-
 Ukraine says Abu Dhabi talks with Russia 'substantive and productive'
Ukraine says Abu Dhabi talks with Russia 'substantive and productive'
-
Brazil mine disaster victims in London to 'demand what is owed'

-
 AI-fuelled tech stock selloff rolls on
AI-fuelled tech stock selloff rolls on
-
Russia vows to act 'responsibly' as nuclear pact ends with US

-
 White says time at Toulon has made him a better Scotland player
White says time at Toulon has made him a better Scotland player
-
Washington Post announces 'painful' job cuts

-
 All lights are go for Jalibert, says France's Dupont
All lights are go for Jalibert, says France's Dupont
-
Artist rubs out Meloni church fresco after controversy

-
 Palestinians in Egypt torn on return to a Gaza with 'no future'
Palestinians in Egypt torn on return to a Gaza with 'no future'
-
US removing 700 immigration officers from Minnesota

-
 Who is behind the killing of late ruler Gaddafi's son, and why now?
Who is behind the killing of late ruler Gaddafi's son, and why now?
-
Coach Thioune tasked with saving battling Bremen

-
 Russia vows to act 'responsibly' once nuclear pact with US ends
Russia vows to act 'responsibly' once nuclear pact with US ends
-
Son of Norway's crown princess admits excesses but denies rape

-
 US calls for minerals trade zone in rare move with allies
US calls for minerals trade zone in rare move with allies
-
Vowles dismisses Williams 2026 title hopes as 'not realistic'

-
 'Dinosaur' Glenn chasing skating gold in first Olympics
'Dinosaur' Glenn chasing skating gold in first Olympics
-
Gaza health officials say strikes kill 23 after Israel says shots wounded officer

-
 Italy foils Russian cyberattacks targeting Olympics
Italy foils Russian cyberattacks targeting Olympics
-
Stocks stabilise after Wall St AI-fuelled sell-off

-
 Figure skating favourite Malinin feeling 'the pressure' in Milan
Figure skating favourite Malinin feeling 'the pressure' in Milan
-
Netflix film probes conviction of UK baby killer nurse

-
 Timber hopes League Cup can be catalyst for Arsenal success
Timber hopes League Cup can be catalyst for Arsenal success
-
China calls EU 'discriminatory' over probe into energy giant Goldwind

-
 Sales warning slams Ozempic maker Novo Nordisk's stock
Sales warning slams Ozempic maker Novo Nordisk's stock
-
Can Vonn defy ACL rupture to win Olympic medal?

-
 Breakthrough or prelude to attack? What we know about Iran-US talks
Breakthrough or prelude to attack? What we know about Iran-US talks
-
German far-right MP detained over alleged Belarus sanctions breach

-
 MSF says its hospital in South Sudan hit by government air strike
MSF says its hospital in South Sudan hit by government air strike
-
Merz heads to Gulf as Germany looks to diversify trade ties

-
 Selection process for future Olympic hosts set for reform
Selection process for future Olympic hosts set for reform
-
Serbian minister on trial over Trump-linked hotel plan

-
 UK PM says Mandelson 'lied', regrets appointing him US envoy
UK PM says Mandelson 'lied', regrets appointing him US envoy
-
Cochran-Siegle tops first Olympic downhill training

-
 Gaza health officials say strikes kill 21 after Israel says shots wounded officer
Gaza health officials say strikes kill 21 after Israel says shots wounded officer
-
Injured Vonn's Olympic bid is 'inspirational', ski stars say

-
 Albania arrests 20 for toxic waste trafficking
Albania arrests 20 for toxic waste trafficking
-
US-Africa trade deal renewal only 'temporary breather'

-
 Mir sets pace on Sepang day two, Yamaha absent
Mir sets pace on Sepang day two, Yamaha absent
-
Xi, Putin hail 'stabilising' China-Russia alliance

-
 GSK boosted by specialty drugs, end to Zantac fallout
GSK boosted by specialty drugs, end to Zantac fallout
-
UK's ex-prince leaves Windsor home amid Epstein storm: reports

-
 Sky is the limit for Ireland fly-half Prendergast, says captain Doris
Sky is the limit for Ireland fly-half Prendergast, says captain Doris
-
Stocks fluctuate after Wall St AI-fuelled sell-off

-
 Feyi-Waboso reminds England great Robinson of himself
Feyi-Waboso reminds England great Robinson of himself
-
Starmer faces MPs as pressure grows over Mandelson scandal

-
 HRW urges pushback against 'aggressive superpowers'
HRW urges pushback against 'aggressive superpowers'
-
Russia demands Ukraine give in as UAE talks open

-
 Gaza civil defence says 17 killed in strikes after Israel says shots wounded officer
Gaza civil defence says 17 killed in strikes after Israel says shots wounded officer
-
France's Kante joins Fenerbahce after Erdogan 'support'

| CMSD | -0.36% | 23.855 | $ | |
| SCS | 0.12% | 16.14 | $ | |
| RBGPF | 0.12% | 82.5 | $ | |
| RYCEF | -1.19% | 16.8 | $ | |
| VOD | 2.34% | 15.615 | $ | |
| RIO | -0.86% | 95.55 | $ | |
| CMSC | -0.55% | 23.53 | $ | |
| NGG | 1.89% | 87.89 | $ | |
| BTI | -0.34% | 61.66 | $ | |
| BCE | 1.17% | 26.41 | $ | |
| BCC | 4.73% | 89.15 | $ | |
| RELX | -1.56% | 30.04 | $ | |
| GSK | 6.35% | 56.955 | $ | |
| JRI | 0.22% | 13.149 | $ | |
| BP | 0.77% | 39.12 | $ | |
| AZN | 1.18% | 186.53 | $ |

