-
 NASA reports record heat but omits reference to climate change
NASA reports record heat but omits reference to climate change
-
Trump praises 'terrific' new Venezuela leader after call

-
 Real Madrid crash out of Copa del Rey at Albacete on Arbeloa debut
Real Madrid crash out of Copa del Rey at Albacete on Arbeloa debut
-
Trump says Iran killings stopped as US scales back Qatar base

-
 Arsenal beat Rosenior's Chelsea in League Cup semi first leg
Arsenal beat Rosenior's Chelsea in League Cup semi first leg
-
US stocks fall again as Iran worries lift oil prices

-
 Inter extend Serie A lead to six points after Napoli slip
Inter extend Serie A lead to six points after Napoli slip
-
Bayern beat Cologne to move 11 points clear in Bundesliga

-
 Mane takes Senegal past Egypt into final of his last AFCON
Mane takes Senegal past Egypt into final of his last AFCON
-
Trump says Greenland will 'work out' after Denmark fails to bridge gap

-
 'Bridgerton' premieres in Paris promising 'Cinderella with a twist'
'Bridgerton' premieres in Paris promising 'Cinderella with a twist'
-
California begins probe of Musk's Grok over sexualized AI images

-
 Astronauts set to leave ISS in first-ever medical evacuation
Astronauts set to leave ISS in first-ever medical evacuation
-
Napoli's stalemate with Parma opens door for Serie A leaders Inter

-
 Syrian leader urges Kurdish integration as army sends troops east of Aleppo
Syrian leader urges Kurdish integration as army sends troops east of Aleppo
-
Denmark says White House talks failed to alter US designs on Greenland

-
 Venezuela looking to 'new era' after Maduro ouster, says interim leader
Venezuela looking to 'new era' after Maduro ouster, says interim leader
-
Mane takes dominant Senegal past Egypt into AFCON final

-
 UK police admit 'mistakes' over Maccabi Tel Aviv fan ban
UK police admit 'mistakes' over Maccabi Tel Aviv fan ban
-
Promoter says Joshua will return to ring when 'time is right' after horror crash

-
 California investigating Grok AI over lewd fake images
California investigating Grok AI over lewd fake images
-
Wales's Faletau set to miss bulk of Six Nations

-
 Denmark, Greenland wrap up crunch White House talks
Denmark, Greenland wrap up crunch White House talks
-
England sweating on Fin Smith's fitness for Six Nations opener

-
 NASA acknowledges record heat but avoids referencing climate change
NASA acknowledges record heat but avoids referencing climate change
-
England rugby league coach Wane quits role

-
 Oil prices extend gains on Iran worries
Oil prices extend gains on Iran worries
-
European basketball pioneer Schrempf lauds 'global' NBA

-
 Denmark, Greenland in crunch White House talks as Trump ups pressure
Denmark, Greenland in crunch White House talks as Trump ups pressure
-
Mitchell hits ton as New Zealand down India to level ODI series

-
 Syrian army tells civilians to stay away from Kurdish positions east of Aleppo
Syrian army tells civilians to stay away from Kurdish positions east of Aleppo
-
Spurs sign England midfielder Gallagher from Atletico Madrid

-
 Russian captain tried to avoid North Sea crash: court
Russian captain tried to avoid North Sea crash: court
-
Battle over Chinese-owned chipmaker Nexperia rages in Dutch court

-
 Transatlantic ties 'disintegrating': German vice chancellor
Transatlantic ties 'disintegrating': German vice chancellor
-
Five problems facing Ukraine's new defence chief

-
 Italian influencer Ferragni acquitted in Christmas cake fraud trial
Italian influencer Ferragni acquitted in Christmas cake fraud trial
-
UK interior minister says 'lost confidence' in police chief over Maccabi fan ban

-
 Ryanair hits out at 'stupid' Belgium over aviation taxes
Ryanair hits out at 'stupid' Belgium over aviation taxes
-
Burkina Faso sack coach Traore after AFCON exit

-
 African manufacturers welcome US trade deal, call to finalise it
African manufacturers welcome US trade deal, call to finalise it
-
What happens when fire ignites in space? 'A ball of flame'

-
 Death of author's baby son puts Nigerian healthcare in spotlight
Death of author's baby son puts Nigerian healthcare in spotlight
-
France bans 10 British anti-migrant activists

-
 2025 was third hottest year on record: climate monitors
2025 was third hottest year on record: climate monitors
-
Hydrogen planes 'more for the 22nd century': France's Safran

-
 Julio Iglesias, the Spanish crooner who won global audience
Julio Iglesias, the Spanish crooner who won global audience
-
'We can't make ends meet': civil servants protest in Ankara

-
 UK prosecutors appeal Kneecap rapper terror charge dismissal
UK prosecutors appeal Kneecap rapper terror charge dismissal
-
UK police chief blames AI for error in evidence over Maccabi fan ban


