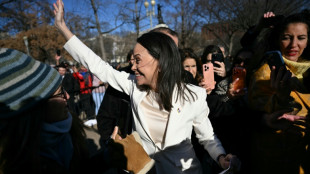 Venezuela's Machado meets Trump for 'positive' talks despite snub
Venezuela's Machado meets Trump for 'positive' talks despite snub
-
NBA Europe 'must respect tradition', says commissioner Silver

-
 Thieves steal Pokemon cards in armed robbery at US store
Thieves steal Pokemon cards in armed robbery at US store
-
French Olympic champion Papadakis claims she was under partner's 'control'

-
 Fury over Grok sexualized images despite new restrictions
Fury over Grok sexualized images despite new restrictions
-
US says Iran halts executions as Gulf allies pull Trump back from strike

-
 Frank says Spurs taking 'small steps' in right direction
Frank says Spurs taking 'small steps' in right direction
-
Syrian activist Sarah Mardini acquitted of migrant trafficking in Greece

-
 Goldman Sachs' profits jump on hot merger market
Goldman Sachs' profits jump on hot merger market
-
Platini says Infantino has become 'more of an autocrat'

-
 Scottish Borders, Lake District to grace 2027 Tour de France
Scottish Borders, Lake District to grace 2027 Tour de France
-
Venezuela's sidelined Machado arrives at White House for Trump talks

-
 French mother superior bullied nuns at Paris order: inquiry
French mother superior bullied nuns at Paris order: inquiry
-
Cuba pays tribute to soldiers killed in Maduro capture

-
 UK politician joins hard-right Reform just hours after Tories sack him
UK politician joins hard-right Reform just hours after Tories sack him
-
'Gigantic explosion', fire in Dutch city, four hurt

-
 French mother superior bullied nuns at Paris convent - inquiry
French mother superior bullied nuns at Paris convent - inquiry
-
Deprived of heating, Kyiv enters survival mode to beat big freeze

-
 Oil prices slump after Trump eases concerns over Iran
Oil prices slump after Trump eases concerns over Iran
-
French mother superior bullied nuns in Montmartre: report

-
 Rosenior refuses to back Sanchez as Chelsea number one
Rosenior refuses to back Sanchez as Chelsea number one
-
Harry due to testify to UK court next week in last tabloid case

-
 Trump threatens to invoke Insurrection Act over Minnesota protests
Trump threatens to invoke Insurrection Act over Minnesota protests
-
Niger faces dilemma over uranium shipment stuck at airport

-
 UN chief attacks world leaders putting cooperation on 'deathwatch'
UN chief attacks world leaders putting cooperation on 'deathwatch'
-
Morocco and Senegal prepare for final showdown but Salah's AFCON dream fades

-
 Polls close in Uganda after delays, internet blackout
Polls close in Uganda after delays, internet blackout
-
Forced confession fears as Iran chief justice interrogates protesters

-
 Al-Attiyah closes on sixth Dakar Rally as Ekstrom wins 11th stage
Al-Attiyah closes on sixth Dakar Rally as Ekstrom wins 11th stage
-
Luis Enrique has no doubts about PSG's title credentials

-
 England off-spinner Bashir signs for Derbyshire after Ashes exile
England off-spinner Bashir signs for Derbyshire after Ashes exile
-
Trump convinced 'to give Iran a chance' after threats over protest crackdown

-
 European military mission in Greenland as US aim 'remains intact'
European military mission in Greenland as US aim 'remains intact'
-
UK's Hockney warns moving Bayeux Tapestry would be 'madness'

-
 Senior UK opposition politican sacked over 'plot' to join hard-right party
Senior UK opposition politican sacked over 'plot' to join hard-right party
-
Syrians flee Kurdish-controlled area near Aleppo

-
 Pressure piles on Musk's X to curb sexualised deepfakes
Pressure piles on Musk's X to curb sexualised deepfakes
-
Chinese dissident artist Ai Weiwei debuts in India

-
 Arbeloa must act fast to avert Real Madrid crisis
Arbeloa must act fast to avert Real Madrid crisis
-
Top Bangladesh cricket official sacked amid World Cup row

-
 Iran vows to defend itself as Trump says will 'watch it and see'
Iran vows to defend itself as Trump says will 'watch it and see'
-
Spain hosted record 97 mn foreign tourists in 2025