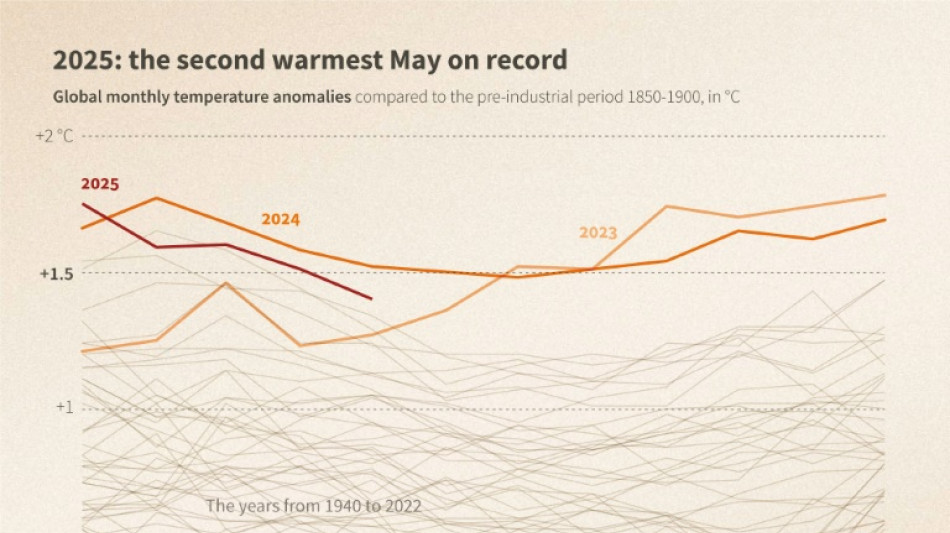
May 2025 second warmest on record: EU climate monitor
Global heating continued as the new norm, with last month the second warmest May on record on land and in the oceans, according to the European Union's climate monitoring service.
The planet's average surface temperature dipped below the threshold of 1.5 degree Celsius above preindustrial levels, just shy of the record for May set last year, according to the Copernicus Climate Change Service.
The same held for the world's oceans. With a surface temperature of 20.79C, last month was second only to May 2024, with some unprecedented warmth regionally.
"Large areas in the northeast North Atlantic, which experienced a marine heatwave, had record surface temperatures for the month," Copernicus reported. "Most of the Mediterranean Sea was much warmer than average."
The increasingly dire state of the oceans is front-and-centre at the third UN Ocean Conference (UNOC), which kicked off Monday in Nice, France.
Ocean heatwaves are driving marine species to migrate, damaging ecosystems, and reducing the ability of ocean layers to mix, thus hindering the distribution of nutrients.
Covering 70 percent of the globe's surface, oceans redistribute heat and play a crucial role in regulating Earth's climate.
Surface water warmed by climate change drive increasingly powerful storms, causing new levels of destruction and flooding in their wake.
Some parts of Europe, meanwhile, "experienced their lowest levels of precipitation and soil moisture since at least 1979," Copernicus noted.
Britain has been in the grips of its most intense drought in decades, with Denmark and the Netherlands also suffering from a lack of rain.
- 'Brief respite' -
Earth's surface last month was 1.4C above the preindustrial benchmark, defined as the average temperature from 1850 to 1900, before the massive use of fossil fuels caused the climate to dramatically warm.
"May 2025 interrupts an unprecedentedly long sequence of months above 1.5C," noted Carlo Buontempo, director of the Copernicus Climate Change Service.
All but one of the previous 22 months crossed this critical threshold, which marks the 2015 Paris Agreement's most ambitious target for capping global warming.
"This may offer a brief respite for the planet, but we expect the 1.5C threshold to be exceeded again in the near future due to the continued warming of the climate system," he added.
Over the 12-month period June 2024 to May 2025, warming averaged 1.57C compared to the 1850-1900 benchmark.
The Paris treaty target, however, is pegged to a 20-year average, in order to account for the influence of natural variability.
The UN's climate science advisory panel, the IPCC, has said there's a 50-percent change of breaching the 1.5C barrier in line with these criteria between 2030 and 2035.
Using this method of calculation, the world today has warmed by at least 1.3C.
The UN's World Meterological Organization (WMO), meanwhile, has said there's a 70 percent chance the five-year period 2025-2029, on average, will exceed the 1.5C limit.
Scientists stress the importance of limiting global warming as soon and as much as possible because every fraction of a degree increases the risks of more deadly and destructive impacts, on land and in the sea.
Limiting warming to 1.5C rather than 2C would significantly reduce the most catastrophic consequences, the IPCC concluded in a major report in 2018.
O.Farraj--SF-PST