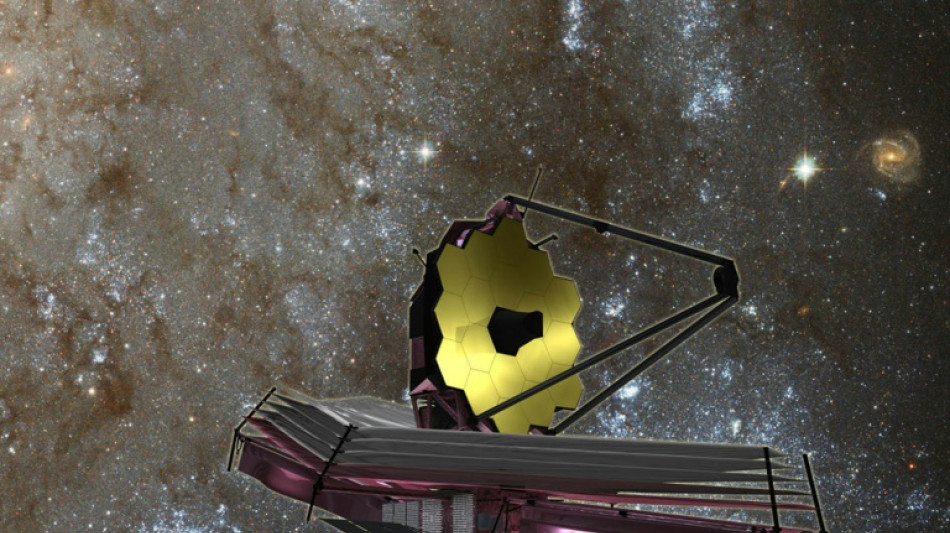
Webb spots surprisingly massive galaxies in early universe
The James Webb Space Telescope has spotted six massive galaxies that emerged not long after the Big Bang, a study said Wednesday, surprising scientists by forming at a speed that contradicts our current understanding of the universe.
Since becoming operational last July, the Webb telescope has been peering farther than ever before into the universe's distant reaches -- which also means it is looking back in time.
For its latest discovery, the telescope spied galaxies from between 500 to 700 years million years after the Big Bang 13.8 billion years ago, meaning the universe was under five percent of its current age.
Webb's NIRCam instrument, which operates in the near infrared wavelength invisible to the naked eye, observed the six galaxies in a little-known region of the sky, according to a study published in the journal Nature.
Two of the galaxies had previously been spotted by the Hubble Space Telescope but were so faint in those images that they went unnoticed.
These six new "candidate galaxies", so-called because their discovery still needs to be confirmed by other measurements, contain many more stars than scientists expected.
One galaxy is even believed to have around 100 billion stars.
That would make it around the size of the Milky Way, which is "crazy," the study's first author Ivo Labbe told AFP.
- 'Off a cliff' -
It took our home galaxy the entire life of the universe for all its stars to assemble.
For this young galaxy to achieve the same growth in just 700 million years, it would have had to grow around 20 times faster than the Milky Way, said Labbe, a researcher at Australia's Swinburne University of Technology.
For there to be such massive galaxies so soon after the Big Bang goes against the current cosmological model which represents science's best understanding of how the universe works.
"According to theory, galaxies grow slowly from very small beginnings at early times," Labbe said, adding that such galaxies were expected to be between 10 to 100 times smaller.
But the size of these galaxies "really go off a cliff," he said.
What could be going on? One suspect is mysterious dark matter, which makes up a sizeable amount of the Universe.
While much about dark matter remains unknown, scientists believe it plays a key role in the formation of galaxies.
When dark matter "clumps" together into a halo, it attracts gas from the surrounding universe which in turn forms a galaxy and its stars, Labbe said.
But this process is supposed to take a long time, and "in the early universe, there's just not that many clumps of dark matter," he said.
- 'Model is cracking' -
The newly discovered galaxies could indicate that things sped up far faster in the early universe than previously thought, allowing stars to form "much more efficiently," said David Elbaz, an astrophysicist at the French Atomic Energy Commission not involved in the research.
This could be linked to recent signs that the universe itself is expanding faster than we once believed, he added.
This subject sparks fierce debate among cosmologists, making this latest discovery "all the more exciting, because it is one more indication that the model is cracking," Elbaz said.
Elbaz is one of many scientists working on the European Space Agency's Euclid space telescope, which is scheduled to launch in July to join Webb in space.
Euclid's mission is to uncover the secrets of dark matter and dark energy -- and it could also help solve this latest mystery, Elbaz said.
Labbe referred to the "black swan theory", under which just one unexpected event can overturn our previous understanding -- such as when Europeans saw the first black swans in Australia.
He called the galaxies "six black swans -- if even one of them turns out to be true, then it means we have to change our theories."
P.AbuBaker--SF-PST