-
 Ex-Olympic swim champion Agnel to face trial on rape claims
Ex-Olympic swim champion Agnel to face trial on rape claims
-
Danish PM says US ambition to take Greenland 'remains intact'

-
 In remote Senegal, chimp researchers escape gold mines' perils
In remote Senegal, chimp researchers escape gold mines' perils
-
Senegal's spear-wielding savannah chimps yield clues on humanity's past

-
 Russia expels UK diplomat accused of being spy
Russia expels UK diplomat accused of being spy
-
Uganda election hit by delays after internet blackout

| SCS | 0.12% | 16.14 | $ | |
| CMSC | 0.74% | 23.525 | $ | |
| BCC | 2.6% | 86.295 | $ | |
| BTI | 1.12% | 58.09 | $ | |
| RIO | 0.52% | 86.332 | $ | |
| CMSD | 0.22% | 23.96 | $ | |
| BCE | 0.08% | 24.24 | $ | |
| NGG | 0.61% | 79.365 | $ | |
| RBGPF | -0.26% | 81.36 | $ | |
| GSK | -3.4% | 49.12 | $ | |
| JRI | -0.47% | 13.563 | $ | |
| AZN | -2.5% | 93.99 | $ | |
| RYCEF | -1.12% | 16.95 | $ | |
| BP | -1.92% | 35.145 | $ | |
| RELX | -0.14% | 41.86 | $ | |
| VOD | 0.59% | 13.45 | $ |

WHO holds first traditional medicine summit
The World Health Organization holds its first summit on traditional medicine on Thursday, with warnings that treatments rooted in natural products can be effective alternative healthcare only if scientifically proven.
Traditional medicines are a "first port of call for millions of people worldwide", the UN health agency said, with the talks in India bringing together policymakers and academics aiming to "mobilise political commitment and evidence-based action" towards them.
WHO chief Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus said traditional medicine could boost healthcare "access gaps", but was of value only if used "appropriately, effectively, and above all, safely based on the latest scientific evidence", in a statement ahead of the conference.
The two-day WHO Traditional Medicine Global Summit takes place alongside a meeting of G20 health ministers in the Indian city of Gandhinagar.
"Advancing science on traditional medicine should be held to the same rigorous standards as in other fields of health," WHO research chief John Reeder said in a statement.
"This may require new thinking on the methodologies to address these more holistic, contextual approaches and provide evidence that is sufficiently conclusive and robust to lead to policy recommendations."
Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi, who is expected to open the WHO conference via a video message, has repeatedly promoted the health benefits of yoga, extolling it as a "panacea" for stress and even hate.
The summit, set to become an annual event, follows the opening last year of a WHO Global Centre for Traditional Medicine, also in India's Gujarat state.
- Lack of regulatory oversight -
While traditional medicines are widely used in some parts of the world, they also face fierce criticism.
The UN health agency defines traditional medicine as the knowledge, skills and practices used over time to maintain health and prevent, diagnose and treat physical and mental illness.
But many traditional treatments have no proven scientific value and conservationists say the industry drives a rampant trade in endangered animals -- including tigers, rhinos and pangolins -- threatening the existence of entire species.
Use of homemade remedies soared during the Covid-19 pandemic, including a green herbal drink based on Artemisia that was promoted by Madagascar's president as a cure.
The plant has a proven efficacy in malaria treatment, but its use to combat Covid was widely scorned by many doctors.
In China, traditional medicine has a distinguished history, but top European medical bodies have previously demanded it be subject to the same regulatory oversight as conventional Western methods.
Of the WHO's 194 member states, 170 acknowledged their use of traditional and complementary medicine since 2018, but only 124 reported having laws or regulations for the use of herbal medicines -- while only half had a national policy on such methods and medicines.
"Natural doesn't always mean safe, and centuries of use are not a guarantee of efficacy; therefore, scientific method and process must be applied to provide the rigorous evidence required," the WHO said.
Some 40 percent of approved pharmaceutical products currently in use derive from a "natural product basis", according to the WHO, citing "landmark drugs" that derive from traditional medicine, including aspirin, drawing on formulations using willow tree bark.
R.Shaban--SF-PST



